New features of the 2015.j version
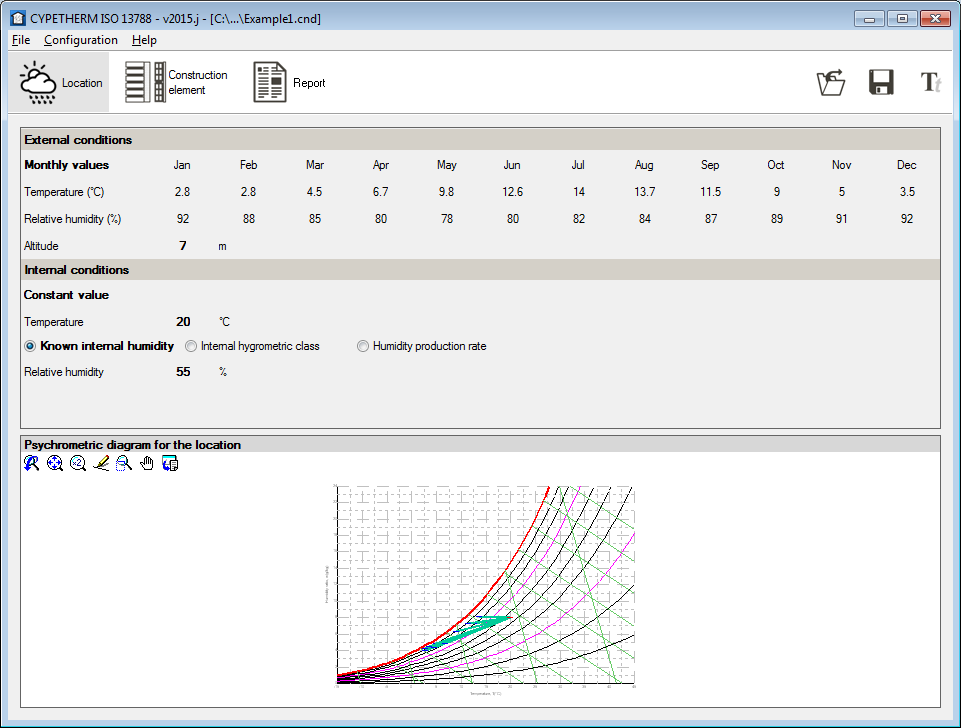
CYPETHERM ISO 13788 (new program)
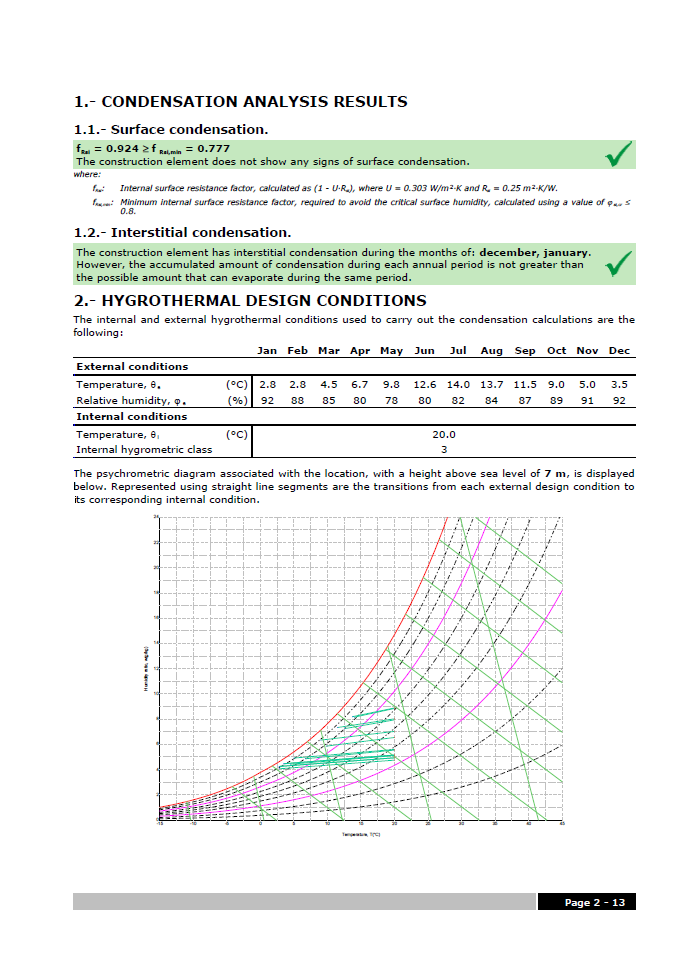
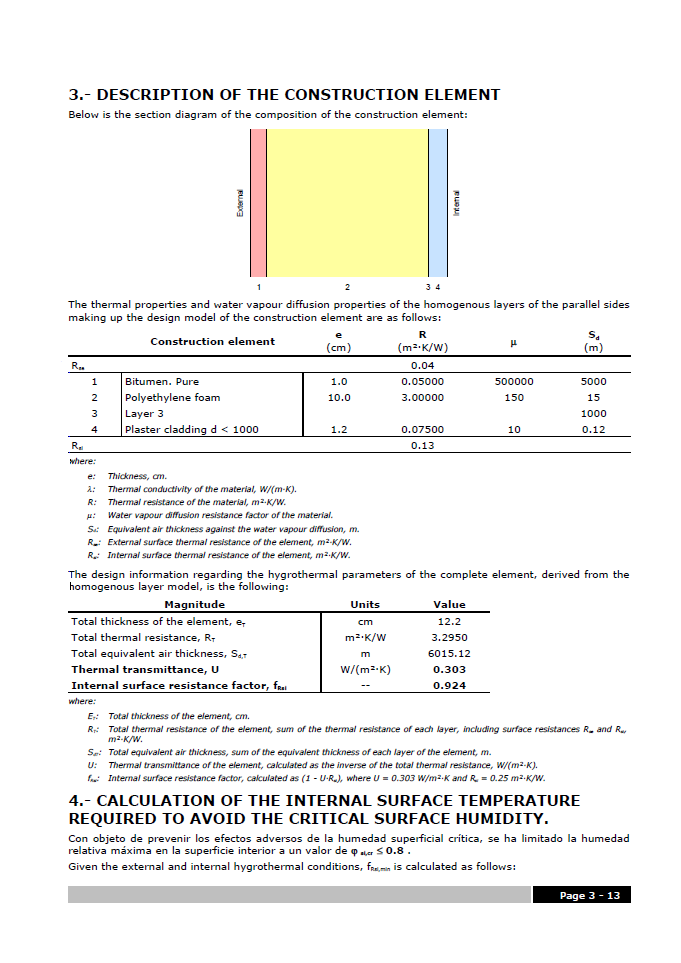
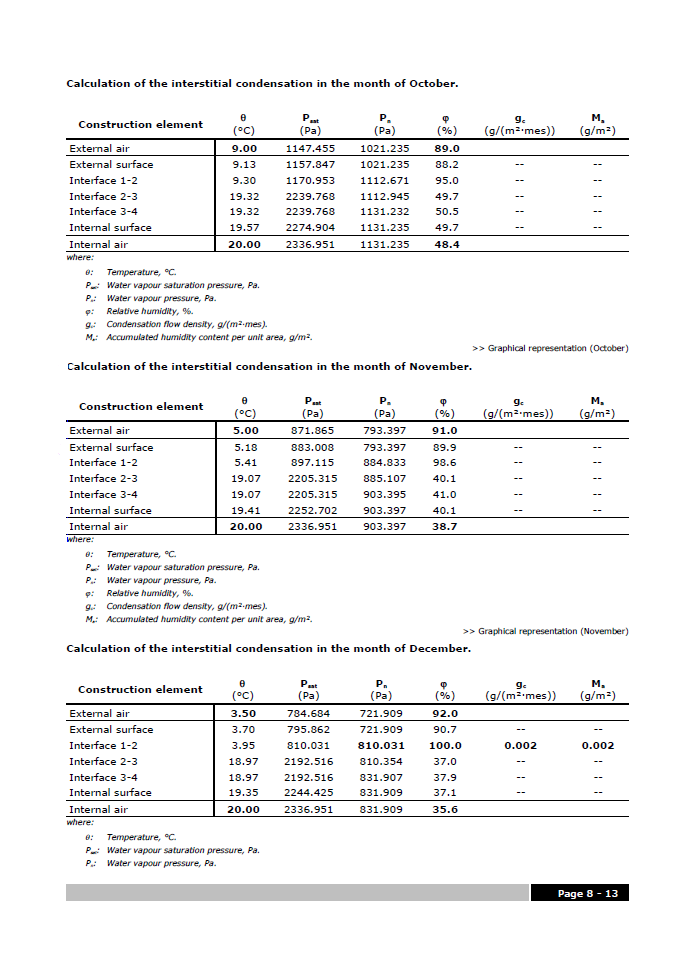
CYPETHERM ISO 13788 (located in the Building Services group of the main CYPE program menu) is an easy-to-use application which allows users to analyse the internal surface resistance factor by taking into account the critical surface humidity and interstitial condensation in construction elements. The program carries out the analysis based on the hygrothermal behaviour of the building materials and products, and in accordance with the analysis method of the ISO 13788: 2012 code.
The main features of CYPETHERM ISO 13788 include: Analysis in accordance with EN ISO 13788, weather data import, material libraries and catalogues, and its analysis results.
More information on this new CYPE program can be found on the CYPETHERM ISO 13788 webpage.
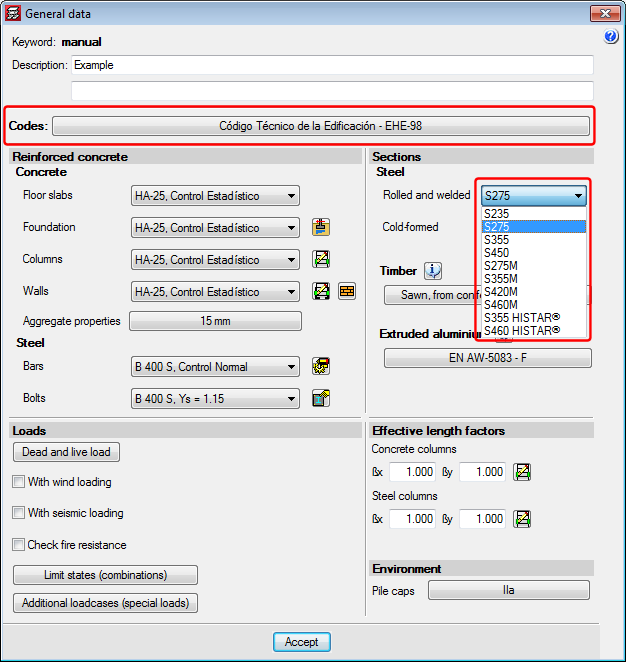
Reduction of the elastic limit of rolled steel and implementation of thermomechanically rolled steels and Histar® steel (ArcelorMittal) for CTE DB SE-A, EAE 2011 and Eurocodes
When the selected steel code is the CTE DB SE-A (Spain), EAE 2011 (Spain) or Eurocodes 3 and 4 (EU or any of Eurocode adaptations to other countries), the program allows users to choose thermomechanical rolled steel and Histar® rolled steel (ArcelorMittal).
Compared to conventional steels, the elastic limit for these steels has been reduced depending on the nominal thickness of the section, and so, it may be useful to use them with large sections.
Depending on the selected code, the steel types users can choose amongst are:
- CTE DB SE-A (Spain)
- Conventional rolled steel with elastic limit reduction in accordance with CTE DB SE-A:
S235, S275, S355 and S450. - Thermomechanical rolled steel with elastic limit reduction in accordance with CTE DB SE-A (2015.j version):
S275M, S355M, S420M and S460M. - Histar® rolled steel (ArcelorMittal) (2015.j version):
S355 HISTAR® and S460 HISTAR®.
- Conventional rolled steel with elastic limit reduction in accordance with CTE DB SE-A:
- EAE 2011 (Spain)
- Conventional rolled steel with elastic limit reduction in accordance with EAE 2011:
S235 (EAE), S275 (EAE), S355 (EAE). - Conventional rolled steel with elastic limit reduction in accordance with EN 10025-2 (Hot rolled products of structural steels. Part 2: Technical delivery conditions for non-alloy structural steels) (2015.j version):
S235 (EN 10025-2), S275 (EN 10025-2), S355 (EN 10025-2) and S450 (EN 10025-2). - Thermomechanical rolled steel with elastic limit reduction in accordance with EN 10025-4 (Hot rolled products of structural steels. Part 4: Technical delivery conditions for thermomechanical rolled weldable fine grain structural steels) (2015.j version):
S235 (EN 10025-4), S275 (EN 10025-4), S355 (EN 10025-4) and S450 (EN 10025-4). - Histar® rolled steel (ArcelorMittal) (2015.j version):
S355 HISTAR® and S460 HISTAR®.
- Conventional rolled steel with elastic limit reduction in accordance with EAE 2011:
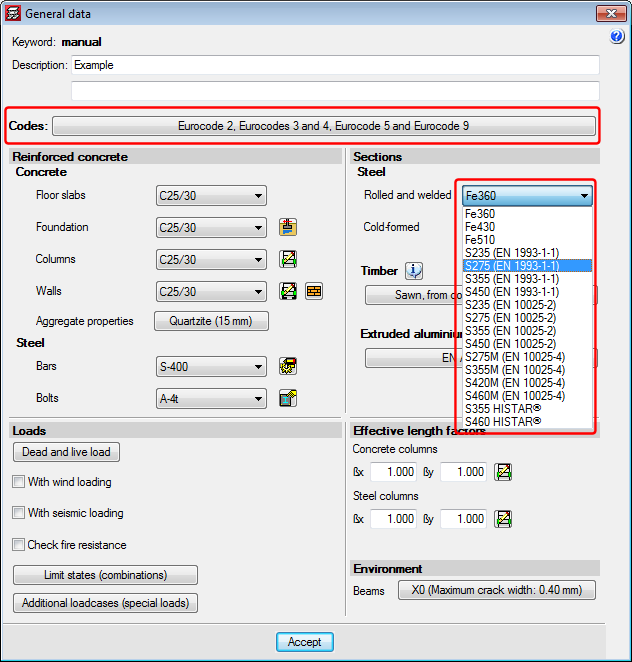
- Eurocodes 3 and 4
- Conventional rolled steel with elastic limit reduction in accordance with EN 1993-1-1:
S235 (EN 1993-1-1), S275 (EN 1993-1-1) and S355 (EN 1993-1-1). - Conventional rolled steel with elastic limit reduction in accordance with EN 10025-2 (Hot rolled products of structural steels. Part 2: Technical delivery conditions for non-alloy structural steels) (2015.j version):
S235 (EN 10025-2), S275 (EN 10025-2), S355 (EN 10025-2) and S450 (EN 10025-2). - Thermomechanical rolled steel with elastic limit reduction in accordance with EN 10025-4 (Hot rolled products of structural steels. Part 4: Technical delivery conditions for thermomechanical rolled weldable fine grain structural steels) (2015.j version):
S235 (EN 10025-4), S275 (EN 10025-4), S355 (EN 10025-4) and S450 (EN 10025-4). - Histar® rolled steel (ArcelorMittal) (2015.j version):
S355 HISTAR® and S460 HISTAR®. - Rolled steel no longer in use, which are available for compatibility reasons for older jobs:
Fe360, Fe430 and Fe510.
- Conventional rolled steel with elastic limit reduction in accordance with EN 1993-1-1:
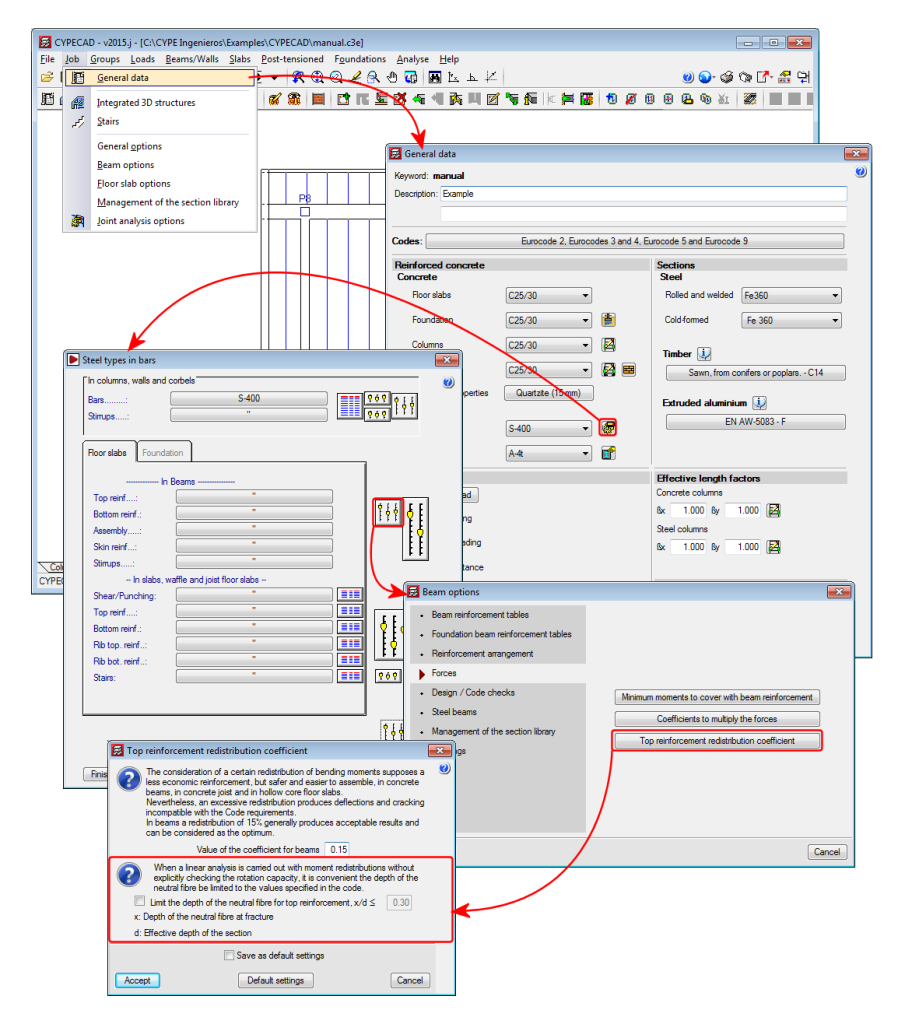
Limit the depth of the neutral fibre
When a moment redistribution analysis is carried out without explicitly checking the rotation capacity, it is convenient that the depth of the neutral fibre be limited to the values specified by the code that is being applied.
As of the 2015.j version, CYPECAD allows users to limit this depth, so it can be considered in the design, by introducing the "x/d" ratio, where "x" is the depth of the neutral fibre and "d" is the effective depth of the beam section.
This option can be activated in the "Top reinforcement distribution coefficient" dialogue box (see image).
Justification of seismic action report. Combined seismic shear per floor
In the 2015.j version, the "Justification of seismic action report" generated by CYPECAD has been extended to include the following sections:
- Combined seismic shear per floor
- Combined seismic shear and equivalent seismic force per floor
- Seismic shear percentage resisted per type of support and per floor
- Seismic shear percentage resisted per type of support at starts
The maximum calculated responses for each mode, for floor forces and shears, are combined using the CQC mode superposition method to obtain the total effect in each analysis direction. The results are displayed in graphs and tables.
This information allows users to assimilate the dynamic analysis that has been carried out to an equivalent static analysis. This data is both informative and descriptive, and provides a graphical and intuitive reference on the behaviour of the structure. Nonetheless, bear in mind that the program carries out a complete dynamic analysis with modal expansion for the design.
Another new feature displayed in the report is the percentage of seismic shear that is resisted depending on the type of the support. Many seismic codes classify resistance systems as "frame-type", "wall-type" or "mixed" depending on the seismic shear each element resists.
The structural systems are classified and then a numerical value is attributed to each category which reflects the energy absorption and dissipation of the structure, which in turn reduces the defined seismic action.
The percentage seismic shear that is resisted by column-type supports and the percentage resisted by shear wall-type supports are provided in the new section of the report, for each loadcase, per floor and at starts. This data allows users to check the type of resistance system used in the analysis and verify that the reduction in the applied seismic action, based on this classification, is adequate.