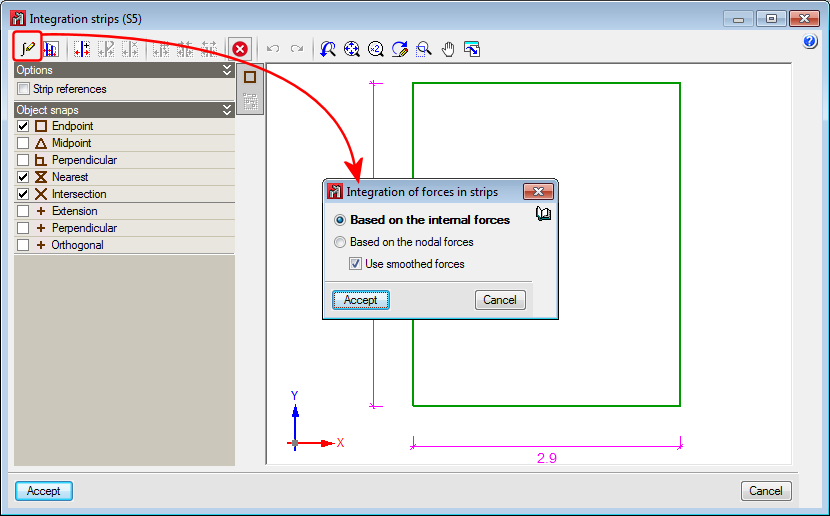
Once CYPE 3D has analysed a shell, “Integration strips” are generated in the two-dimensional element to process the nodal solutions provided by the finite element method and calculate the resultant force at specific sections of interest for the analysis.
As of the 2017.a version, the resultant can be calculated by applying one of the following methods:
- Internal forces integration method
The internal forces method is based on integrating the forces of the shell (forces per linear unit) calculated at certain points of the analysis section, determined by the program. The forces at each point are obtained by interpolating the corresponding nodal values of the element to which they belong. Once the forces are known at the points of the section, they are integrated to obtain its acting resultant.
The program offers the possibility to “Use smoothed forces”. The smoothing of forces consists in averaging the value at a vertex based on the values of each triangle that converge towards it. For the force interpolation process, the value at the vertices of the elements can be the actual value of each triangle, or the averaged value, depending on whether this option is selected or not.
This method provides very good results with a reduced integration strip width. - Nodal forces integration method
The nodal forces integration method calculates the resultant in a section of the shell using the forces at the nodes of the triangles. These are obtained by multiplying the stiffness matrix of the element by its displacement vector. Once the nodal forces are known, a part or portion of the shell in, where one of its edges is the analysis section, is isolated. The resultant in this section is obtained by reaching equilibrium of all the forces acting on the element: forces in the nodes of the perimeter and forces on the isolated portion.
This method provides very good results when the integration strip to calculate the resultant, has the entire width of the strip. When the width of the strip is smaller and this method is being used, it is recommended a refined discretisation of the shell be used or, alternatively, the method described previously: “Internal forces integration method”.
Thanks to the implementation of this option for CYPE 3D, StruBIM design allows users to select either method to integrate the forces in slabs and walls. More information on which method should be applied depending on the element whose forces are going to be obtained, can be found in the section: “Preferential methods for force integrations in 2D elements” in the new features of “StruBIM Design”.