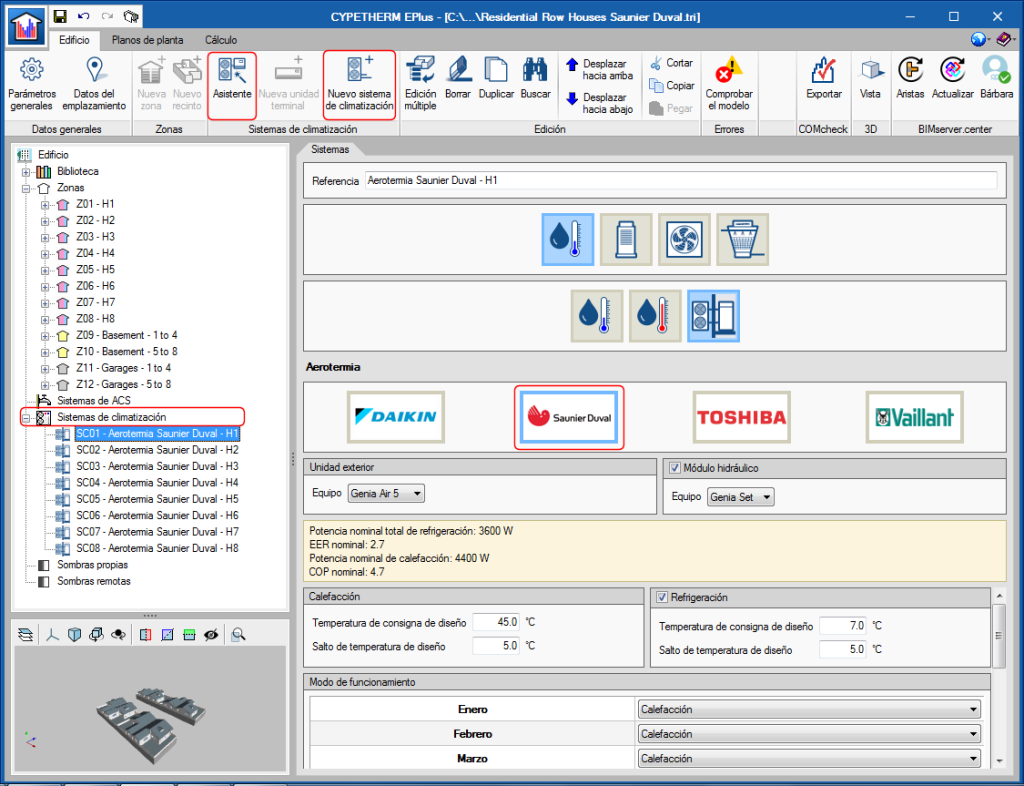
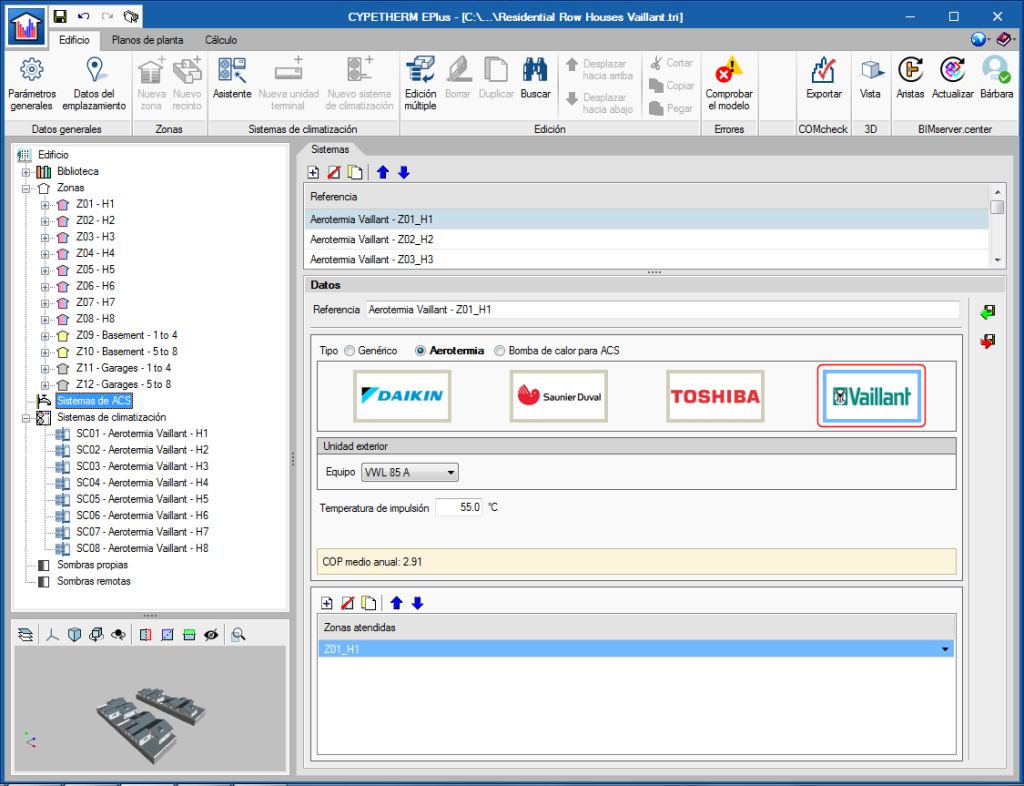
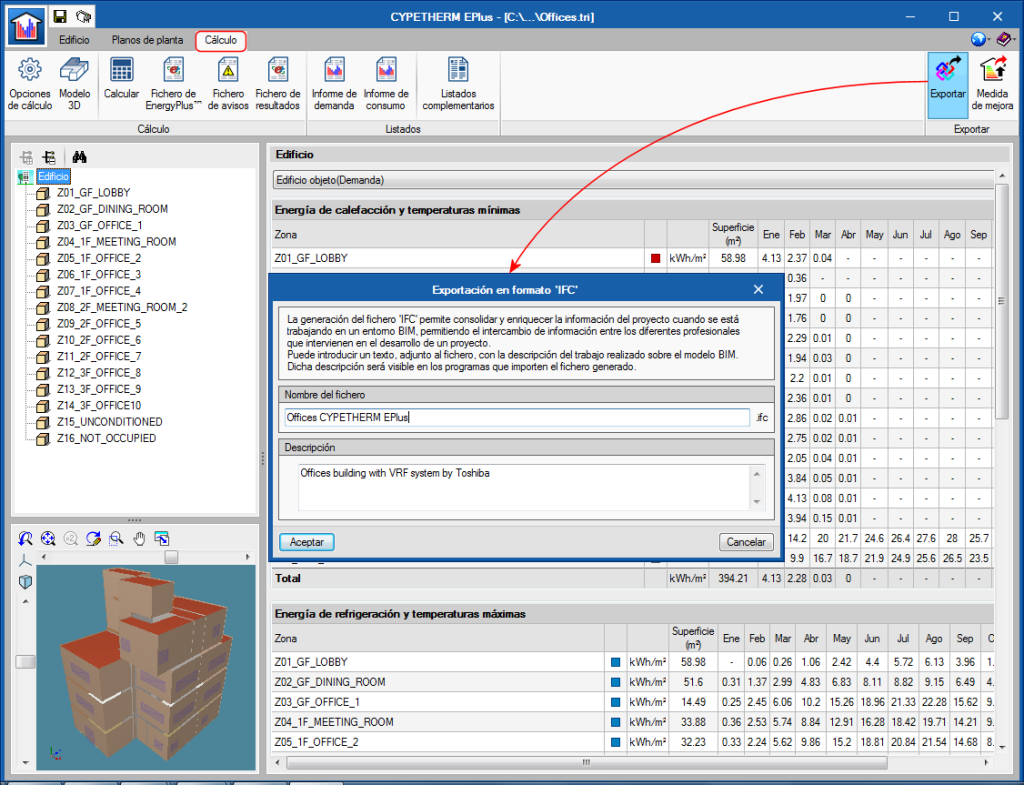
The "Genia Air" by Saunier Duval aerothermal systems catalogue has been incorporated. The Saunier Duval logo appears in the Aerothermal-type water air-conditioning systems. In the panel that opens when the logo is clicked on, users can choose between the different "Genia Air compacta" models of the range and add the "Genia Set” hydaulic module.
As occurs with other aerothermal systems, users can choose whether the system will be used only for heating or also for cooling. Users must also specify the working temperature conditions of the installation and its operating mode during the year.
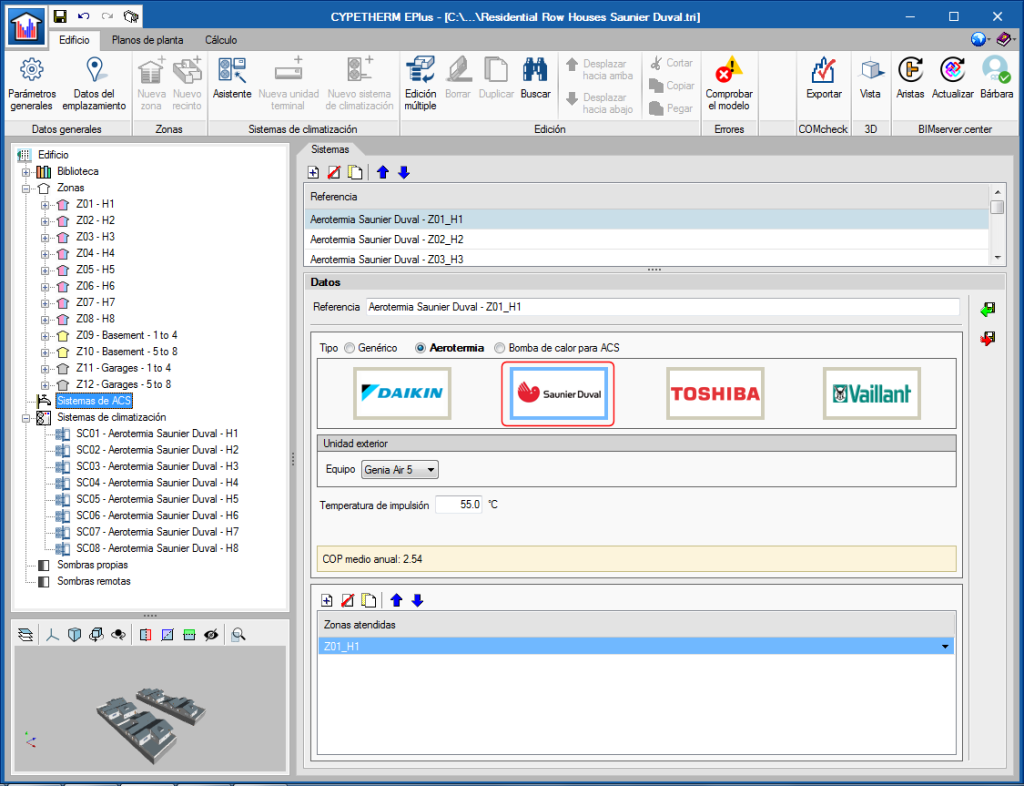
The “Genia Air compacta” aerothermal equipment by Saunier Duval have also been incorporated into the "DHW Systems" panel.