A new option has been implemented whereby users can define a different maximum aggregate size for each type of element: floor slabs, foundations, columns or walls (Job ˃ General data ˃ Aggregate properties in the reinforced concrete section).
Additionally, when the concrete EHE-08 (Spain) or ABNT NBR 6118 Projeto Junho 2013 (Brazil) codes are used, the nature of the aggregate can also be defined, with different values for floor slabs, foundations, columns or walls if users indicate it so. These design codes contain a correction coefficient of the longitudinal deformation module of the concrete, which depends on the nature of the aggregate used for its elaboration.
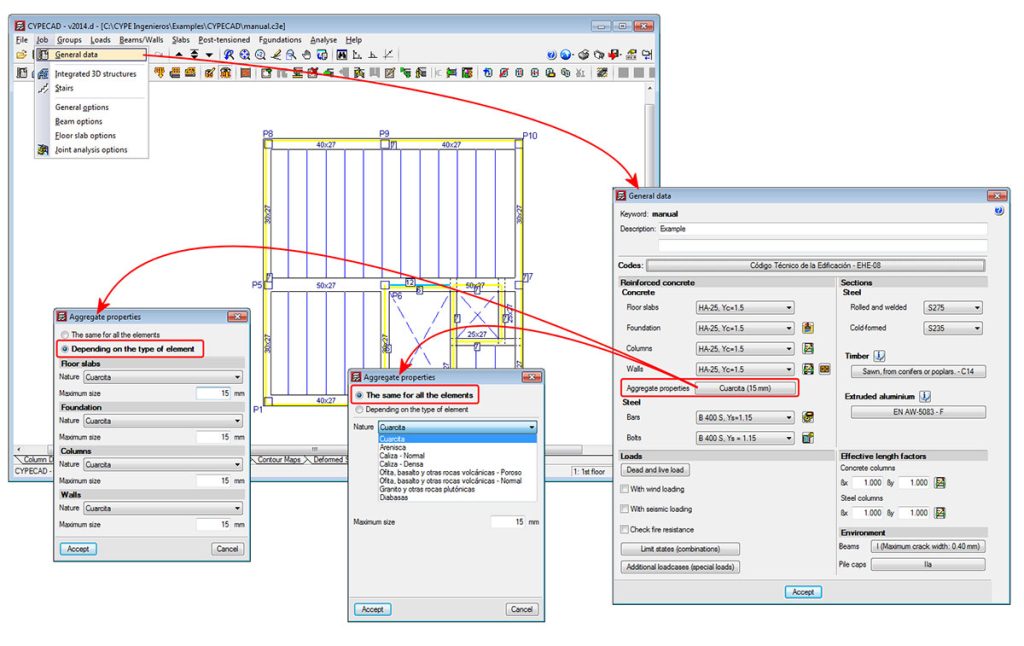
Using the EHE-08 code, the following aggregate nature types can be selected in accordance with that indicated in Table 39.6 (belonging to the comments of article “39.6. Módulo de deformación longitudinal del hormigón”):
- Cuarcita
- Arenisca
- Caliza normal
- Caliza densa
- Ofita basalto y otras rocas volcánicas - Poroso
- Ofita basalto y otras rocas volcánicas - Normal
- Granito y otras rocas plutónicas
- Diabasas
In the EHE-08 design code, the correction coefficient of the modulus of elasticity of the concrete is contained within the comments of the code, and so it is not obligatory for users to comply with it. When the nature of the aggregate is quartzite (cuarcita), the correction factor of the elasticity modulus has a value of 1, and this would be the option to be used if the reduction factor is not to be applied or, obviously, if this is the real nature of the aggregate that is used.
Using the ABNT NBR 6118 Projeto Junho 2013 code, the following aggregate natures can be selected as indicated in article “8.2.8. Módulo de elasticidade”:
- Basalto
- Diabásio
- Granito
- Gnaisse
- Calcário
- Arenito
Using the ABNT NBR 6118 Projeto Junho 2013 code, when a value of 1 is assigned to the correction coefficient of the modulus of elasticity of the concrete, it belongs to aggregates with “Granito” and “Gnaisse” natures.


