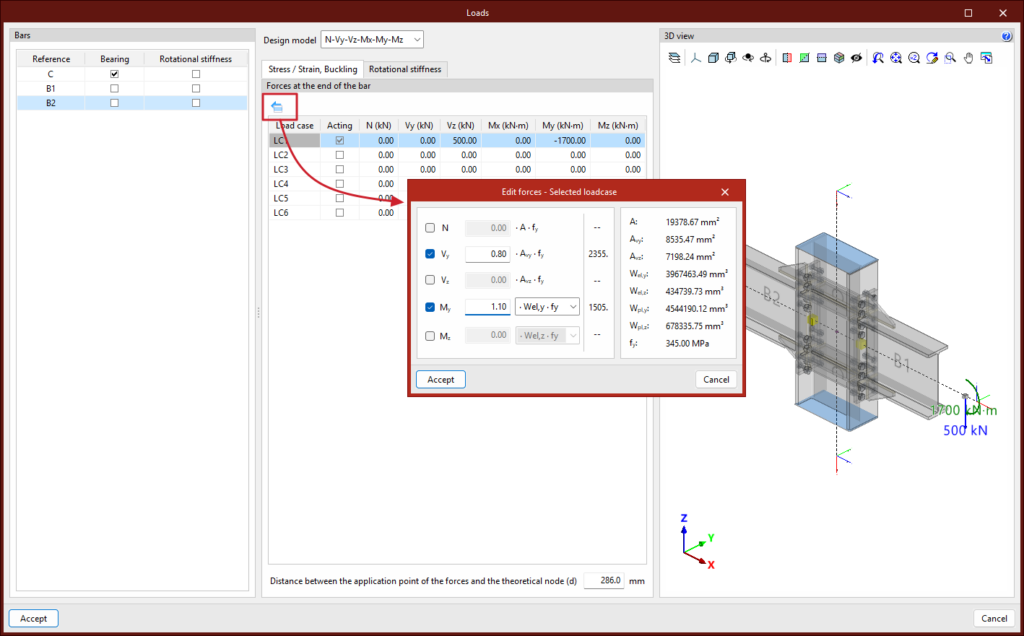
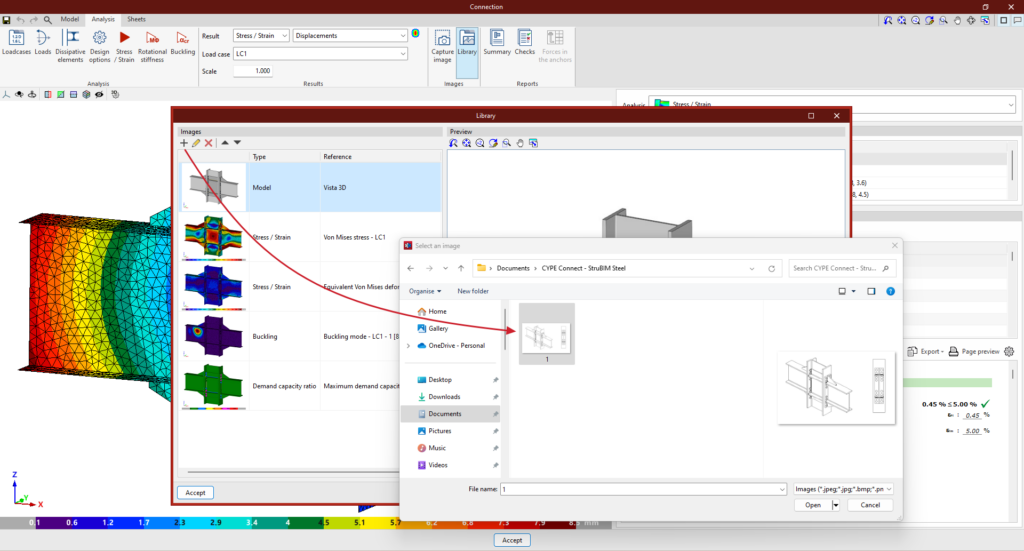
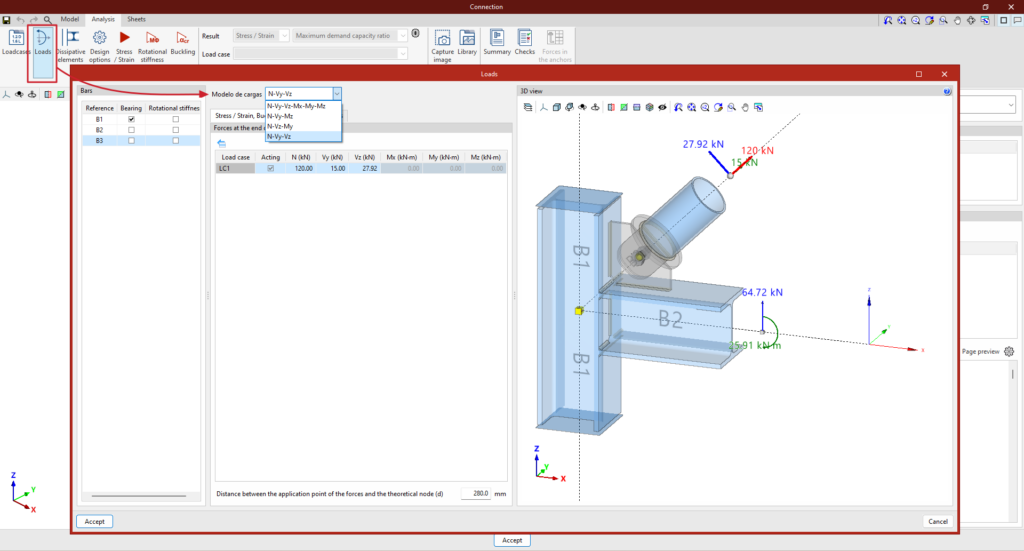
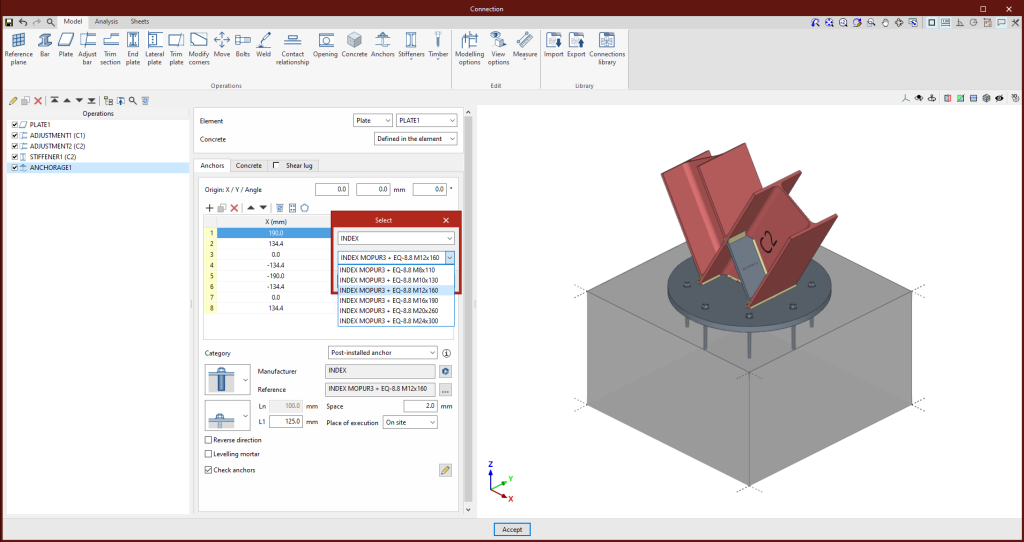
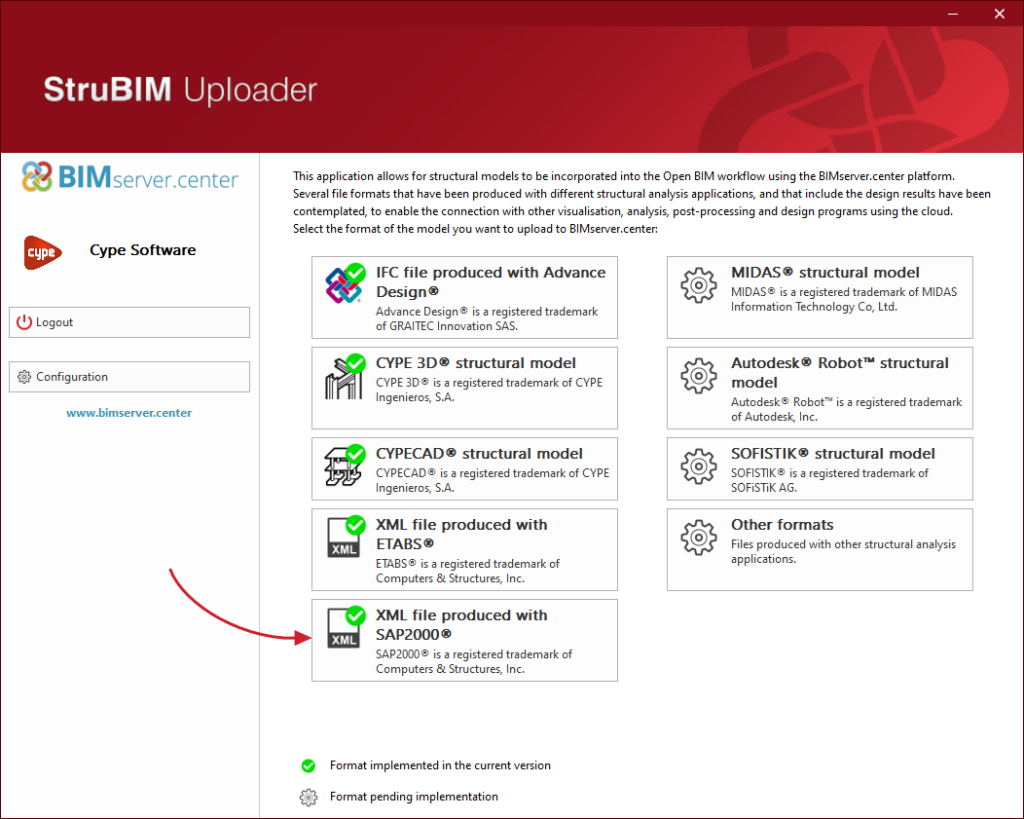
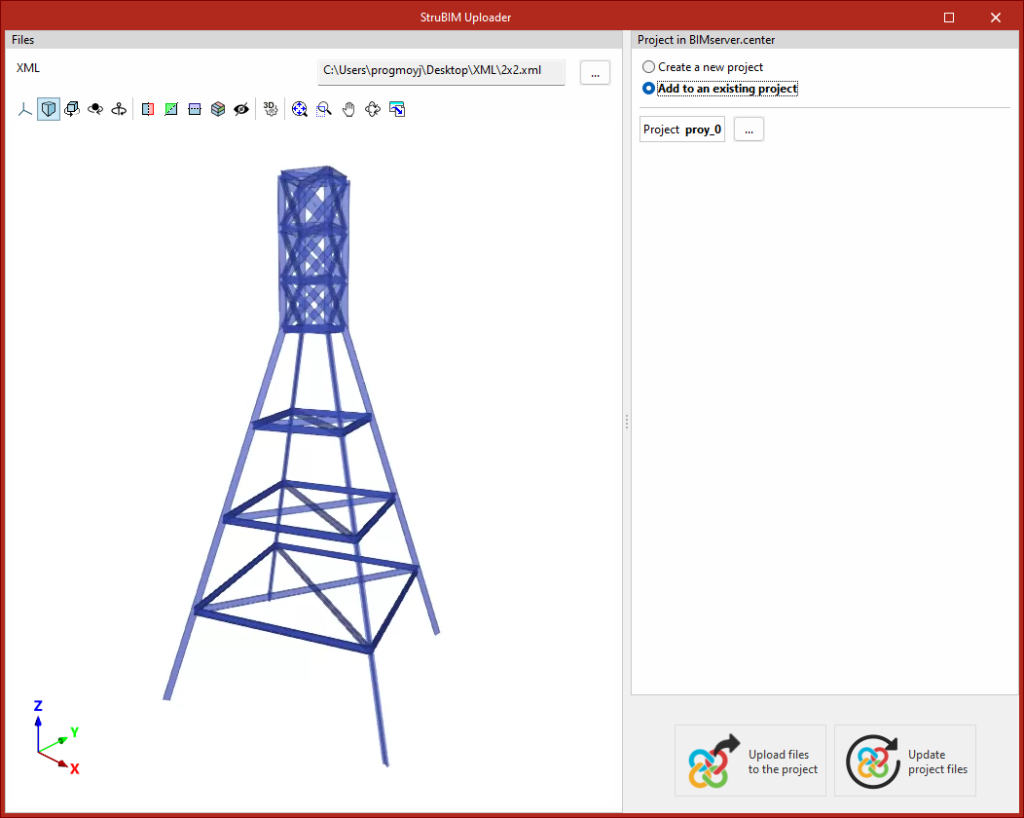
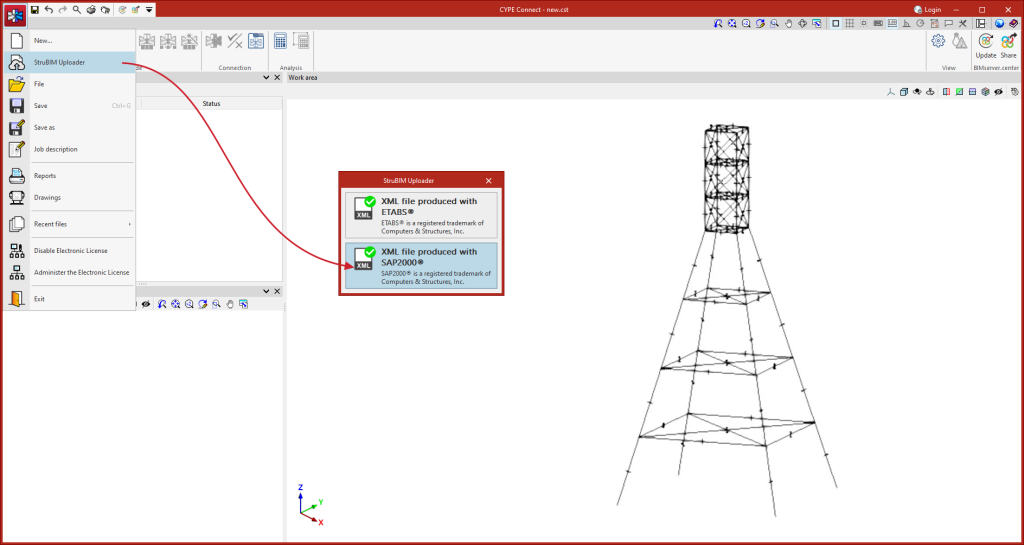
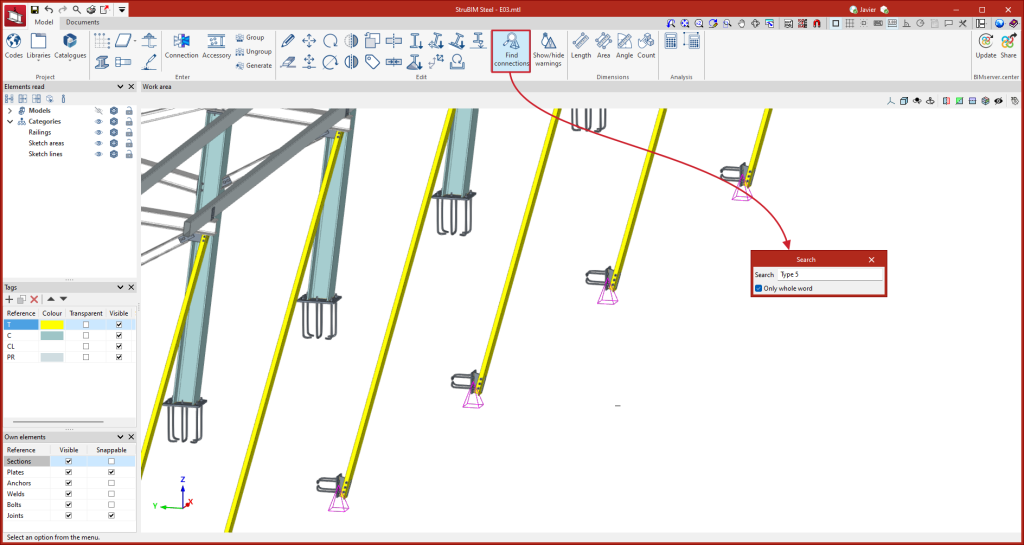
In version 2025.d, a tool has been implemented to define the loads applied to each bar based on the mechanical properties of its section. In the load edition panel, on the force table for each bar, the wizard for modifying the forces of the selected load case appears.
This tool changes the table value of each force by the new value calculated from a user-defined factor, the mechanical properties of the bar section and the yield strength of the bar steel. The factor can be defined with a positive or negative sign. To the right of each force activated by the user, the calculated force is displayed. On the right side of the panel, the mechanical properties of the bar section are displayed.