Defining the building element
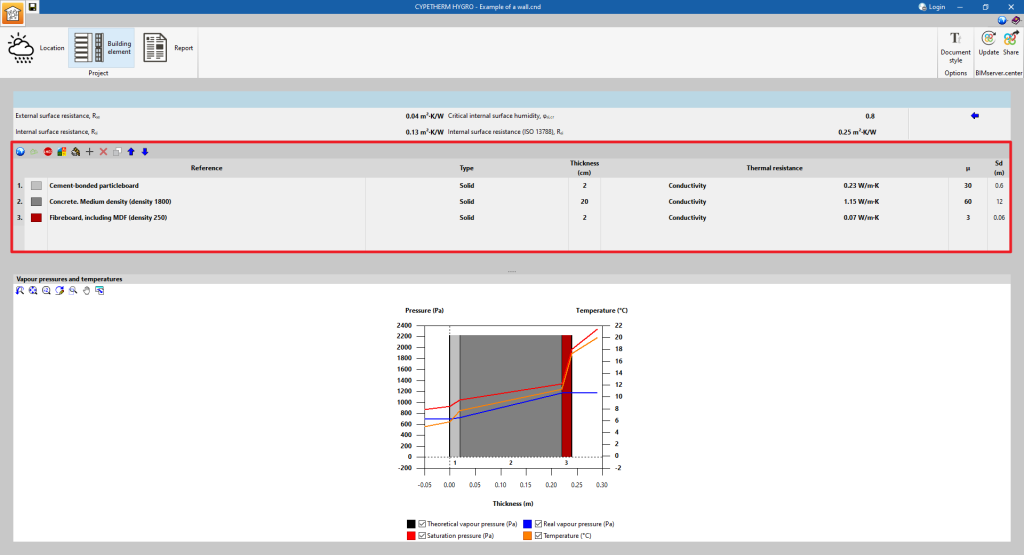
From the "Building element" section of the program's general interface, the model of the building element to be analysed can be defined by entering the different layers it is made of. In this interface, users can modify the order of the material layers or their properties to reduce or avoid the appearance of condensation and consult the results immediately on the screen.

Surface resistance and critical internal surface humidity
The following data is displayed at the top:
- External surface resistance, Rse (m2·K/W)
- Internal surface resistance, Rse (m2·K/W)
- Critical internal surface humidity, φsi,cr
- Internal surface resistance (ISO 13788), Rsi (m2·K/W)
Importing data according to the element arrangement
The above data can be imported automatically depending on the element arrangement, which can be the following:
- Vertical
- Horizontal, with ascending flow
- Horizontal, with descending flow
Furthermore, by ticking the corresponding box, users can indicate whether "It is an internal partition in contact with an unoccupied space".
The critical internal surface humidity for the surface condensation calculation can be defined manually or one of the following options can be selected:
- Designed to prevent mildew from forming
- Design to prevent corrosion
Material layers
In the central table, the different layers of materials that make up the element are entered, specifying the following data:
- Colour
- Reference
- Type (solid/air cavity/vapour barrier)
- Thickness (cm)
- Thermal resistance, defined by its "Thermal Resistance" (m2-K/W) or by its "Conductivity" (W/m-K)
- Water vapour diffusion resistance factor, µ
- Equivalent air thickness, Sd (m)
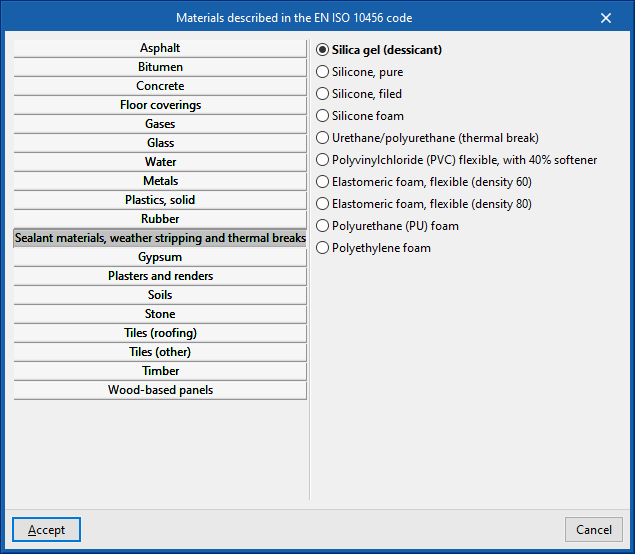
Libraries and material catalogues
All this data can be imported using the various libraries and material catalogues available.
- EN ISO 10456:2012
- Materials from the HULC library (Spain)
- Materials from the LIDER library (Spain)
- BINAYATE (Morocco)
- LNEC (Portugal)
- RT 2012 (France)
- UNI 10351 (Italy)
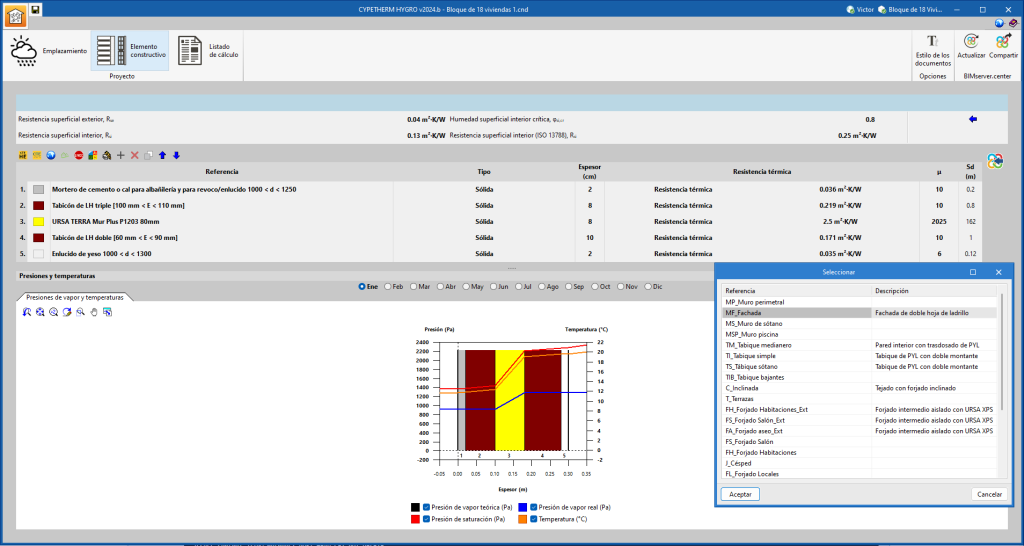
Importing construction systems defined in the BIMserver.center project
To generate the material layers, users can also import the "Construction systems defined in the project". To do this, the corresponding button on the right-hand side of the screen is used. When clicking on this option, a list of all available construction systems from the project input is displayed. Once the element has been selected, the material layers and their properties are automatically added.
Vapour pressures and temperatures
When defining layers, the "Vapour pressures and temperatures" graph for the different calculation periods is displayed at the bottom. The calculation of interstitial condensation includes the generation of the following graphs:
- Theoretical vapour pressure (Pa)
- Saturation pressure (Pa)
- Real vapour pressure (Pa)
- Temperature (ºC)
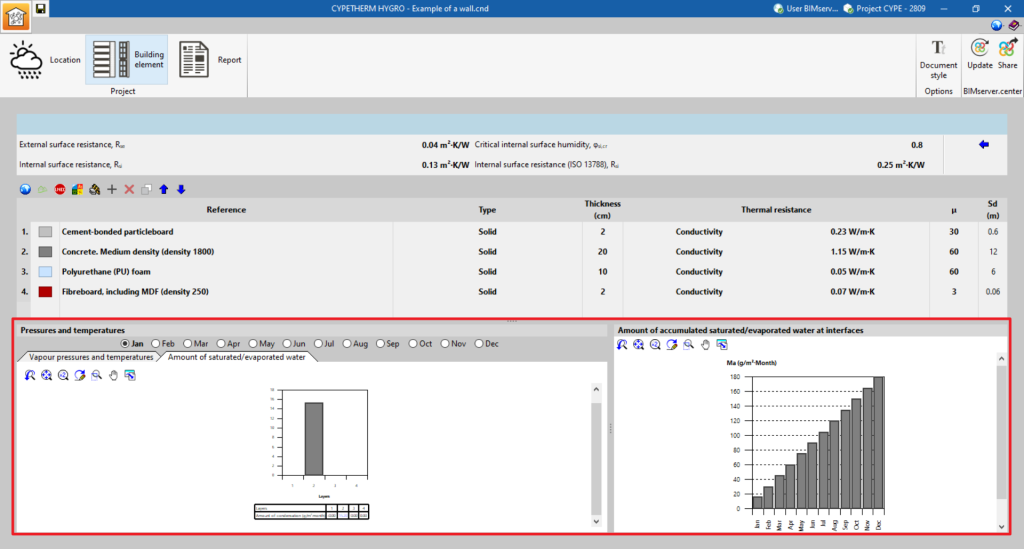
Saturated/evaporated water graphs
If there is interstitial condensation, the program displays a graph of the "Amount of saturated/evaporated water" (g/m2-month) for each layer and analysis period. Further to the right, in the case of a calculation with monthly values, the "Amount of accumulated saturated/evaporated water at interphases" is displayed month by month.