Managing building element libraries
The definition of building elements in the thermal model libraries is necessary to detail the data related to their thermal behaviour, including the possibility of specifying the composition of material layers and the technical characteristics of each of them, such as thermal conductivity or thermal resistance. This data can be entered manually or based on different catalogues and reference standards with predefined materials and will affect the thermal load analysis carried out by the program.
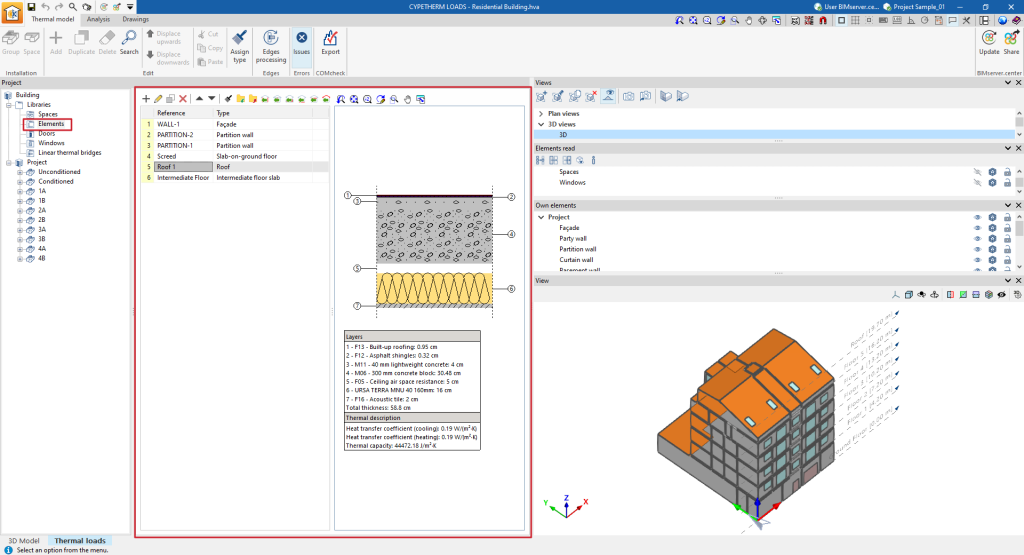
The management tools for the libraries of building elements of the thermal model are located in the lower tab "Thermal loads", in the upper tab "Thermal model" and, in the "Project" definition area, in the "Libraries" tree located by default on the left-hand side.
Elements library
General definition of building elements
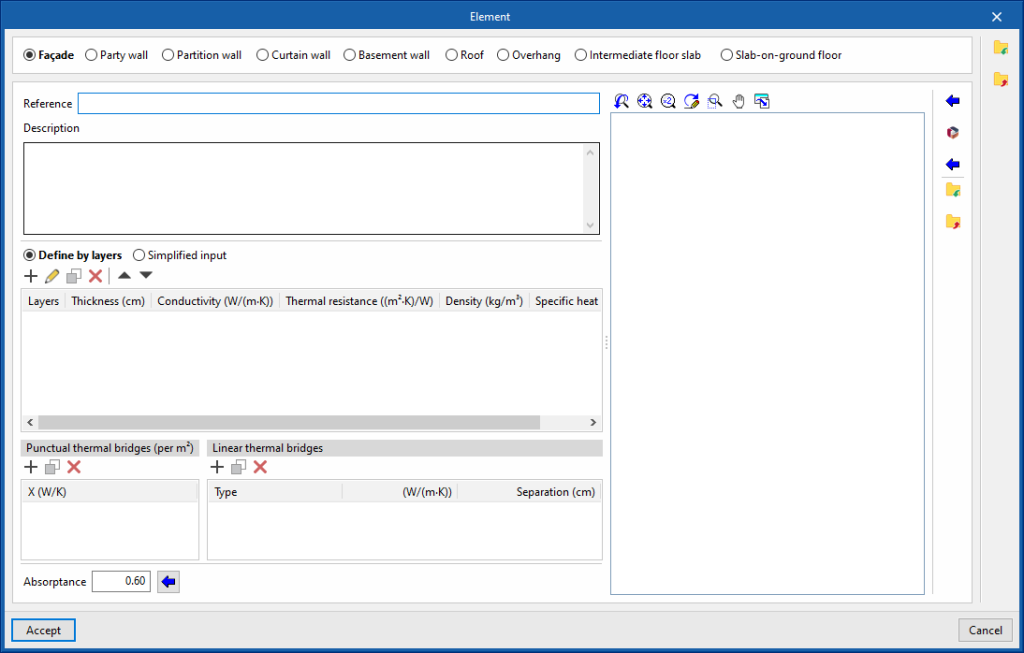
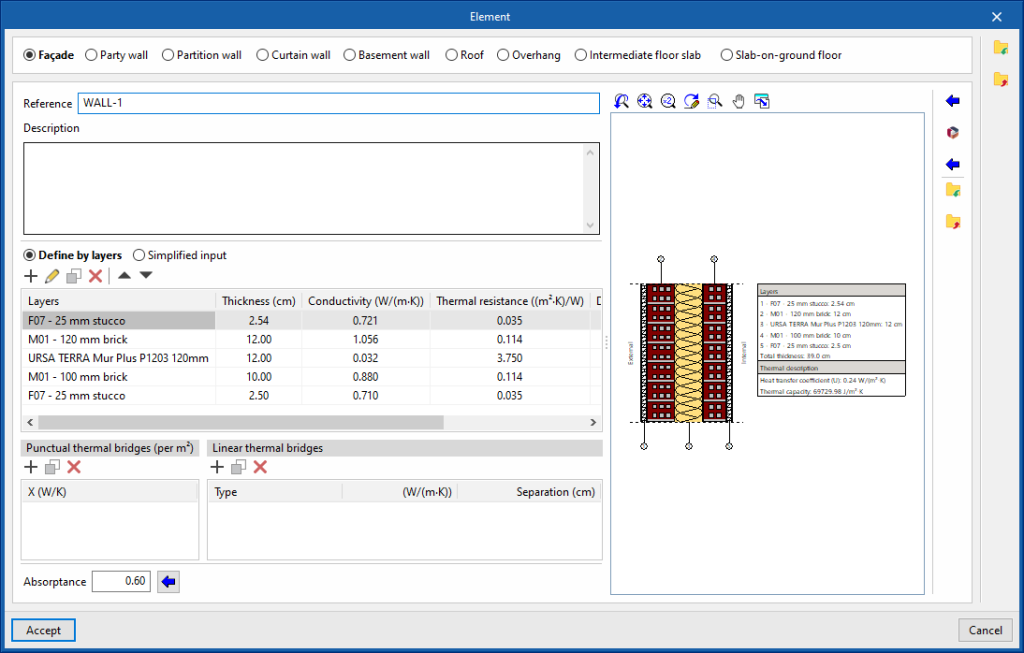
When adding or editing an element type in the library, the following parameters must be configured:
- Type of element (Façade / Party wall / Partition wall / Curtain wall / Basement wall / Roof / Overhang / Intermediate floor slab / Screed)
- Reference
- Description
- Define by layers / Simplified input
Specifies whether the thermal characteristics of the element are defined by entering the data for each of the component material layers or by a simplified definition. - Absorptance (in elements such as "Façade", "Party wall", "Partition wall", "Roof", "Overhang", or "Intermediate floor slabs")
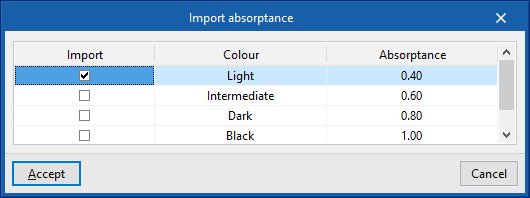
The absorption fluctuates between 0 and 1. The value can be imported with the wizard available on the right:- Import absorptance
The value of this coefficient is lower on light surfaces, and higher on dark surfaces.
- Import absorptance
- Soil thermal conductivity (in "Basement wall" or "Screed" type elements)
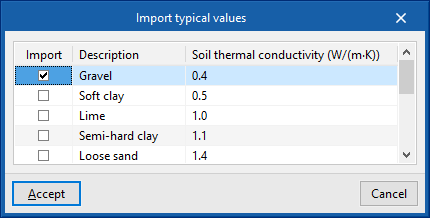
The conductivity of the soil varies according to its type. The value can be imported with the wizard available on the right:- Importing the thermal conductivity according to the type of soil
The lowest values correspond to gravels and silts; sands provide intermediate values, while rock provides higher values.
- Importing the thermal conductivity according to the type of soil
Additionally, the options in the right-hand column of the "Element" window allow the import of complete building systems from catalogues and databases such as the Open BIM Database.
Defining material layers
If the element is defined by layers, the program offers a table where the material layers of the element can be added, edited, copied, deleted or reordered:
- Define by layers
- Layers
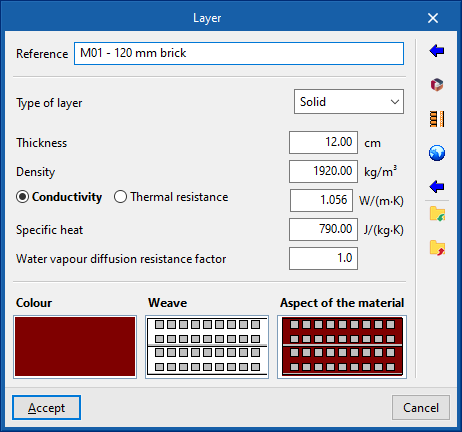
When entering a material layer, the following parameters must be specified:- Reference
- Type of layer
A choice must be made as to whether the coating is solid, an air cavity or a vapour barrier.- Solid
- Thickness
- Density
- Conductivity / Thermal resistance
- Specific heat
- Water vapour diffusion resistance factor
- Air cavity
- Thickness
- Thermal resistance
- Vapour barrier
- Equivalent air thickness
- Solid
- Colour / Weave / Aspect of the material
Adjusts the graphical representation of the layer material.
- Layers
- Importing data
The options in the right column of the "Layer" window allow the automatic import of material data from information provided by different catalogues and standards:- Open BIM Database manufacturer materials
- Open BIM Database catalogue management
- HULC library materials
- Air chambers described in UNE-EN ISO 6946
- Materials described in UNE-EN ISO 10456
- Materials described in EN ISO 10456
- Representative materials (2013 ASHRAE Handbook - Fundamentals)
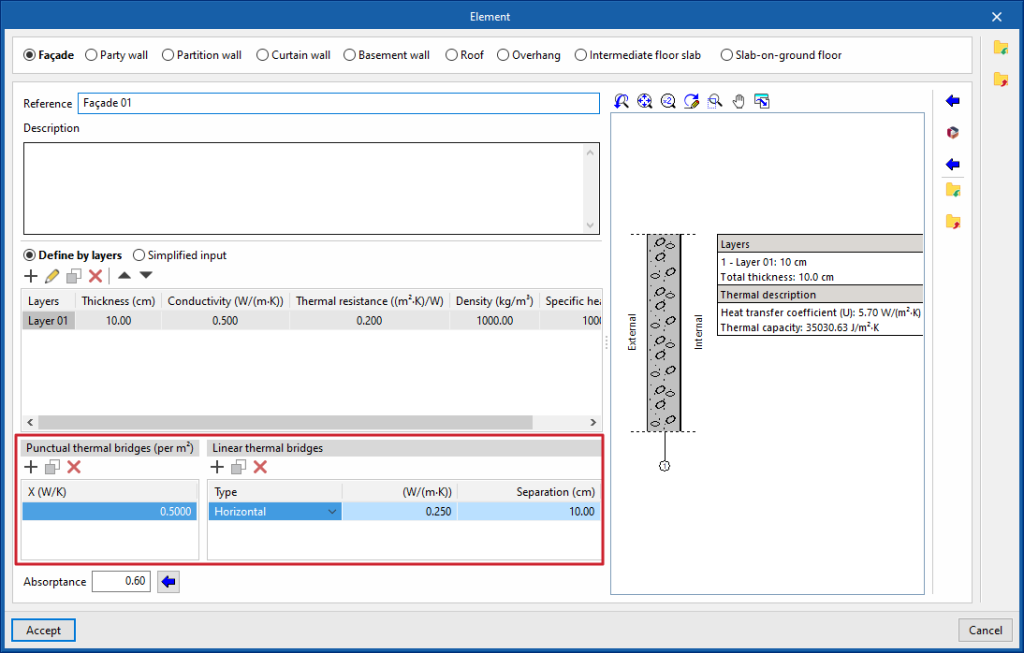
- Punctual thermal bridges
This table is used to declare the existence of point thermal bridges for each surface unit of the element, and their point thermal transmittance value (W/K).
- Linear thermal bridges
This table is used to declare the existence of linear thermal bridges along the surface of the element, in horizontal or vertical direction, and their linear thermal transmittance value (W/(m-K)).
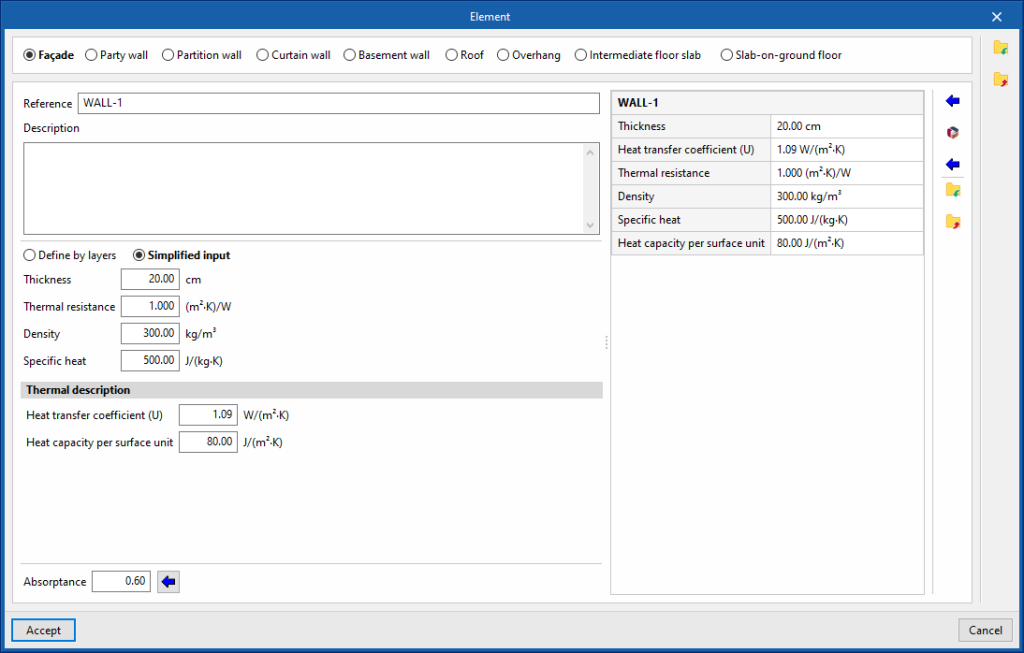
Simplified input
The simplified definition of the element type involves entering its global properties. This is useful if the layer-by-layer data is unknown, if these properties are available or if they have been analysed outside the program.
- Simplified input
- Thickness
- Thermal resistance
- Density
- Specific heat
- Thermal description
- Heat transfer coefficient
- Heat capacity per surface unit
Specific options when defining screeds and raised floor slabs
"Screed" type elements define the following characteristics.
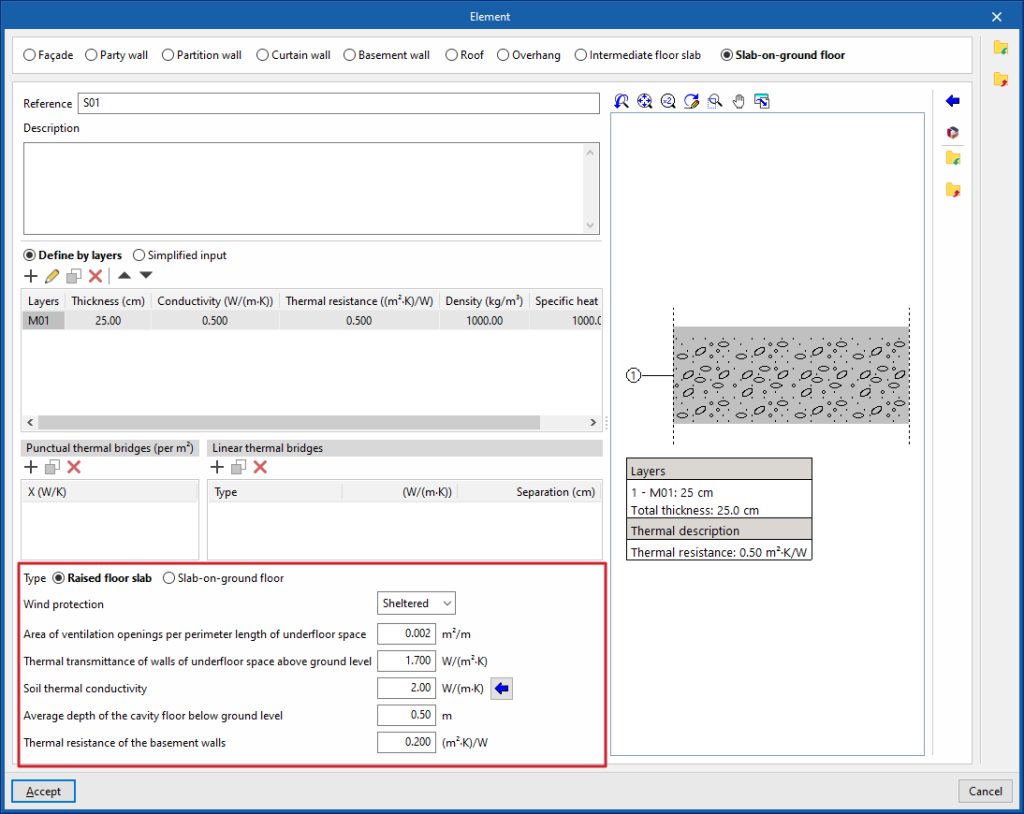
Raised floor slab
Raised floor slabs are defined in the program as a specific type of floor slab. By selecting "Raised floor slab", the program allows users to enter the information about the cavity under the slab and other data such as the following:
- Wind protection (Sheltered / Medium / Exposed)
- Area of ventilation openings per perimeter length of underfloor space
- Thermal transmittance of walls of underfloor space above ground level
- Soil thermal conductivity
- Average depth of the cavity floor below ground level
- Thermal resistance of the basement walls
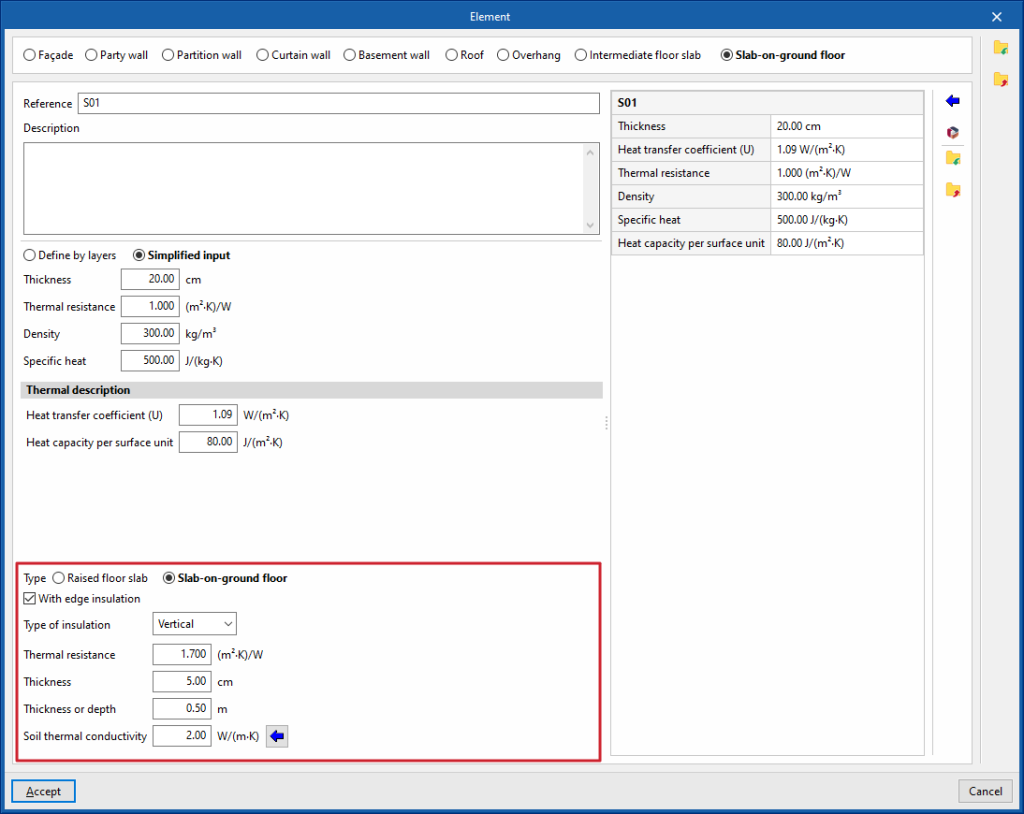
Screed
In the case of screeds alone, peripheral insulation can be added and its characteristics can be defined:
- With edge insulation (optional)
- Type of insulation (Vertical / Horizontal)
- Thermal resistance
- Thickness
- Thickness or depth
- Soil thermal conductivity
- Importing the thermal conductivity according to the type of soil
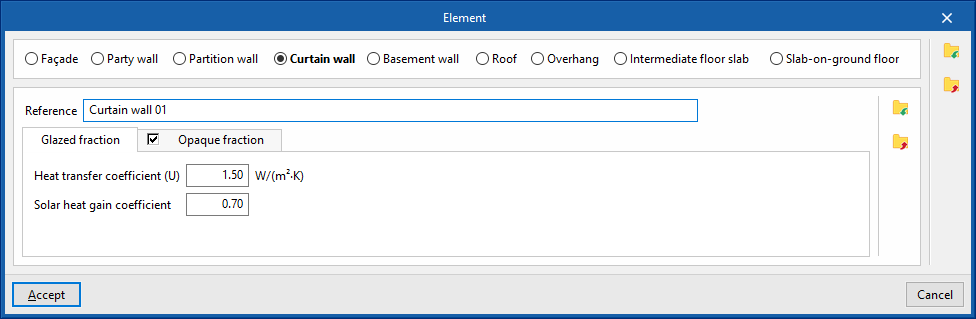
Specific options when defining curtain walls
"Curtain wall" type elements define the following characteristics:
- Reference
- "Glazed fraction" tab
- Thermal transmittance (U)
- Solar factor
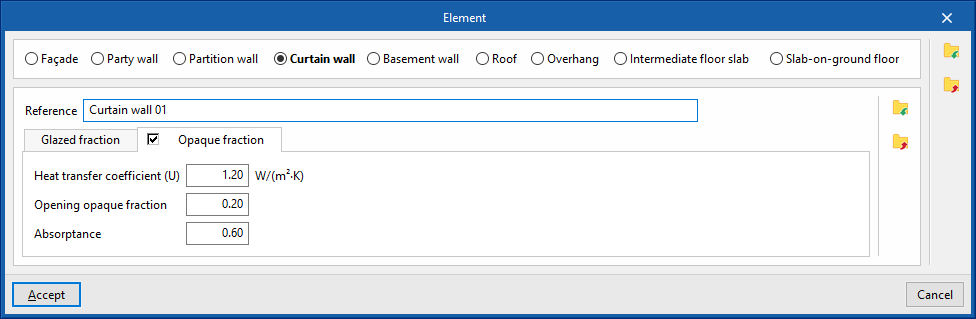
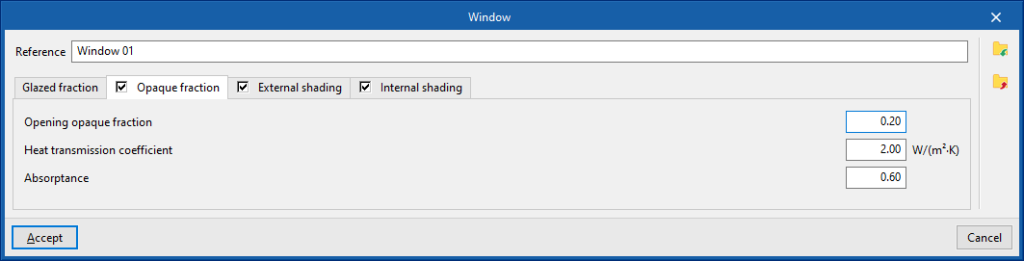
- "Opaque fraction" tab (optional)
- Thermal transmittance (U)
- Opening opaque fraction
This parameter is used to define the proportion of opaque elements covering the total surface of the curtain wall, in percentage. - Absorptance
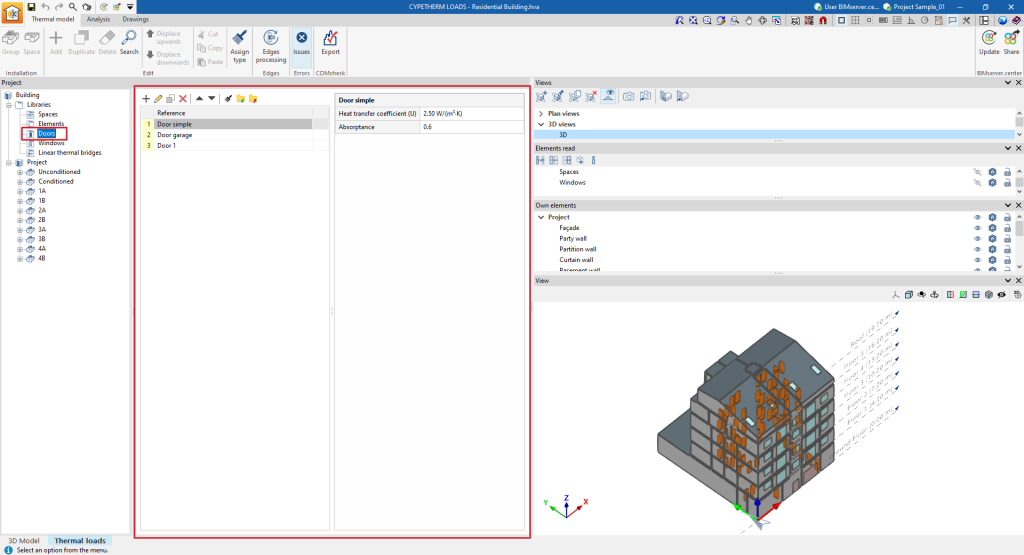
Door library
Like the libraries of the other building elements, the door library can be accessed using the default tree on the left-hand side.
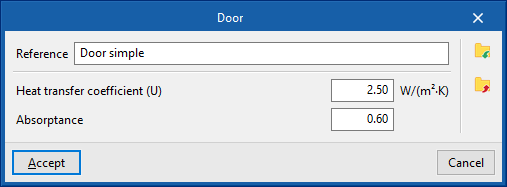
Each door typology entered requires the definition of the following characteristics:
- Reference
- Heat transfer coefficient
- Absorptance
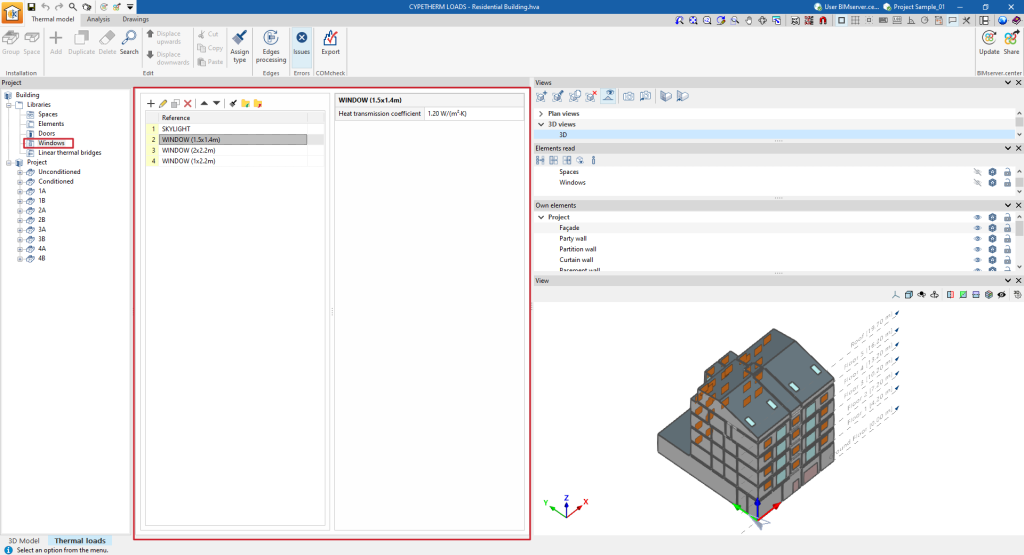
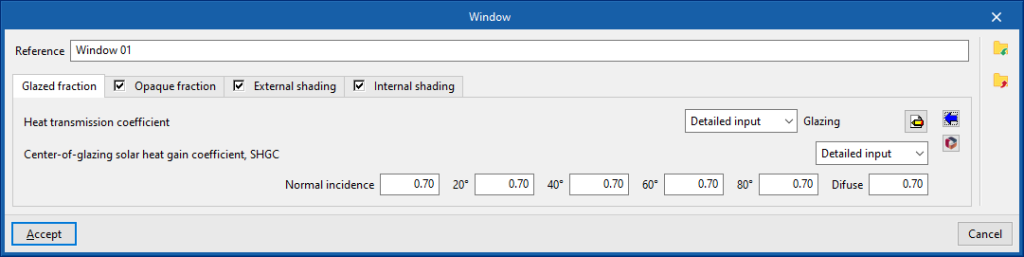
Window library
The window library can also be accessed using the default tree on the left-hand side.
When creating or editing a window type, the data corresponding to its glazing fraction and, optionally, the characteristics of its opaque fraction can be defined, as well as the adjustment of parameters related to its external and internal shading.
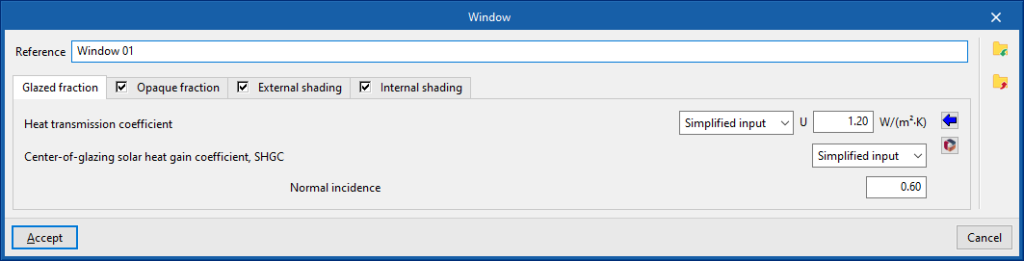
- Reference
Opening reference.
- "Glazed fraction" tab
Defines the glazing data of the opening.- Heat transmission coefficient
Heat transmission coefficient of the glazing fraction of the opening.- Simplified input
This option is used to directly enter the heat transmission coefficient of the glazing fraction:- U
- Detailed input
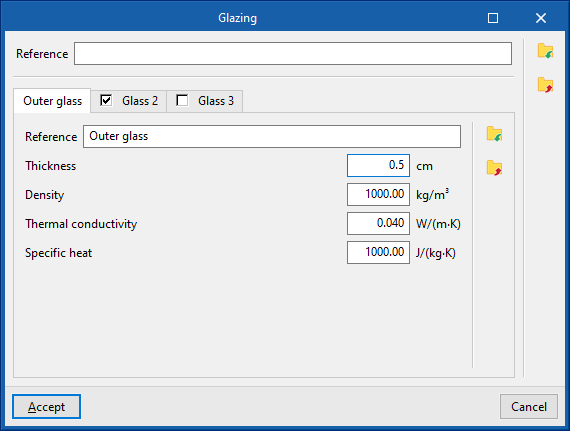
If a detailed definition of the heat transmission coefficient is used, the details of the external glazing and, if available, of the second and third panes, in the case of double or triple glazing, must be given:- "Outer glass" tab
- Thickness
- Density
- Thermal conductivity
- Specific heat
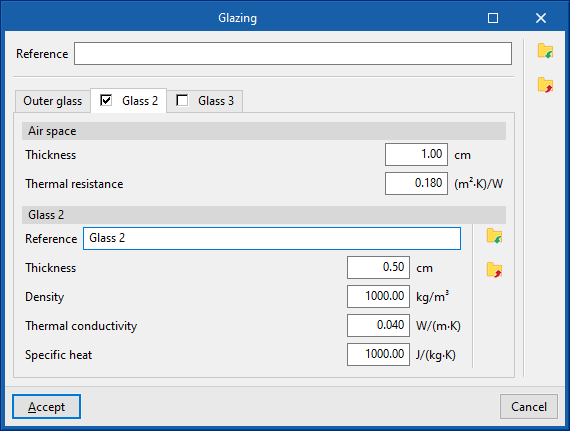
- "Glass 2" tab (optional)
- Air space
- Thickness
- Thermal resistance
- Glass 2
- Thickness
- Density
- Thermal conductivity
- Specific heat
- Air space
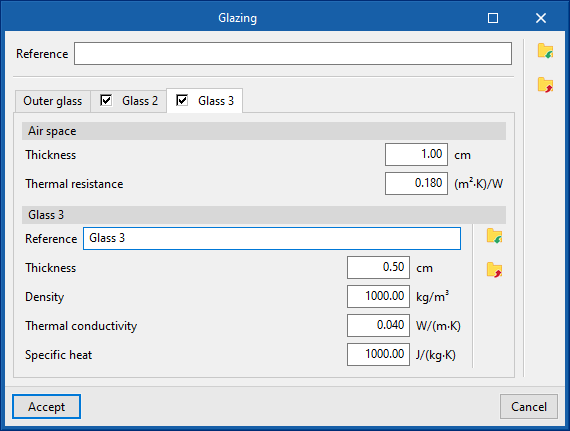
- "Glass 3" tab (optional)
- Air space
- Thickness
- Thermal resistance
- Glass 3
- Thickness
- Density
- Thermal conductivity
- Specific heat
- Air space
- "Outer glass" tab
- Simplified input
- Solar factor of the glass, SHGC
- Simplified input
The solar factor of the glass can be entered, indicating its normal incidence value.- Normal incidence
- Detailed input
The solar factor can be detailed by entering its values according to the angle of incidence.- Normal incidence
- 20º
- 40º
- 60º
- 80º
- Diffuse
- Simplified input
- Importing data from Open BIM Database
- Heat transmission coefficient
- "Opaque fraction" tab (optional)
Defines the data of the opaque part of the opening.- Opening opaque fraction
Fraction of the frame, or area of the opening covered by opaque elements belonging to the frame. It is defined as a percentage of one. - Heat transmission coefficient
Heat transmission coefficient of the glazing fraction of the opening. - Absorptance
- Opening opaque fraction
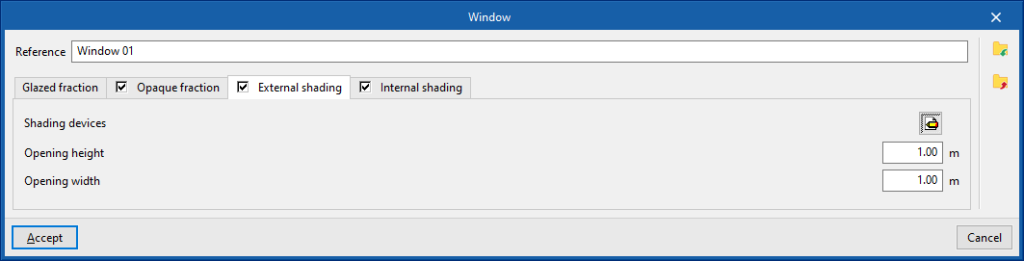
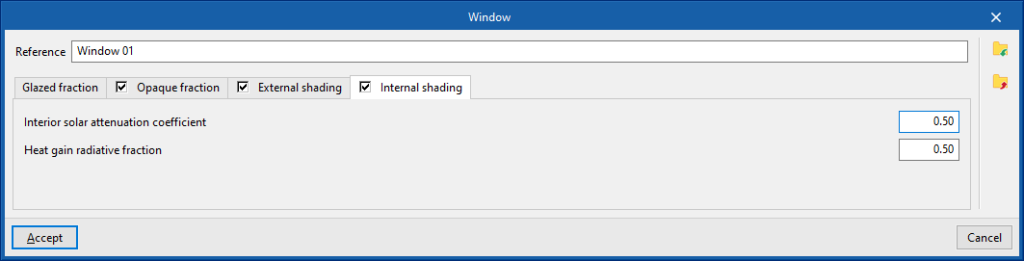
- "External shading" tab (optional)
Simulates the effect of external shading of recesses, window overhangs or side projections if they have not been defined in the geometrical model.- Shading devices
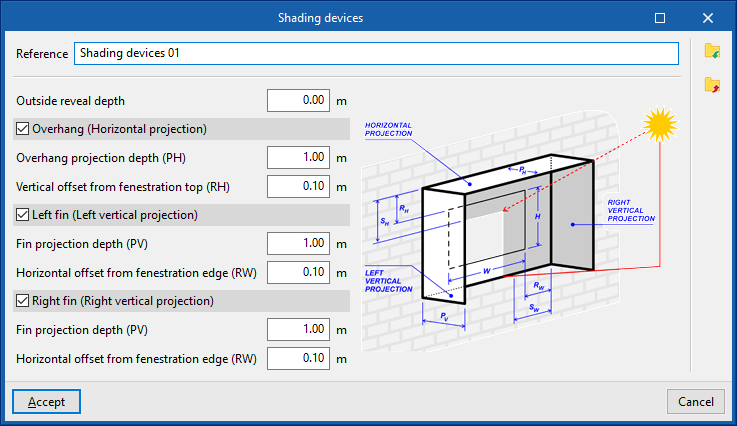
- Reference
- Outside reveal depth
- Overhang (Horizontal projection) (optional)
- Overhang projection depth (PH)
- Vertical offset from fenestration top (RH)
- Left fin (Left vertical projection) (optional)
- Fin projection depth (PV)
- Horizontal offset from fenestration edge (RW)
- Right fin (Right vertical projection) (optional)
- Fin projection depth (PV)
- Horizontal offset from fenestration edge (RW)
- Opening height
- Opening width
- Shading devices
The options for defining the external shading of windows allow this data to be entered in a specific way if it cannot be obtained from these other sources of information.