Water-cooled system
Water-cooled systems include condensing systems for reversible heat pumps, using cooling towers and boilers, condensing systems for chillers, using single or two-speed cooling towers, and water-cooled systems at a defined, constant or time-controlled temperature.
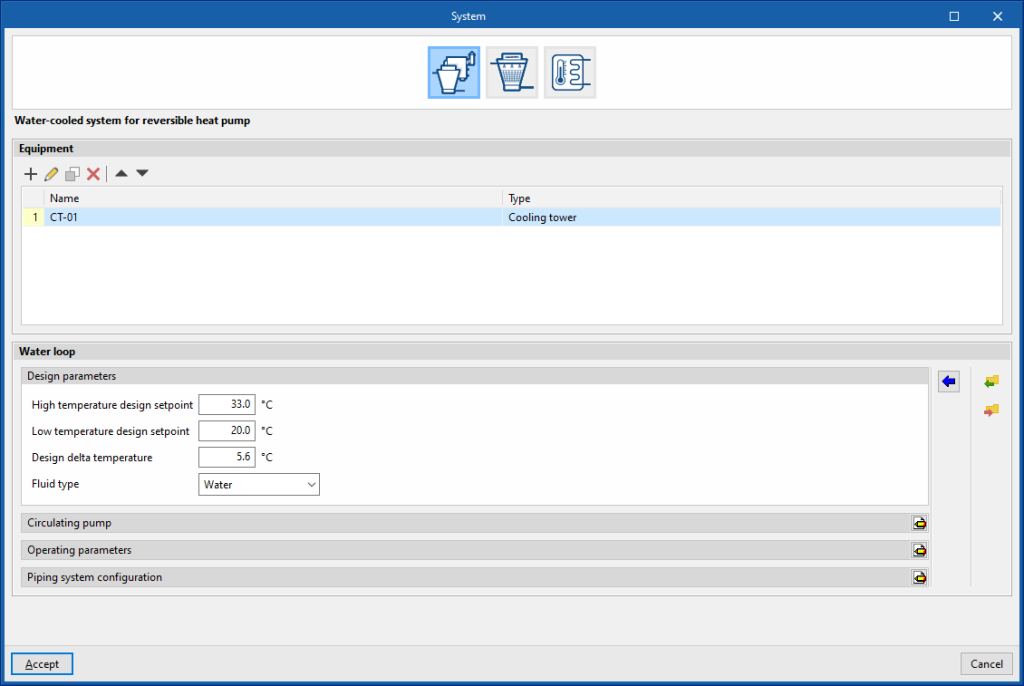
Water-cooled system for reversible heat pump
Equipment
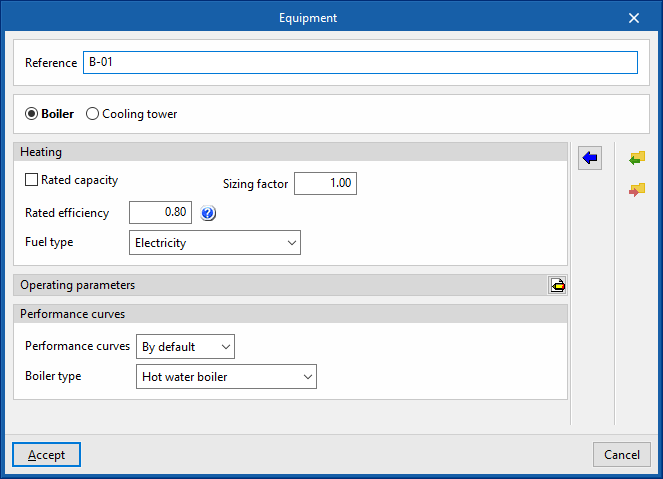
Boiler
- Reference
Reference of the unit. - Heating
- Gross rated capacity (optional)
- Sizing factor
- Rated efficiency
If the performance curve is not defined, the efficiency value of the boiler measured at the following nominal conditions must be given:- Conventional boiler: water outlet at 82°C / Condensing boiler: water inlet at 70°C.
- Fuel type (Electricity / Natural gas / LPG / Diesel / Coal / Biomass / Densified biomass (pellets))
- Gross rated capacity (optional)
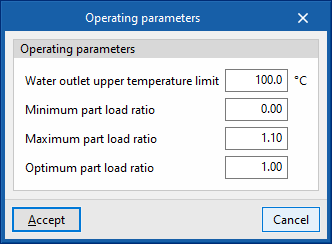
- Design parameters
- Water outlet upper temperature limit
- Minimum part load ratio
- Maximum part load ratio
- Optimum part load ratio
- Performance curves
- Default
- Conventional boiler / Condensing boiler
- User-defined
- Default
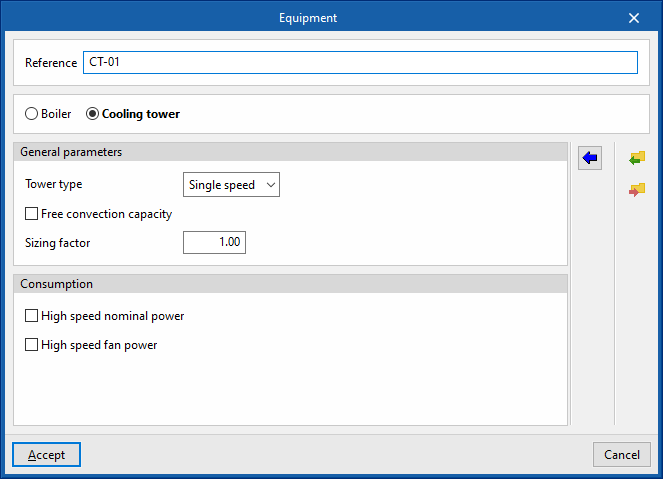
Cooling tower
- Reference
Reference of the unit. - Cooling tower
- Tower type (Single speed / Two speed)
- Free convection capacity
- Sizing factor
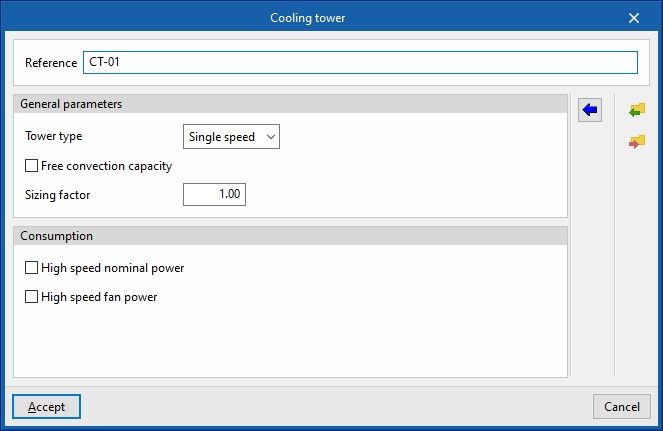
- Consumption
- In single-speed cooling towers:
- High speed nominal power (optional)
- High speed fan power (optional)
- In two-speed cooling towers:
- High speed nominal power (optional)
- High speed fan power (optional)
- Low speed nominal power (optional)
- Low speed fan power (optional)
- In single-speed cooling towers:
Water distribution
- Design parameters
- High temperature design setpoint
- Low temperature design setpoint
- Design delta temperature
- Type of fluid (Water / Ethylene glycol / Propylene glycol)
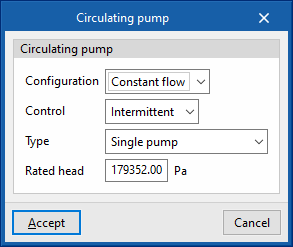
- Circulating pump
- Configuration (Variable flow / Constant flow)
- Control (Intermittent / Continuous)
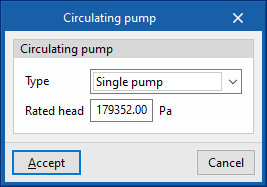
- Primary loop pump type (Single pump / Pump per chiller / Two headered pumps / Three headered pumps / Four headered pumps / Five headered pumps)
- Primary loop pump rated head
- Primary loop pump rated head
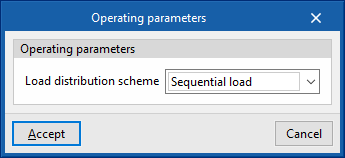
- Load distribution scheme (Optimal / Sequential load / Uniform load / Uniform PLR / Sequential uniform PLR)
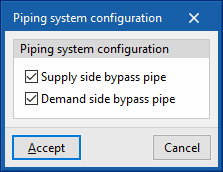
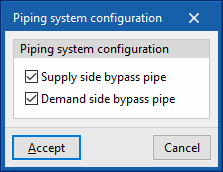
- Piping system configuration
- Supply side bypass pipe (optional)
- Demand side bypass pipe (optional)
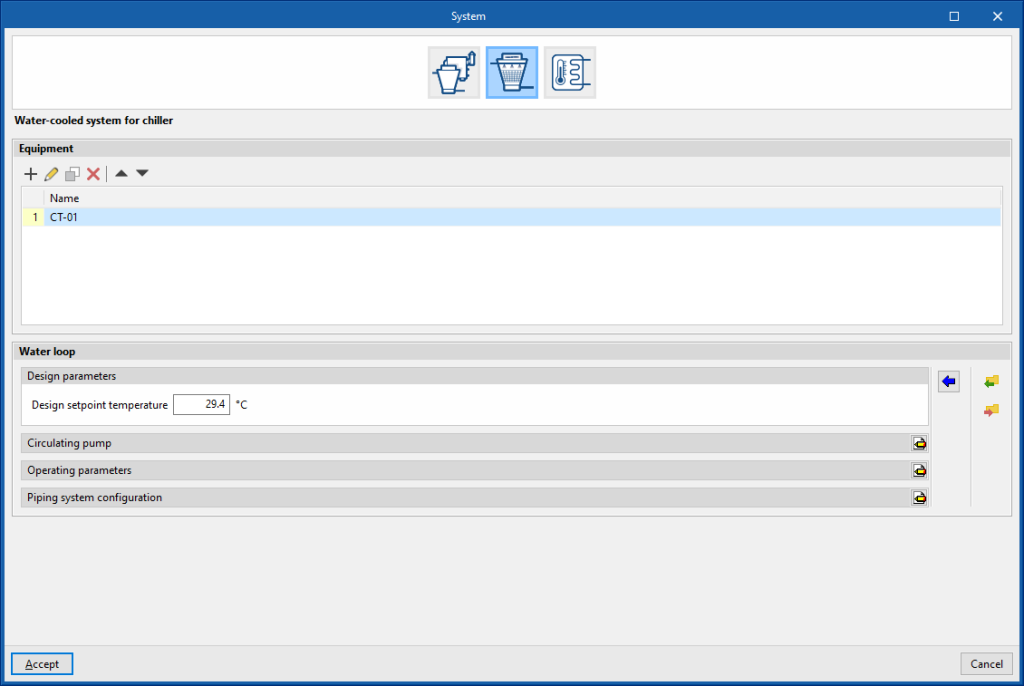
Water-cooled systems for chiller
Equipment
Cooling tower
- Reference
- General parameters
- Tower type (Single speed / Two speed)
- Free convection capacity
- Sizing factor
- Consumo
- In single-speed cooling towers:
- High speed nominal power (optional)
- High speed fan power (optional)
- In two speed cooling towers:
- High speed nominal power (optional)
- High speed fan power (optional)
- Low speed nominal power (optional)
- Low speed fan power (optional)
- In single-speed cooling towers:
Water distribution
- Design parameters
- Design setpoint temperature
- Circulating pump
- Setpoint temperature control (Depending on the outdoor air wet bulb temperature / Design setpoint temperatur)
- Load distribution scheme (Optimal / Sequential load / Uniform load / Uniform PLR / Sequential uniform PLR)
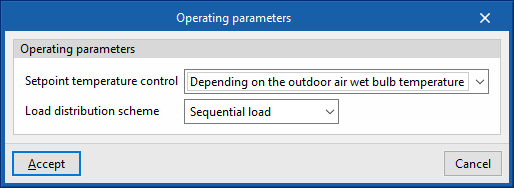
- Operating parameters
- Setpoint temperature control (Depending on the outdoor air wet bulb temperature / Design setpoint temperatur)
- Load distribution scheme (Optimal / Sequential load / Uniform load / Uniform PLR / Sequential uniform PLR)
- Piping system configuration
- Supply side bypass pipe (optional)
- Demand side bypass pipe (optional)
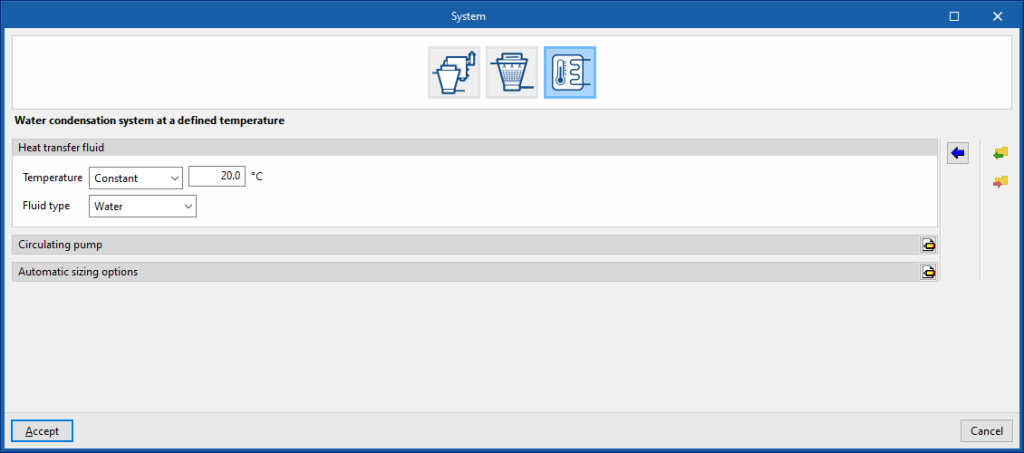
Water condensation systems at a defined temperature
This type of system allows users to simulate any water or glycol circuit connected to the external exchangers of the air-conditioning units. For example, it can be used to simulate a field of geothermal collectors or a groundwater flow. To do this, users simply need to define the temperature of the fluid at the outlet of the circuit and the characteristics of the circulation pump.
This condensing system is compatible with VRF chillers and outdoor units with water-cooled condensers as well as with the water-air heat pump.
Heat transfer fluid
- Temperature (Constant / Hourly profile
- Fluid type (Water / Ethylene glycol / Propylene glycol)
If an hourly profile is defined, users can distinguish between summer and winter conditions, and subtract or add a few degrees to the ground temperature to obtain the temperature of the heat transfer fluid.
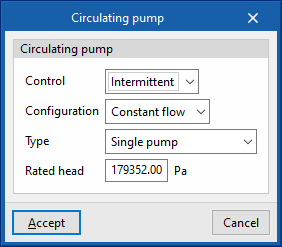
Circulating pump
- Control (Intermittent / Continuous)
- Configuration (Variable flow / Constant flow)
- Primary loop pump type (Single pump / Pump per chiller / Two headered pumps / Three headered pumps / Four headered pumps / Five headered pumps)
- Rated head
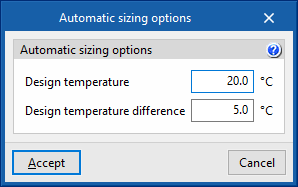
Automatic sizing options
The flow rate of the condensing circuit is equal to the sum of the flow rates defined in the condenser of the units connected to the circuit. If these flow rates have not been defined, the analysis engine will automatically size them, using the design temperature and design temperature difference values.
- Design temperature
- Design temperature difference