Defining hypotheses and zones
The definition of the zone scenarios and the zones considered in each scenario is required to be able to perform the thermal loads analysis. This is done using the tools in the "Installation" group in the upper toolbar of the "Analysis" tab, which is in turn located in the "Thermal loads" tab at the bottom.

The following options are available:
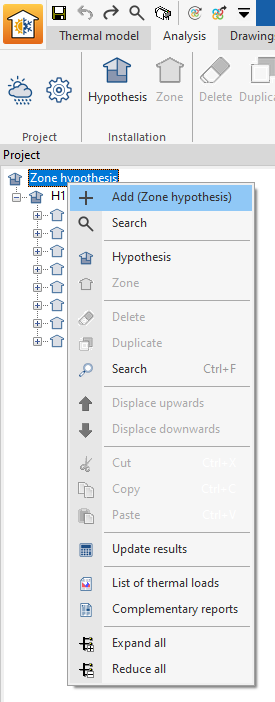
Hypothesis
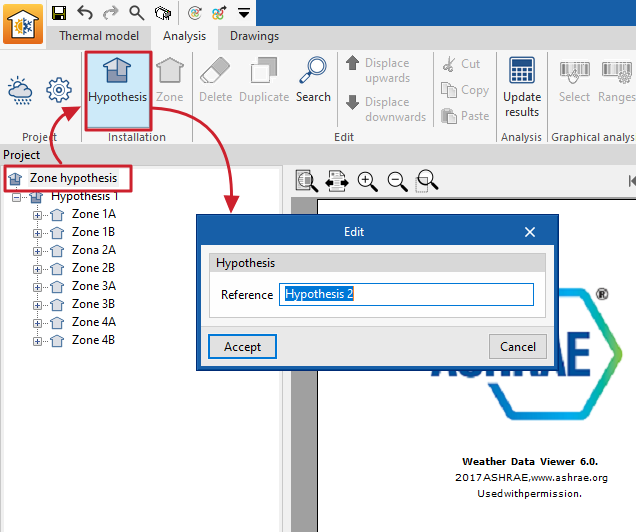
This option is used to add a zone hypothesis to the project.
When adding a zone scenario, the following information is required:
- Reference
Zone scenario reference.
Each zone hypothesis of the building can be used to create a certain number of thermal zones of the building and to assign the desired spaces to each of the zones.
Hypotheses can also be added in the navigation tree of the "Calculation" tab by right-clicking on the base level and selecting "Add (Zone hypothesis)".
For example, in a two-storey office building, one hypothesis can be considered with two zones, one per floor, in case they have an independent use, and a second hypothesis with a single zone for the two floors, in case they have a joint use.
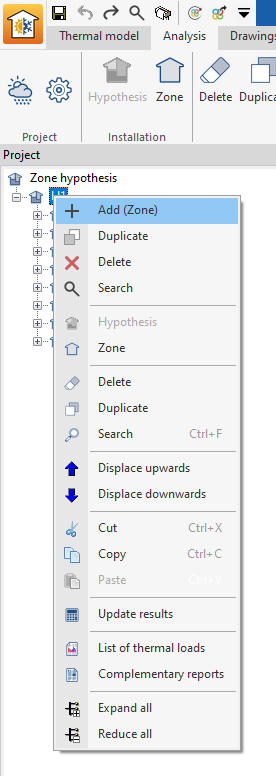
Zone
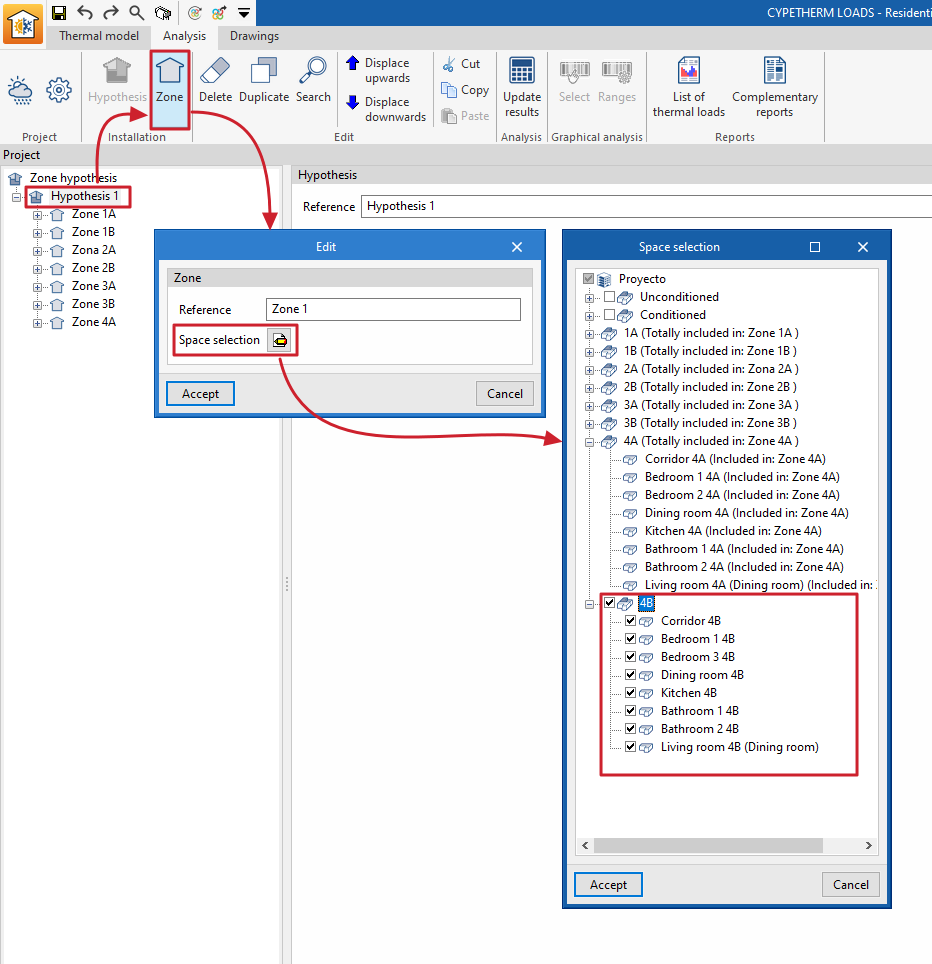
This option adds a zone within the selected zone scenario.
When entering a zone, the following data is required:
- Reference
Zone reference. - Space selection
In this section, the project spaces to be assigned to this zone must be selected. Only those spaces that have not been previously included in other zones of the same hypothesis can be selected.
Zones can also be added in the navigation tree of the "Analysis" tab by right-clicking on the level corresponding to a hypothesis and selecting "Add (Zone)".
For example, in a residential building, each dwelling may constitute a thermal zone. Together with the zones of the dwellings, another thermal zone including the common areas of the building would need to be added.