The aluminium extrusion process has the advantage that as well as being able to obtain standard transverse aluminium alloy sections, specific designs can also be obtained. As of previous versions, the program has allowed users to design structures using standard extruded aluminium sections, i.e. those that are usually found in a manufacturer’s catalogue. As of the 2011.a version, one of the new features is the Extruded aluminium section editor, which allows for the design and check of aluminium alloy bars with specific transverse sections.
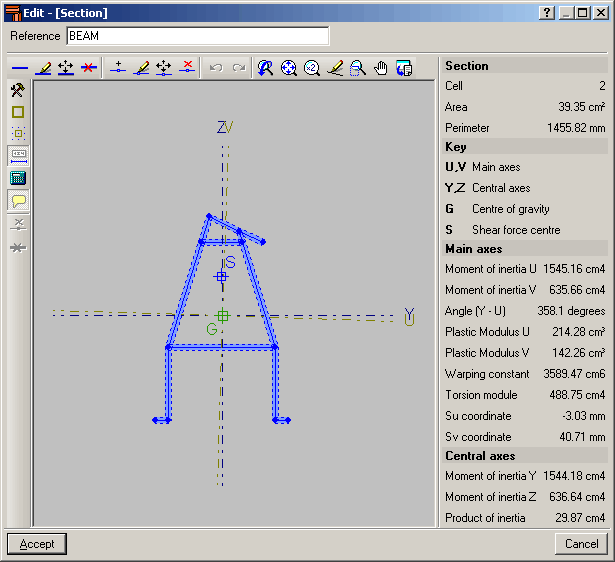
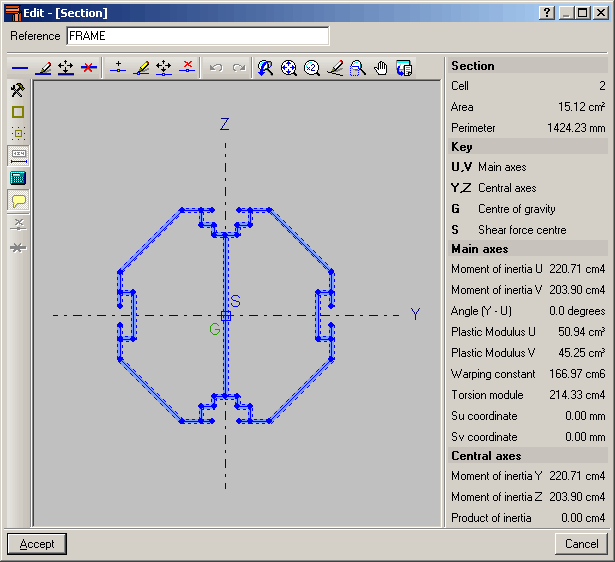
The Special aluminium section option has been included in the Describe section dialogue box (Bar > Describe section > select the bar on screen > right click with mouse button > Special aluminium section). Upon clicking the button, a dialogue box opens with options to create, copy, edit and manage a library of special extruded aluminium sections. Using the create button (or edit button, once special sections have been defined), the extruded aluminium section editor is displayed on screen.
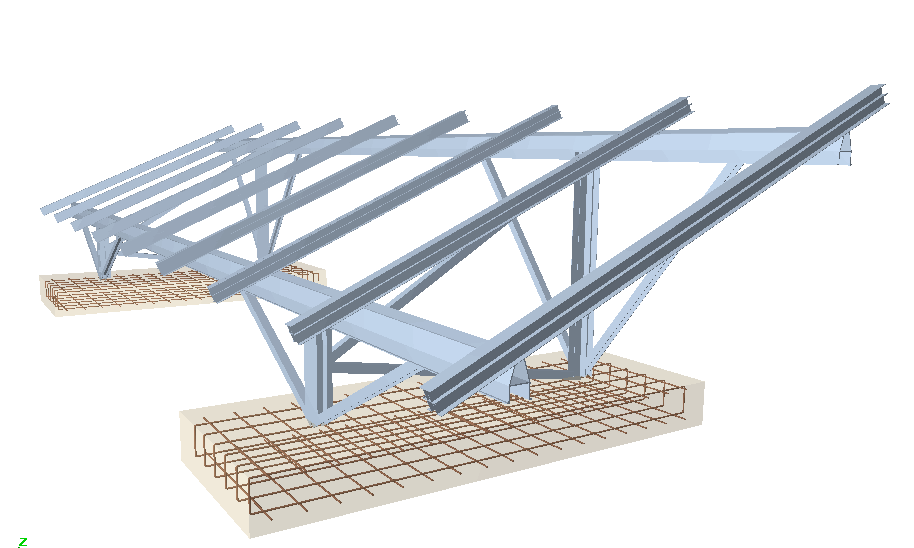
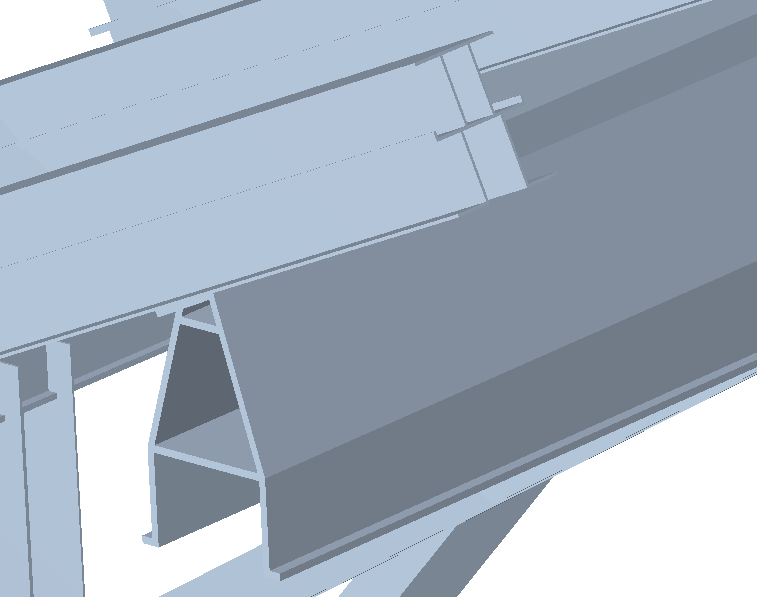
The specific design of the section increases the range of available transverse sections, allowing for an optimum combination which simplifies the constructions process of the structure, with mechanical properties which maximise the resistance effectiveness with minimum weight. The program also offers the possibility of stiffened sections without having to use composite sections, which avoids having to weld or bolt the components.
Using the extruded aluminium sections editor, any section can be created: open, with cells, made up of thin walled flat elements… and used in the structural analysis to proceed with the resistance calculation, including the corresponding check reports.
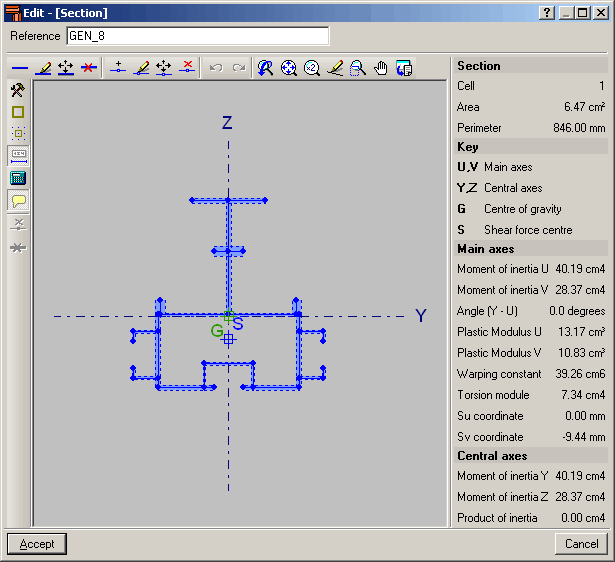
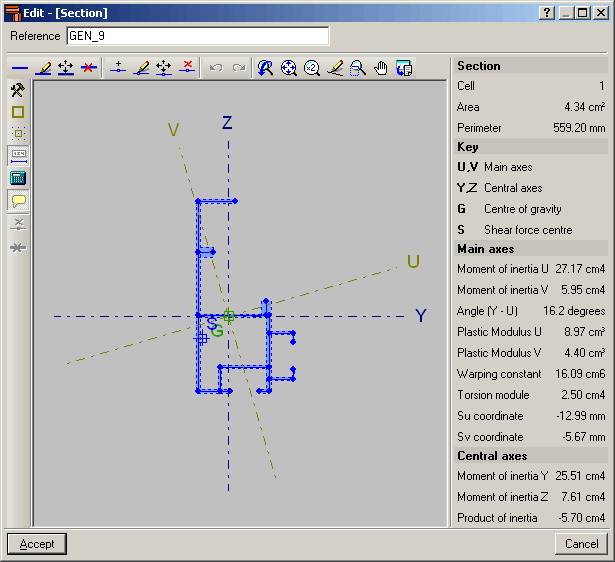
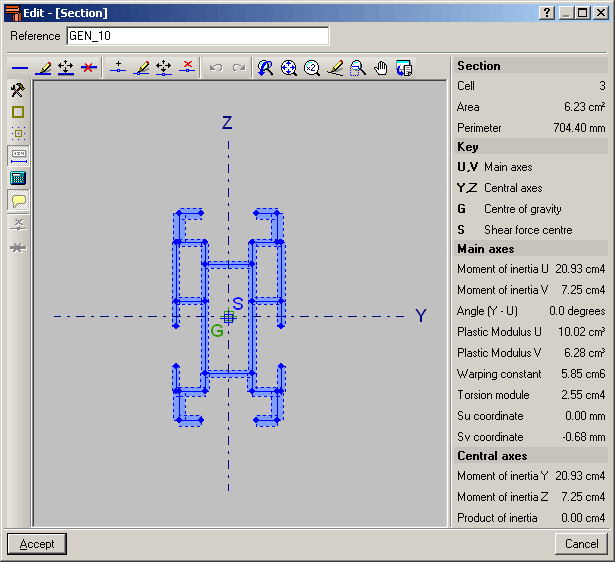
The editor offers information on the mechanical and torsional properties of the gross section, required for the structural analysis, which is updated after any modifications have been carried out. Properties displayed include the section’s area, moment and product of inertia, torsion module, warping constant and shear centre coordinates.
Using the calculated resistance of the sections created with the editor, the section is checked for the forces derived from the structural analysis. The analysis incorporates an automatic calculation of the section’s susceptibility against the local buckling of the thin walled elements making up the transverse section, assuming each one buckles independently. The local buckling coefficient which affects the slenderness parameter of each element can be edited and so be able to consider other buckling modes. The section is classified based on the previous analysis, and with it, the effective properties, elastic or plastic, are obtained which will then be used for the resistance checks.