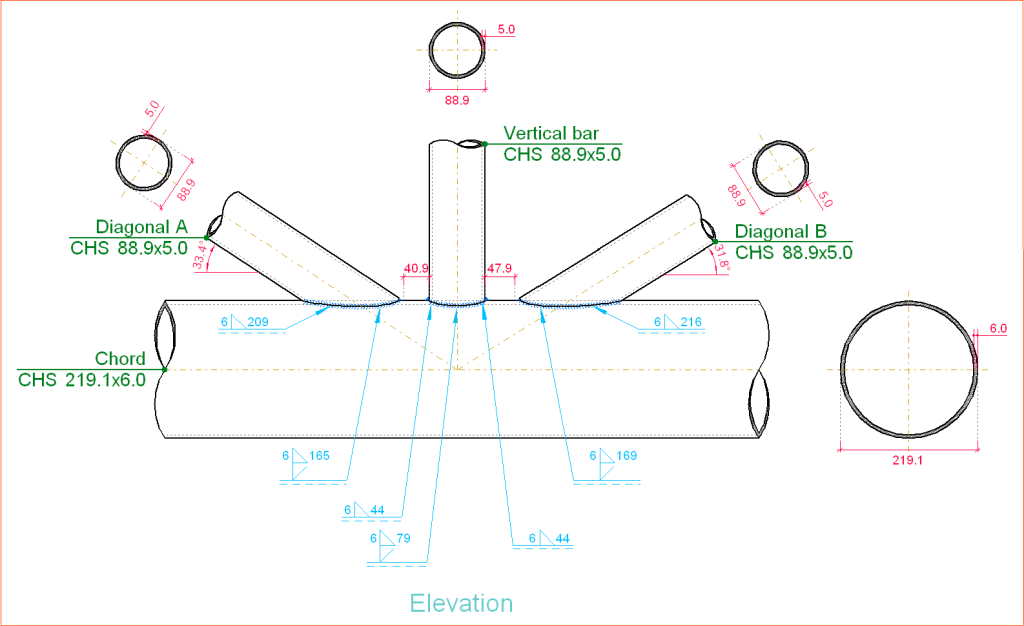
Eurocode 3
The corrections undertaken by the CEN (European Committee for Standardization) have been implemented in the following documents (as of the 2011.a version)
- EN 1993-1-1:2005/AC:2009
- EN 1993-1-2:2005/AC:2009
- EN 1993-1-5:2006/AC:2009
- EN 1993-1-8:2005/AC:2009
These implementations affect the use of Eurocode 3 for any of the countries that may be selected with this code (International, Bulgaria, France and Portugal).
The following National documents of Eurocode 3 for France have been implemented:
- NF EN 1993-1-2:2005/NA:2007
- NF EN 1993-1-5:2007/NA:2007