Managing libraries of opaque building elements
Defining the characteristics of the building elements in the project libraries is necessary to detail the data related to their thermal behaviour, including the possibility of specifying the composition of layers of materials and the technical characteristics of each of them, such as thermal conductivity or thermal resistance. This data can be entered manually or based on different catalogues and reference standards with predefined materials and will affect the energy simulation performed by the program.
The tools for managing the libraries of opaque building elements of the model are found in the "Building" tab and, within the outline of the left-hand side area of the "Project" definition, in the "Library" tree, then selecting the corresponding level.
Categories of opaque building elements
The opaque building elements are classified into the following categories within the library:
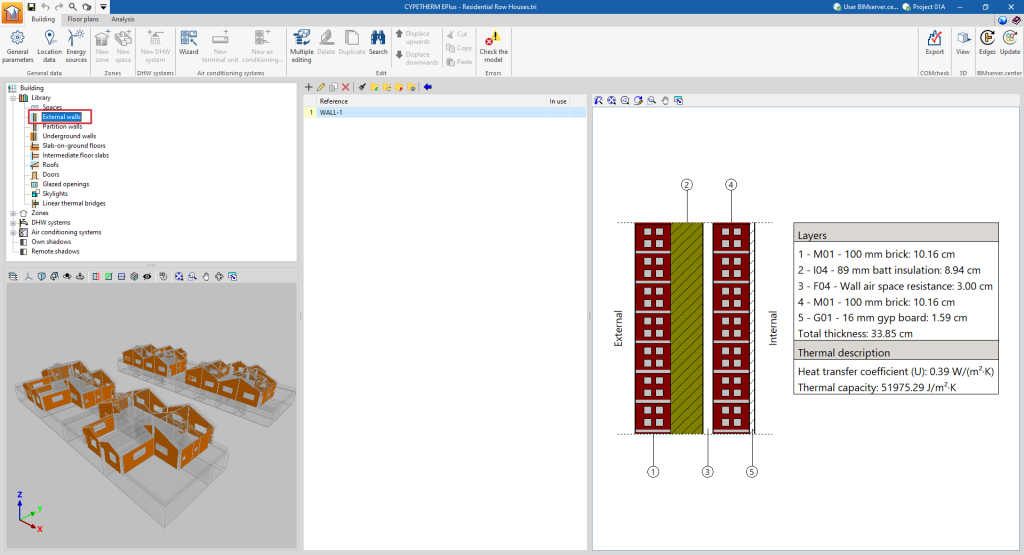
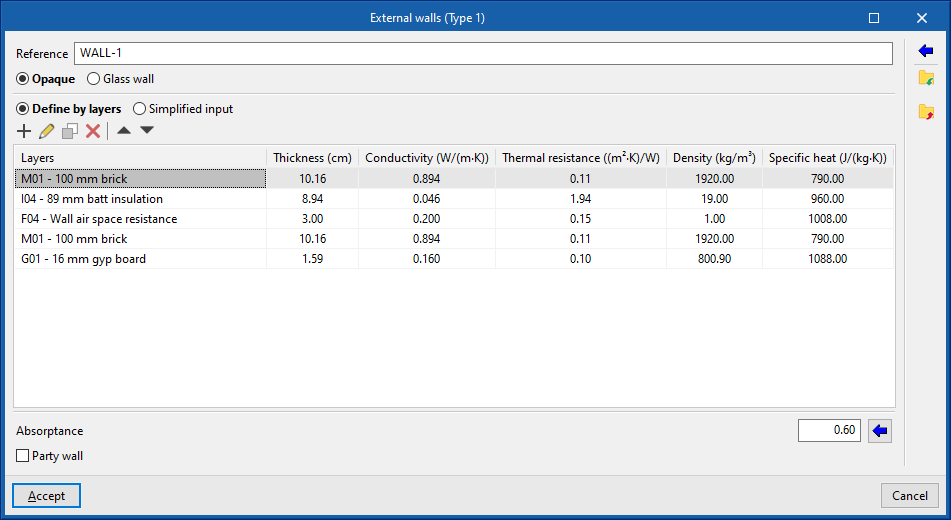
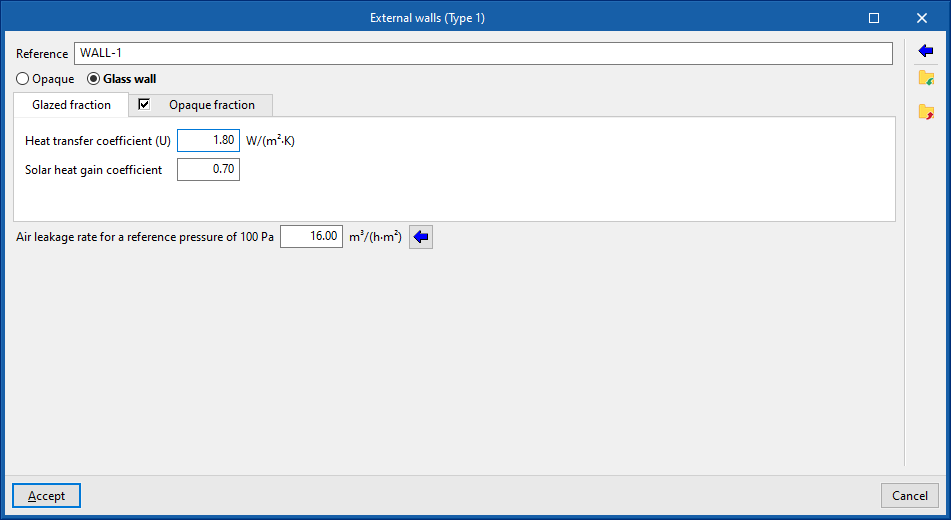
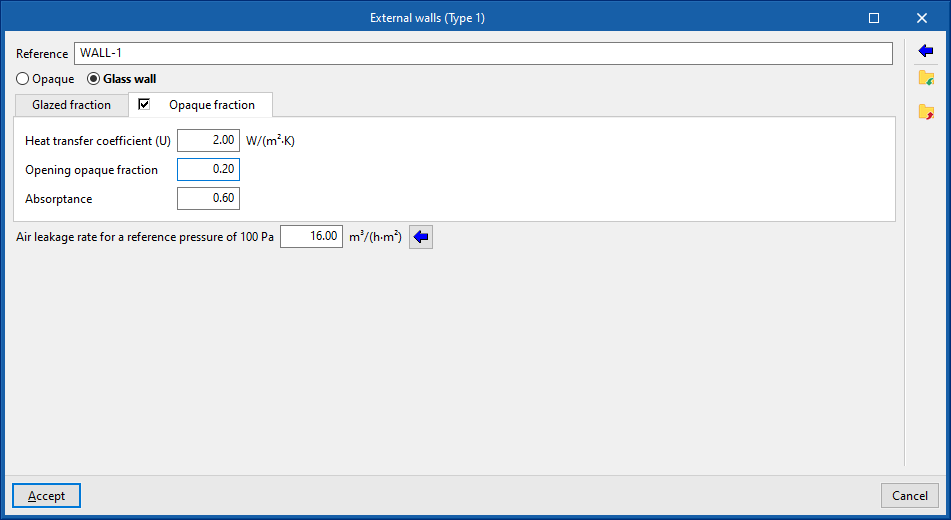
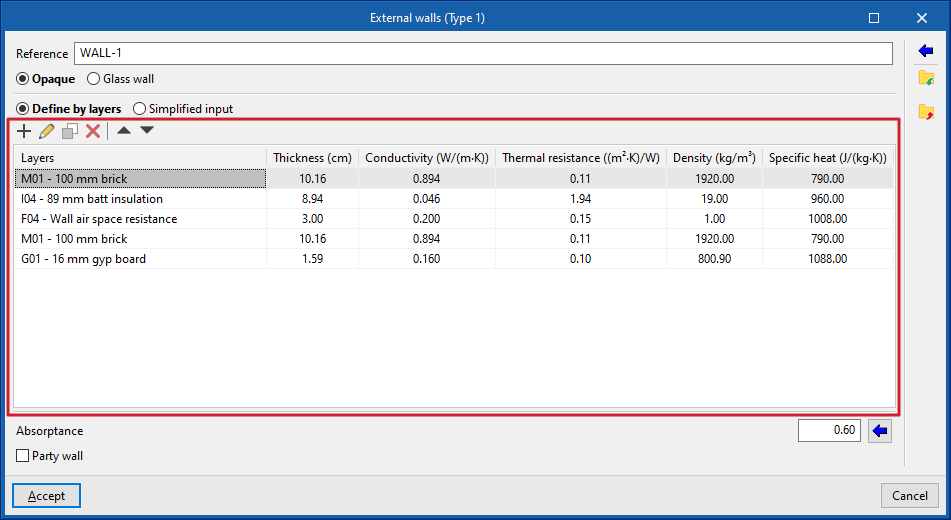
- External walls ("Opaque" option). Vertical external walls in contact with the external environment (façades) or in contact with the spaces of another building (party walls). In the definition of an external wall, users must specify whether it is a "Party wall" and whether it is "Adiabatic".
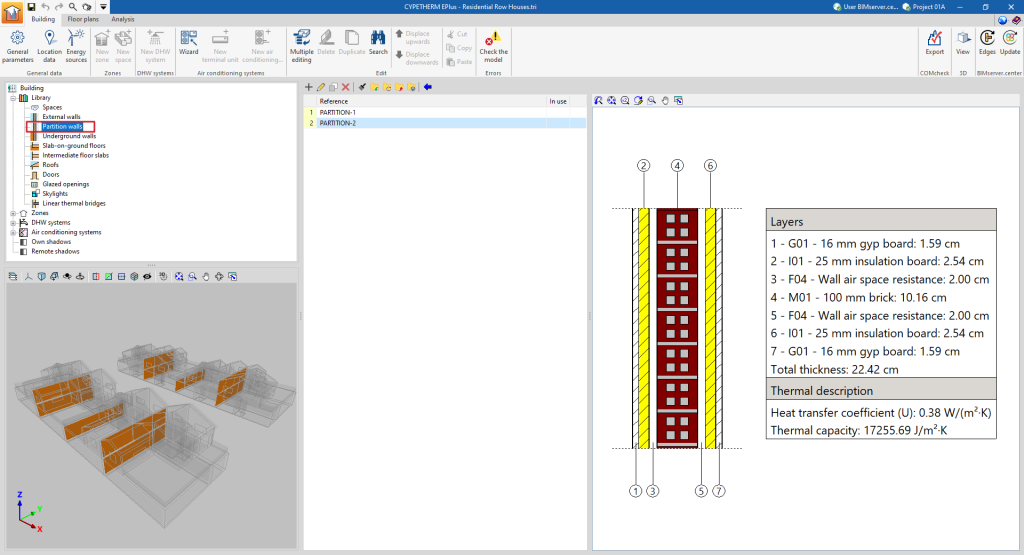
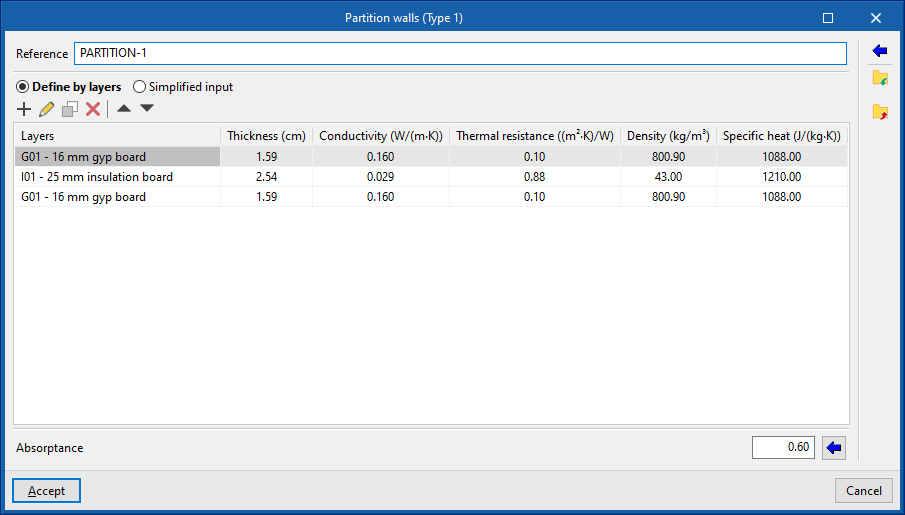
- Partition walls. Interior partitions. They are arranged to separate the interior of the building into different rooms.
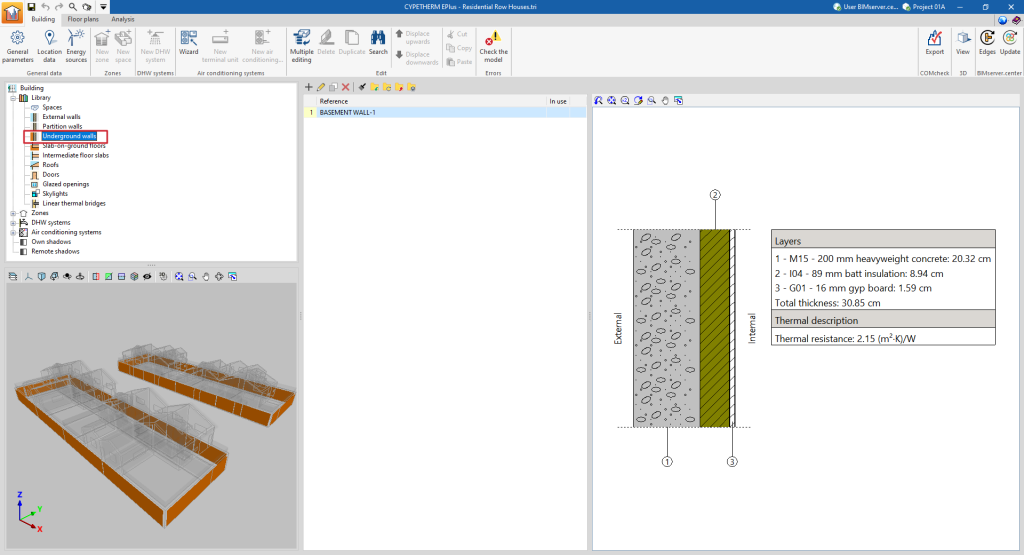
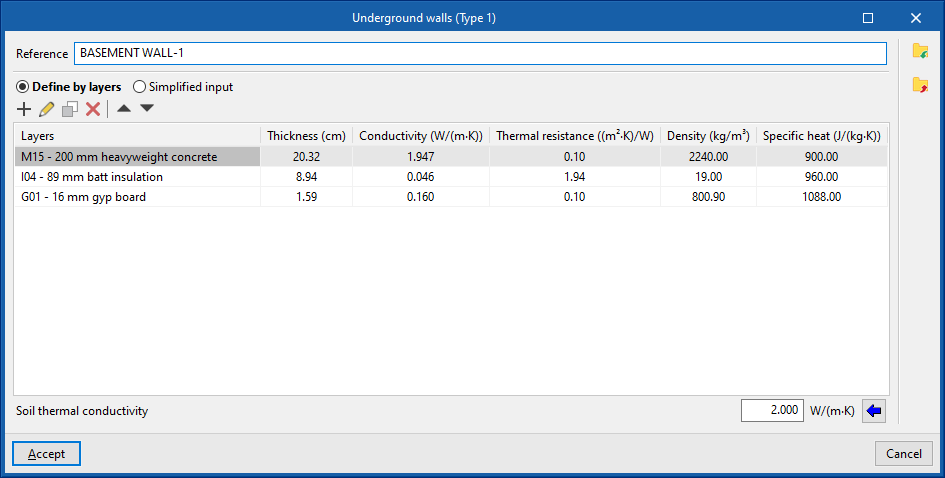
- Underground walls. These vertical external walls in contact with the ground are used to build floors below ground level (basements).
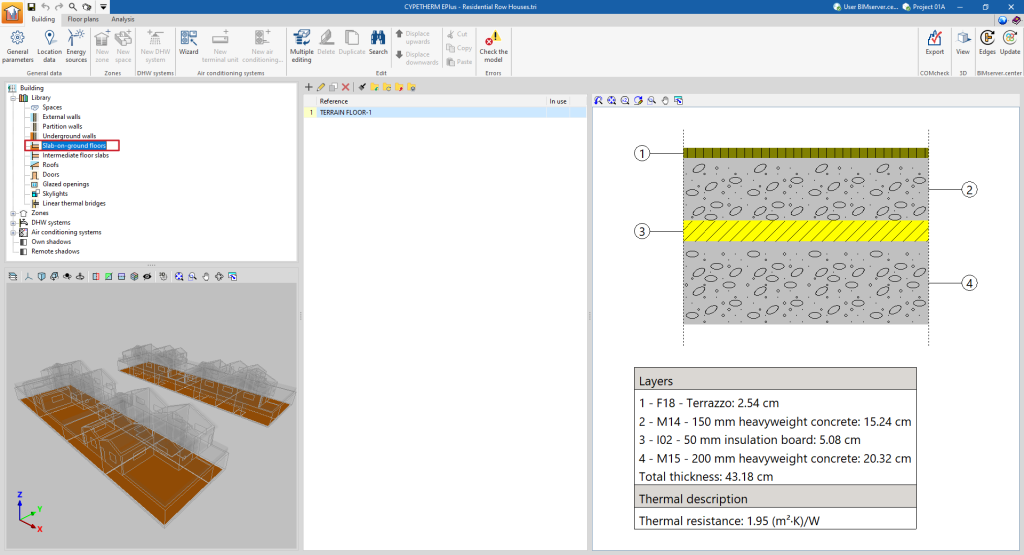
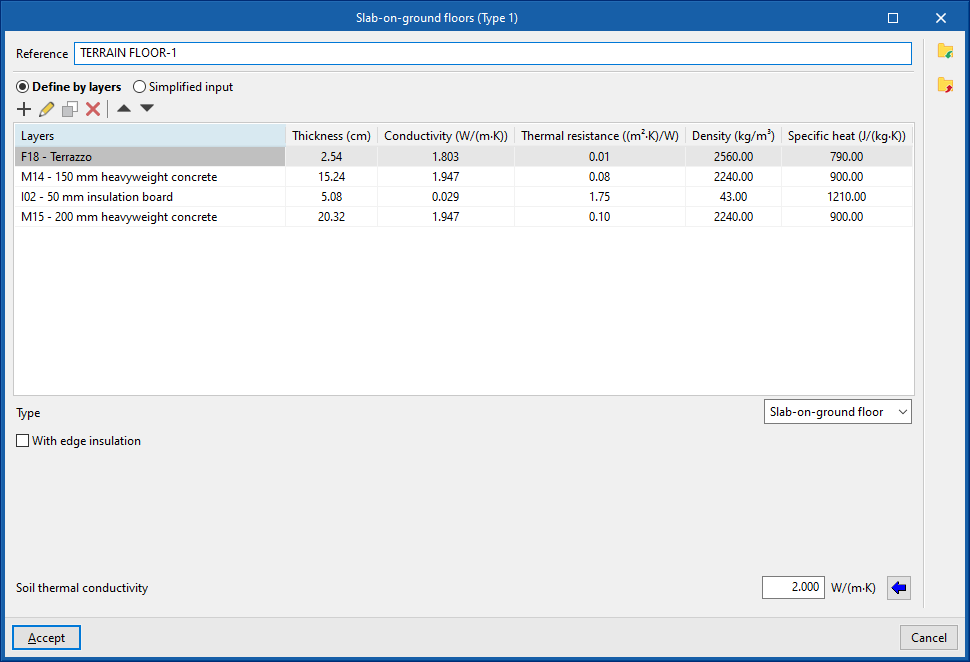
- Slab-on-ground floors. Horizontal envelopes (floor slabs, raised floor slabs) in contact with the ground.
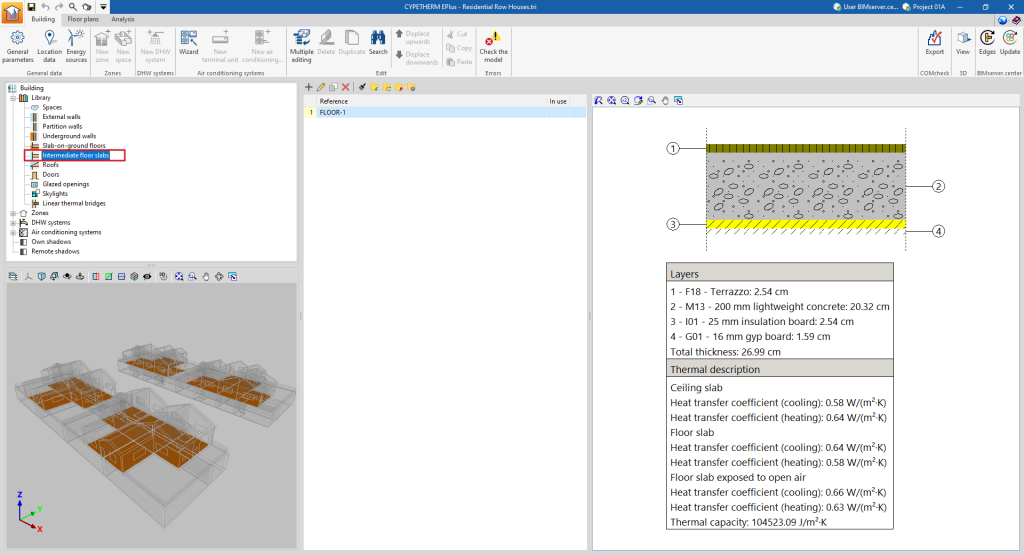
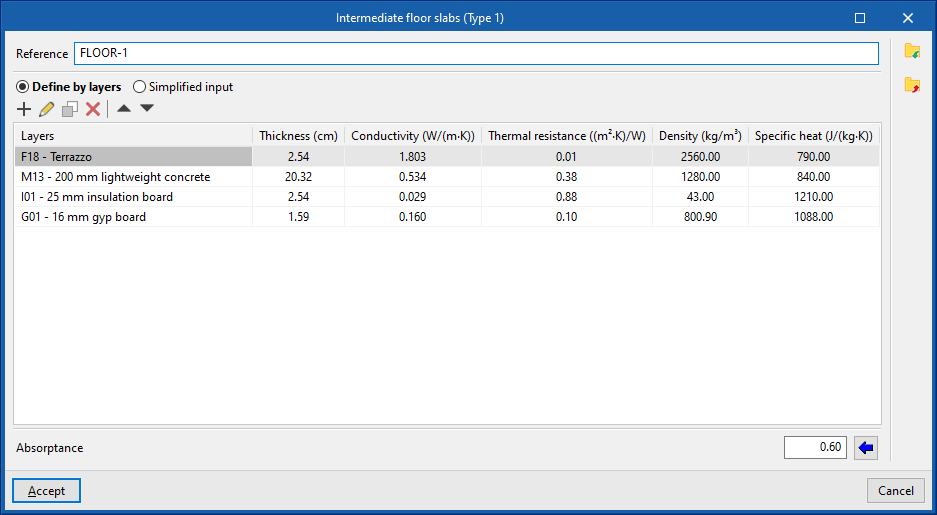
- Intermediate floor slabs. Intermediate floor slabs are the horizontal or slightly inclined lower envelopes between one storey and another, i.e. the floors of each intermediate storey of the building. This category also includes overhangs, i.e. external walls in contact with the exterior at the bottom.
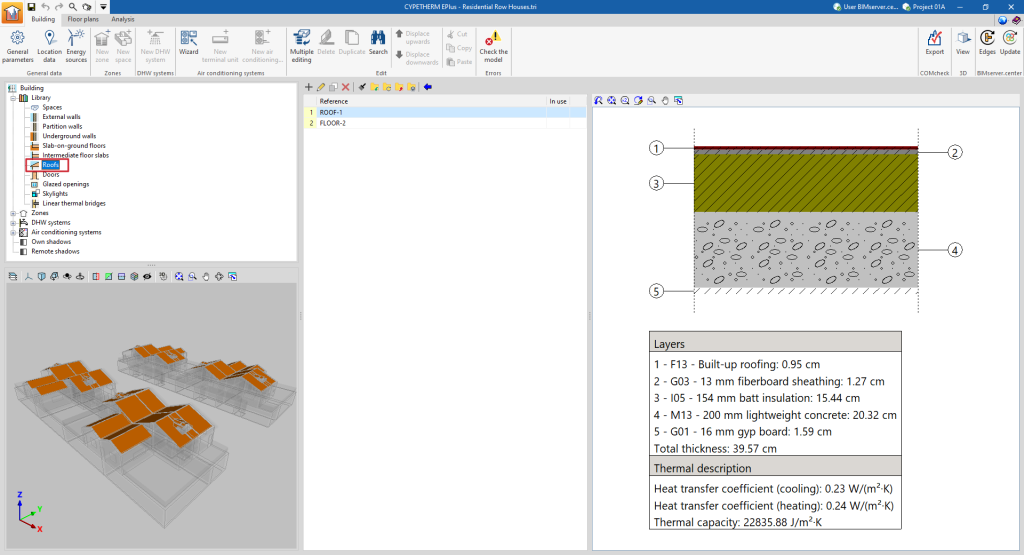
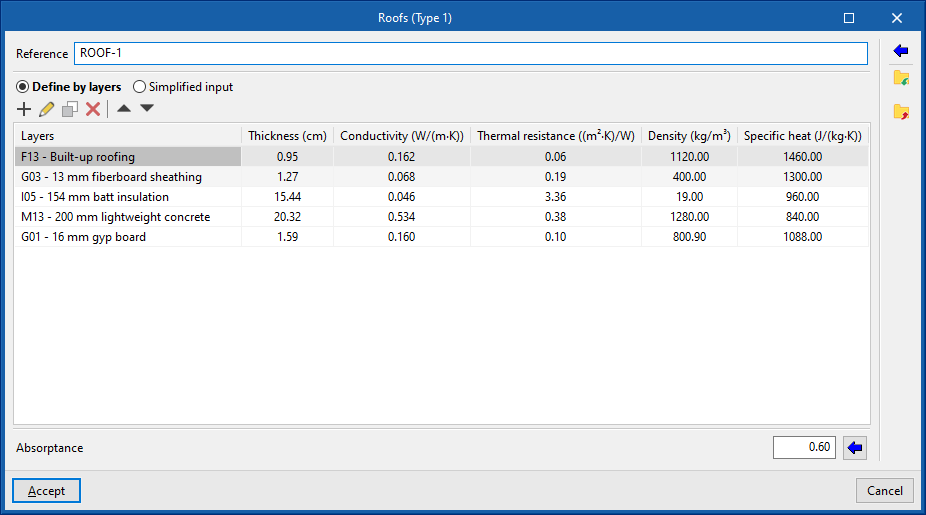
- Roofs. Upper envelopes in contact with the outside environment.
General definition of building elements
When adding or editing an opaque building element type in the library, a window opens where the following aspects can be managed:
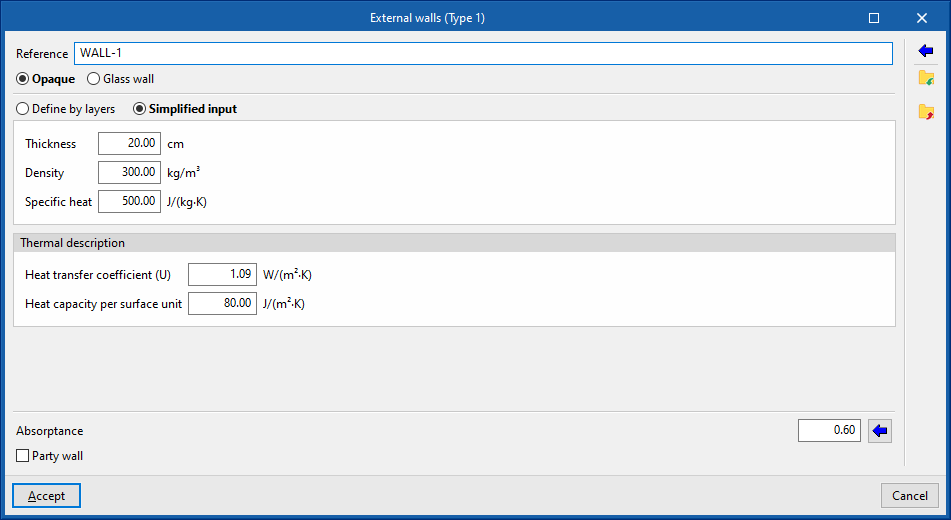
- Reference
Reference of the type of building element. - Define by layers / Simplified input
Indicates whether the thermal characteristics of the element are defined by entering the data for each of the component material layers or through a simplified input.
In some cases, it is also possible to import complete building systems from Open BIM Database:
- Connection to Open BIM Database
Login to the Open BIM Database. - Importing manufacturer data
Imports the data of complete building systems from one of the available manufacturers by selecting the catalogue and the desired product.
Additionally, the options in the right-hand column of the window can be used to import and export the data of the defined element type to files on disk.
Specific options when defining opaque building elements
In addition, the following specific options may appear, depending on the type of element selected:
- Opaque / Glazed (in "External walls")
Indicates whether the envelope is opaque, defined in the same way as the rest of the opaque building elements, or glazed, in which case it is defined by entering the data of the "Opaque fraction" (such as solar transmittance and solar factor) and the "Glazed fraction" (such as thermal transmittance, opaque fraction of the opening and absorptivity), in addition to the "Air permeability for a reference pressure at 100 Pa", as is done in glazed openings. The latter option allows curtain walls to be simulated. - Absorption coefficient (in "External walls", "Partition walls", "Intermediate floor slabs" and "Roofs")
The absorption coefficient fluctuates between 0 and 1. Only one value of the absorption coefficient of the building element is indicated, which must correspond to the external layer (on which the solar radiation strikes). The value can be imported with the wizard available on the right:- Import absorptance
The value of this coefficient is lower on light surfaces, and higher on dark surfaces.
- Import absorptance
- Party wall (optional) (in "External walls")
Indicates that the envelope is a party wall, rather than a façade. In this way, the temperature conditions of the external environment are considered, with no exposure to the sun or wind (zone boundary envelope). The following option is checked if it is to be considered completely adiabatic, i.e. there is no heat transmission through this element:- Adiabatic (optional)
- Soil thermal conductivity (in "Slab-on-ground floors" and "Intermediate floor slabs")
The soil conductivity varies according to its type. The value can be imported with the wizard available on the right:
Import typical values
The lowest values correspond to gravels and silts; sands provide intermediate values, while rock provides higher values.
- Specific options in the definition of "Slab-on-ground floors"
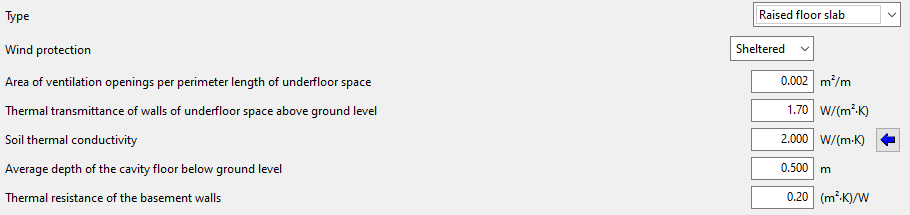
Slab-on-ground floors can be used to define raised floor slabs or screeds:- Raised floor slabs
By selecting "Raised floor slabs", the program allows users to enter the information about the cavity under the slab and other data such as the following:- Wind protection (Sheltered / Average / Exposed)
- Area of ventilation openings per perimeter length of underfloor space
- Thermal transmittance of walls of underfloor space above ground level
- Soil thermal conductivity
- Average depth of the cavity floor below ground level
- Thermal resistance of the basement walls
- Screed
For screeds, peripheral insulation can be added and its characteristics can be defined:- With edge insulation (optional)
- Type of insulation (Vertical / Horizontal)
- Thermal resistance
- Thickness
- Thickness of depth
- Soil thermal conductivity
- Import typical values
- With edge insulation (optional)
- Raised floor slabs
Define by layers
If the building element is defined by layers, the program offers a table where you can add, edit, copy, delete or reorder the material layers included in the building element.
The layers of materials that make up the space are defined in order, from the outside to the inside in the case of vertical spaces (walls), and from the top to the bottom in the case of horizontal spaces (floor slabs).
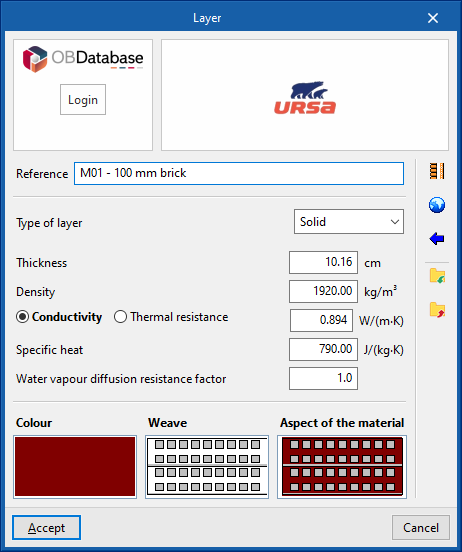
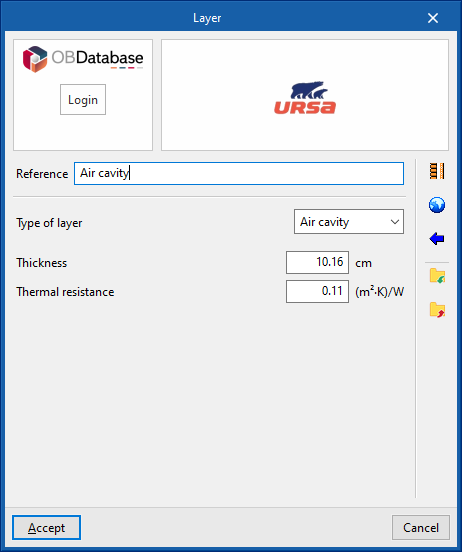
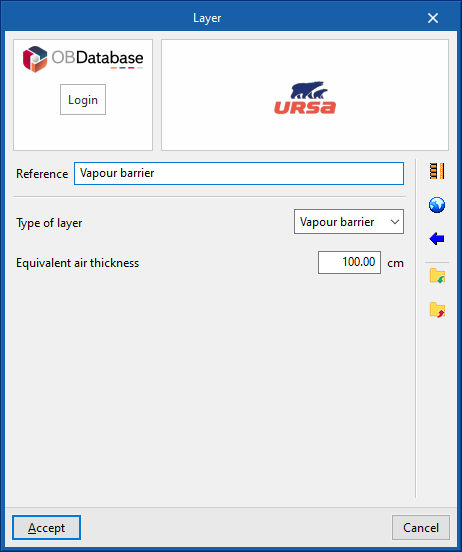
The materials that make up the opaque external walls are classified into solid materials, air cavities (including ventilated ones) and vapour barriers. The thermal properties of each material must be defined, according to their "Type of layer".
When entering a material layer, the following parameters need to be specified in its definition window:
- Connection to Open BIM Database
Login to the Open BIM Database. - Importing manufacturer data
Imports the data of complete building systems from one of the available manufacturers by selecting the catalogue and the desired product. - Reference
Reference of the layer of material. - Type of layer
There is a choice between a solid layer, an air cavity or a vapour barrier.- Solid layer
- Thickness
- Density
- Conductivity / Thermal resistance
- Specific heat
- Water vapour diffusion resistance factor
- Air cavity
- Thickness
- Thermal resistance
- Vapour barrier
- Equivalent air thickness
- Solid layer
- Colour / Weave / Aspect of the material
- Adjusts the graphical representation of the layer material.
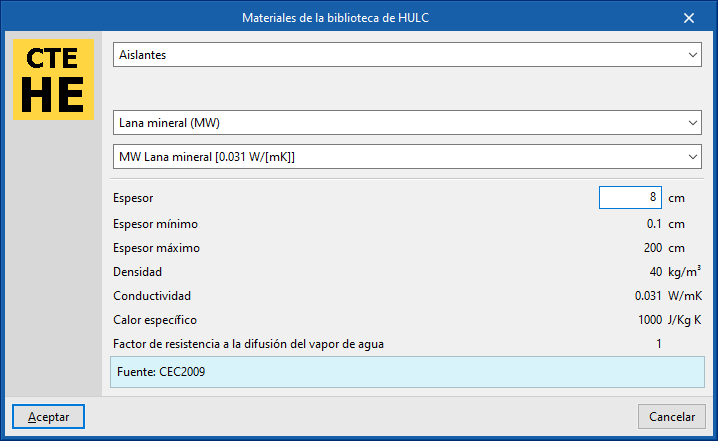
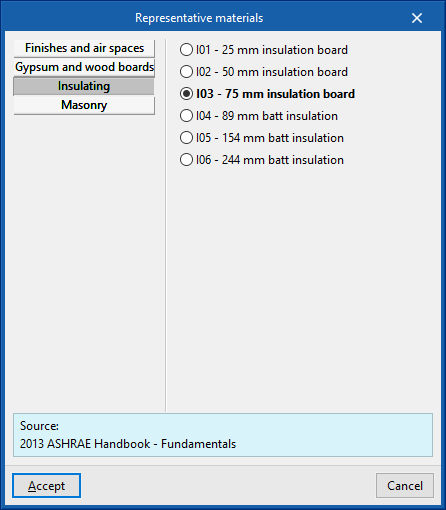
The options in the right column of the definition window of each material layer can be used to automatically import the material data from the information provided by different catalogues and codes, such as the following:
- HULC library materials
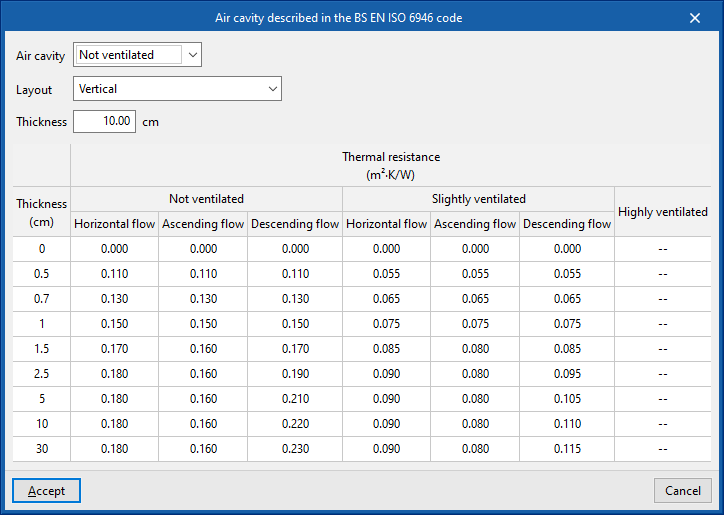
- Air cavities described in UNE-EN ISO 6946
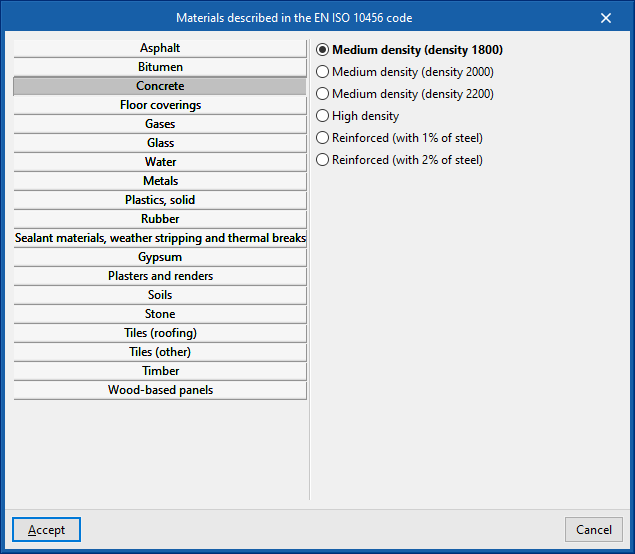
- Materials described in EN ISO 10456
Additionally, there are options in the right-hand column of the window to import and export the defined material data to files on disk.
Simplified input
The simplified input of the element type involves entering its global thermal properties. This is useful if the layer-by-layer data is unknown, if these properties are available or if they have been calculated outside the program.
- Simplified input
- Thickness
- Density
- Specific heat
- Thermal description
- Heat transfer coefficient
- Heat capacity per surface unit
The "Heat capacity per surface unit" property does not play a role in the simulation, it is only used in the wording of the result lists.