Processing edges in the thermal model
The analysis of linear thermal bridges is used to calculate the corresponding linear thermal transmittances according to the characteristics of the construction systems adopted. This analysis is carried out by considering the specifications applicable according to the code selected for calculating thermal transmittance in linear thermal bridges.
The import of building information models (BIM) focuses on the geometric description of the building. The technical information is entered into specific programs. Therefore, for the detection of linear thermal bridges, the program carries out two-step management:
- In the first stage, the edges of the building are imported as purely geometric entities, obtained from the intersection between different building elements. This is done when generating the thermal model, either from the "3D model" or in an import of BIM models in a job linked to BIMserver.center that contains files with this information.
- In the second stage, using edge processing, the linear thermal bridges are obtained from the edges and based on the description of the building from the point of view of thermal analysis (zoning, description of spaces, etc.). The program analyses the building and detects the geometric edges between a habitable room and the outside, and between a habitable room and a non-habitable room. Not all edges can give rise to linear thermal bridges.
This process is carried out by clicking on the "Edge processing" option in the "Edges" group in the top toolbar of the "Thermal model" tab, which in turn is located in the "Thermal loads" tab at the bottom.

By accepting the "Edge processing" window, the program modifies the data related to the "Linear thermal bridges" in the "Project" side tree of the "Thermal model" tab, both with respect to the "Libraries" and with respect to the linear thermal bridges assigned to each enclosure of the "Project" geometry. This generates the necessary types and adjusts the linear thermal transmittance value and the category associated with each of the linear thermal bridges.
Edge processing settings
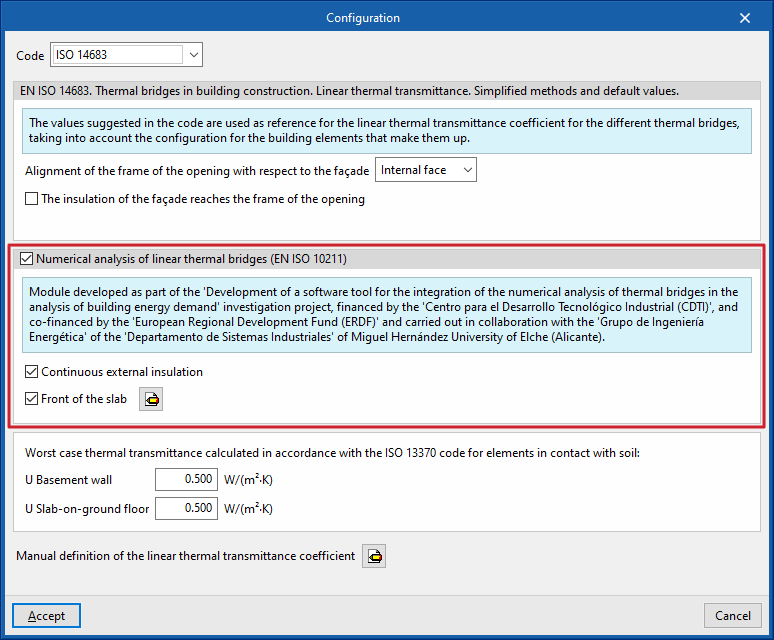
In the "Edges processing" window that appears when using this option, the "Configuration" option is used to adjust the following edge processing parameters:
- Code
- Alineación del marco del hueco respecto al cerramiento (EN ISO 10211) (optional)
- Manual definition of the linear thermal transmittance coefficient
The effects of the configuration of these parameter sets are detailed below.
Code selection
The "Code" drop-down menu allows users to select the reference standard for edge processing. Among the available codes are the following:
ISO 14683
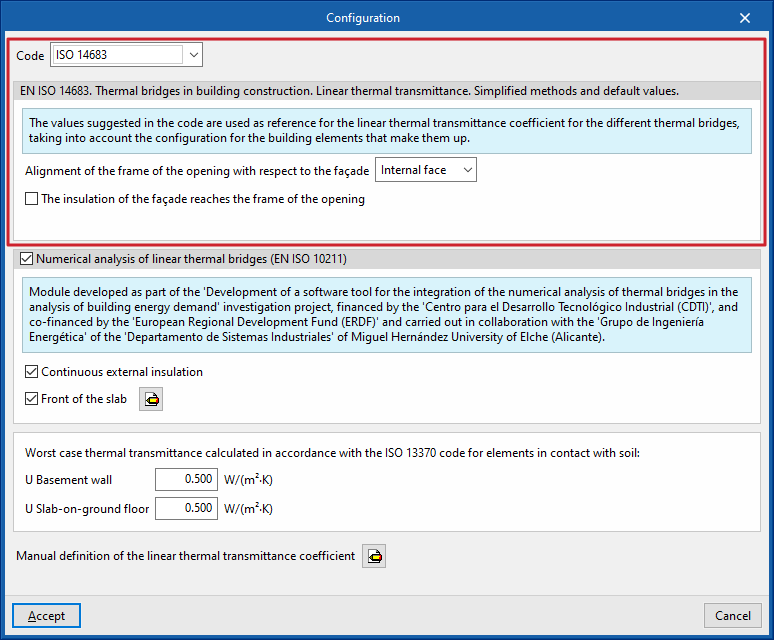
Allows the following standard to be used as a reference: EN ISO 14683. Thermal bridges in building construction. Linear thermal transmittance. Simplified methods and default values.
The values proposed in this code for the linear thermal transmission coefficient of the different thermal bridges are used as a reference, considering the configuration of the building elements that comprise it.
The options available under this code are as follows:
- Alignment of the frame of the opening with respect to the façade (Interal face / External face)
- The insulation of the façade reaches the frame of the opening (optional)
ISO 14683 (Italy)
Allows the following standard to be used as a reference: EN ISO 14683. Thermal bridges in building construction. Linear thermal transmittance. Simplified methods and default values.
HE1 2006
Allows the following standard to be used as a reference: CTE DB HE1. Limitación de demanda energética (2006).
HE1 2013
Allows the following standard to be used as a reference: CTE DB HE1. Atlas de puentes térmicos DA DB-HE / 3.
Règles Th-Bât (France)
Allows the following standard to be used as a reference: Règles Th-Bât (Règles Th-U Fascicule 1 et 5).
REH
Allows the following standard to be used as a reference: SCE. Desempenho Energético dos Edifícios de Habitação (Cálculo de pontes térmicos lineares).
Numerical analysis of linear thermal bridges (EN ISO 10211)
The activation of this section allows the determination of the thermal transmittance in linear thermal bridges through the resolution and post-processing of a finite element heat transfer analysis model, based on EN ISO 10211.
This module is developed as part of the research project "Development of a software tool for the integration of the numerical analysis of thermal bridges in the calculation of the energy demand of buildings", financed by the Spanish centre for the development of industrial technology (CDTI), co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), and carried out in collaboration with the Energy Engineering Group of the Department of Industrial Systems of the Miguel Hernández University of Elche (Alicante).
The options available in this section are as follows:
- Continuous external insulation (optional)
- Front of the floor slab (optional)
Used to characterise the material layers of the front of the floor slab by entering their technical characteristics such as thickness, conductivity, thermal resistance, density or specific heat.
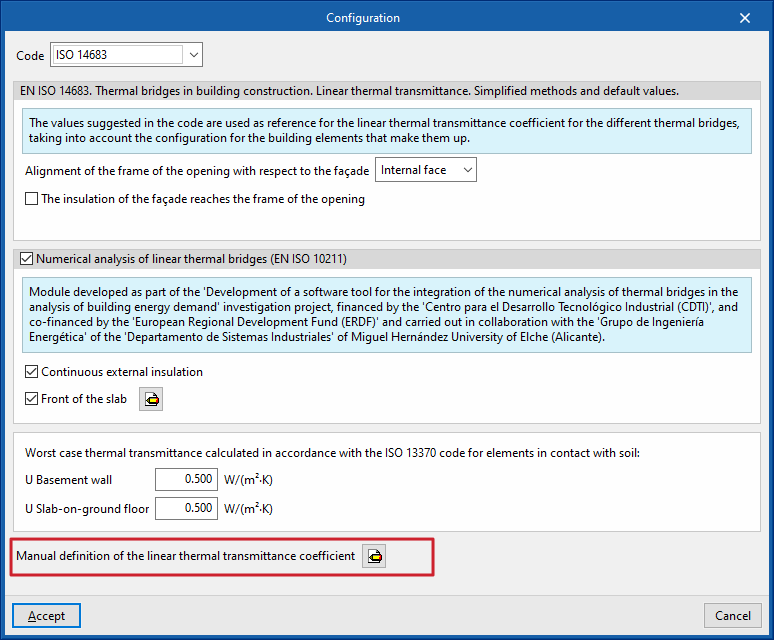
Manual definition of the linear heat transmission coefficient
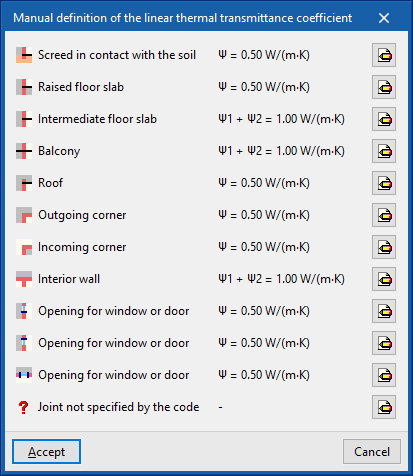
The "Manual definition of the linear thermal transmission coefficient" window opens by clicking on the edit button available in this section, where the thermal bridge types associated with the selected standard are presented.
For each type of thermal bridge, by clicking on the edit button on the right-hand side, the following three options can be selected, which allow the definition of its linear thermal transmittance to be adjusted:
- Never
The thermal characteristics of the selected linear thermal bridge are not considered. - Always
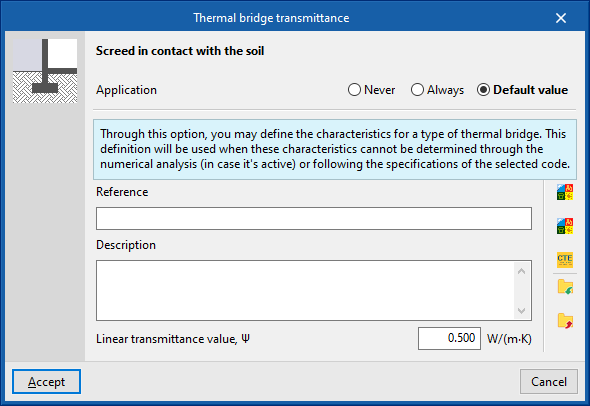
Always considers the thermal characteristics that are defined for the selected linear thermal bridge. The program lets users enter a "Reference", a "Description" and the "Value of the linear thermal transmittance, ψ" for the type of bridge. - Default value
The thermal characteristics defined for the selected linear thermal bridge shall be used in the calculation when it has not been possible to determine them either by numerical analysis (if enabled) or following the specifications of the reference standard used. Similarly, the program lets users enter a "Reference", a "Description" and the "Linear transmittance value, ψ" for the bridge type, which will only be used in the case described.
Additionally, when selecting the "Always" or "Defaults" options, the program offers wizards on the right-hand side for automatically importing data from different code catalogues.
Order of priority for assigning the values of the thermal parameters
As a result, the program follows this order of priority for the assignment of thermal parameter values in edge processing:
- Value entered manually with the "Always" option or the "Never" option
These values can be defined for each type of thermal bridge in the "Configuration" window, by editing the "Manual definition of the linear thermal transmittance coefficient" section, editing a certain type of thermal bridge and finally selecting the option "Always" or "Never". - Value calculated by numerical analysis of linear thermal bridges
If the use of this module is activated in the "Configuration" window and for the types of thermal bridges it analyses. - Value obtained from the reference code
The reference standard is selected in the "Code" section of the "Configuration" window. - Value entered manually with the "Default value" option
These values can be defined for each type of thermal bridge in the "Configuration" window, by editing the "Manual definition of the linear thermal transmittance coefficient" section, editing a certain type of thermal bridge and finally selecting the "Default value" option.