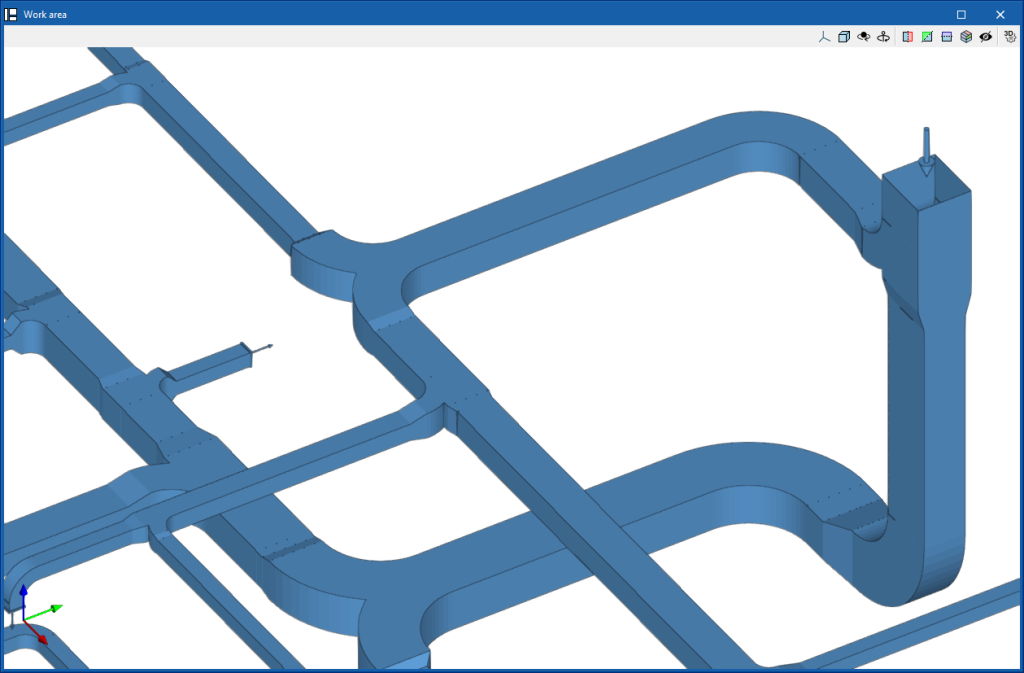
Introduction
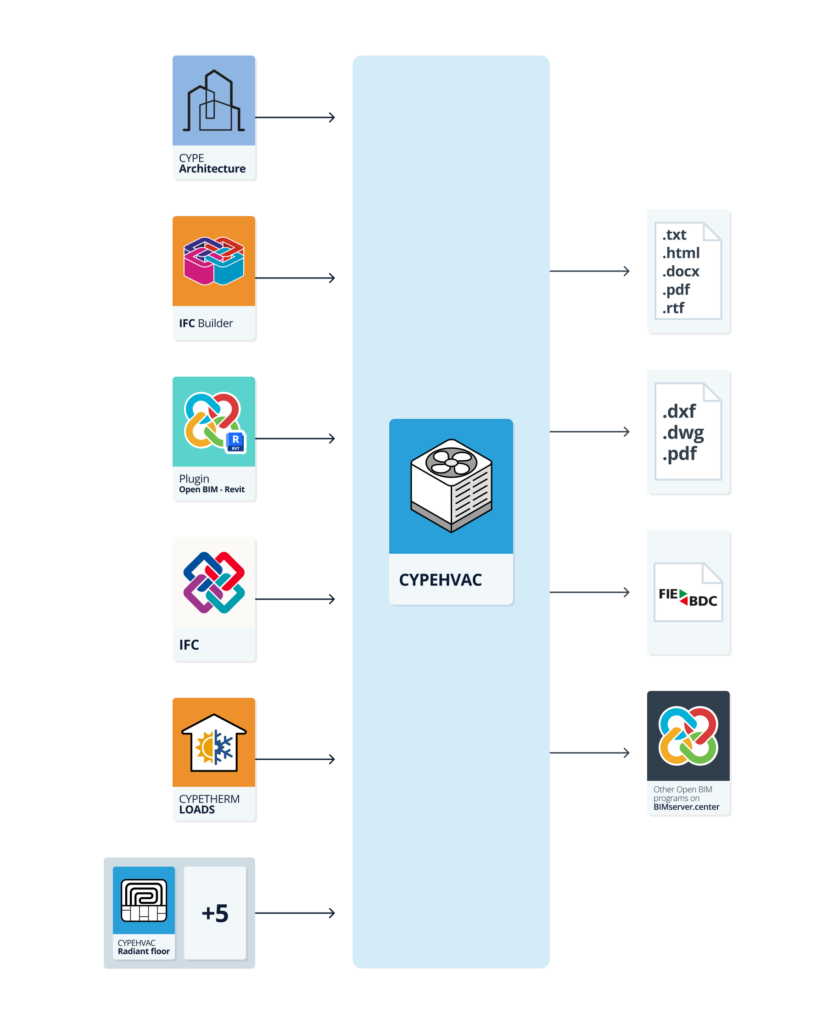
CYPEHVAC is a program for designing HVAC systems covering heating, ventilation and air conditioning. This tool is used to design radiators, fan coils, boilers, heat pumps, ducted ventilation networks, heat recovery units, fans and air handling units.
The application can be used to import the necessary information extracted from other Open BIM tools so that both the architectural models and the results of the thermal load analysis can be used in the system design.
Workflows supported by the program
As CYPEHVAC is an Open BIM tool and is connected to the BIMserver.center platform, it offers different workflow options.
Data entry
Free modelling/with templates
- Designing the system using free entry in CYPEHVAC.
- System design in CYPEHVAC based on DXF-DWG, DWF templates or images (.jpeg, .jpg, .bmp, .wmf).
Importing BIM models
If the CYPEHVAC job is linked to a BIM project from the BIMserver.center platform, the following tasks can be carried out:
- Importing the model with the geometry of a building. This generates the floor plan of the building, import the layout of the spaces (the thermal loads can be estimated directly or associated with the thermal load values calculated in stand-alone programs) and allows users to enter the system elements based on the building geometry. The following options are available:
- Importing models designed in CYPE Architecture.
- Importing models designed in IFC Builder.
- Importing models in IFC format (generated by CAD/BIM programs such as Allplan, ArchiCAD and others) uploaded to the BIMserver.center project via the web platform.
- Importing models designed in Autodesk Revit with the Open BIM - Revit Plugin.
- If the architectural model is generated by IFC Builder or CYPE Architecture, users can also import the DXF or DWG templates contained in that model, or the one generated by the program itself (from the building elements entered) when a model is exported to the BIM project.
- Importing the results of programs that can analyse thermal loads so that they can be used in the system design. The available options include the following:
- Importing thermal loads from CYPETHERM LOADS.
- Importing thermal loads from CYPECAD MEP.
- Importing manifolds from programs that can model and design the radiant floor system. Among the options available are the following, which include BIM programs from radiant floor manufacturers:
- Importing manifolds from CYPEHVAC Radiant Floor.
- Importing manifolds from Open BIM GIACOMINI.
- Importing manifolds from Open BIM ORKLI Radiant Floor.
- Importing manifolds from Open BIM POLYTHERM.
- Importing manifolds from Open BIM ROTH.
- Importing manifolds from Open BIM SAUNIER DUVAL.
Data output
- Exporting reports to HTML, DOCX, PDF, RTF and TXT formats.
- Exporting drawings to DXF, DWG and PDF formats.
- Exporting the bill of quantities to FIEBDC-3 format.
- Exporting the information generated with CYPEHVAC to the BIMserver.center platform using IFC and glTF formats. This allows it to be viewed by authorised project participants. The information generated by CYPEHVAC can be used by the following programs:
- CYPELEC Distribution
This program imports the electrical machines from the HVAC installation and automatically assigns and generates the corresponding receivers in their position.
- CYPELEC Distribution
| Note: |
|---|
| If a geometric model is not available or is not imported, you can enter and analyse the installation directly in CYPEHVAC, but it will not be possible to automatically assign loads to the equipment based on the geometry. However, you can manually create and assign loads to the devices or, alternatively, analyse based on the nominal power of the equipment or by forcing the required power in each of them. |
Work environment
The CYPEHVAC interface is divided into two tabs with different work environments: "Installation" and "Bill of quantities". These environments are similar to those in other CYPE tools and have a dockable window system that can be customised to adapt the workspace to the project's needs.
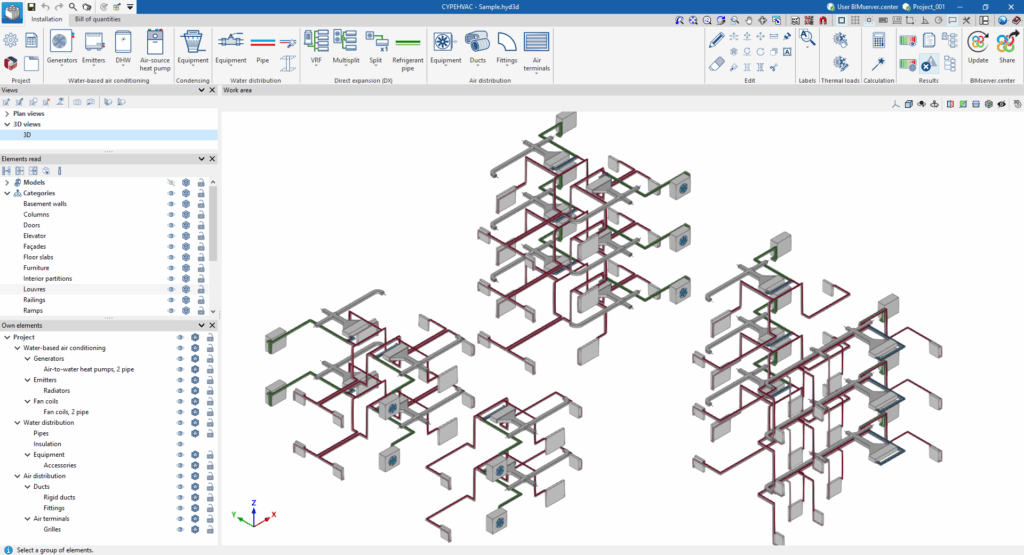
"Installation" tab
The "Installation" tab has a work environment that allows the system design to be carried out quickly and easily, both in a 3D view and in any type of 2D view (such as floor plans and elevations). This allows the elements in the system to be entered using the most appropriate view at any given time.
This tab displays the following:
- The top toolbar contains the tools for managing the project options; entering and editing the elements of the water-air conditioning systems, water-cooled system, air-source heat pump system and water production air conditioning systems; entering direct expansion systems; entering the elements for the air distribution system; and analysing, checking and designing the system.
- The work area, on the right side of the screen, is where the aforementioned elements are entered, edited and displayed.
- On the left-hand side are several panels with tools for defining the project views and managing the visibility of the elements read and own elements.
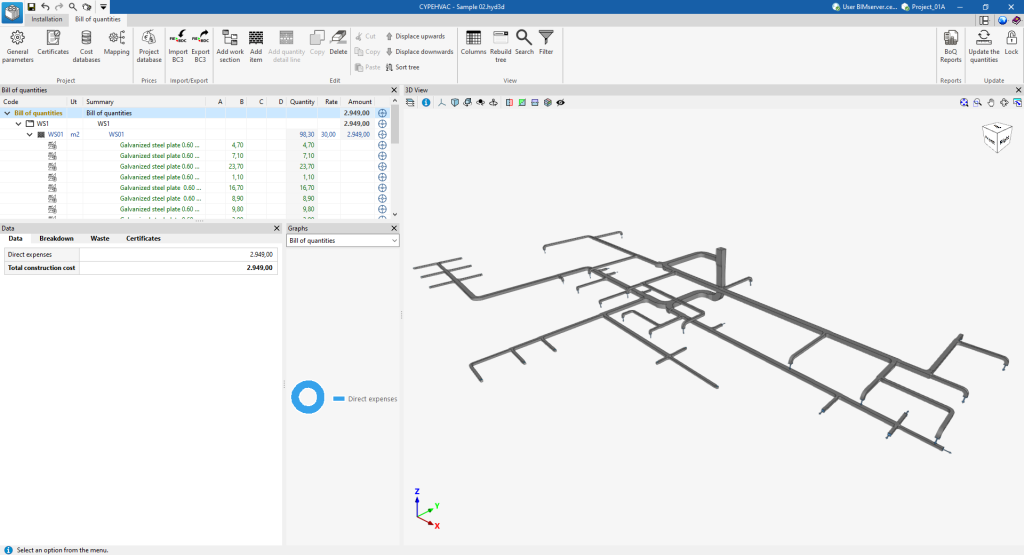
"Bill of quantities" tab
On the other hand, the "Bill of quantities" tab is used to manage the quantities and cost estimations of the installation, and displays the following:
- A top toolbar containing tools for creating and editing bills of quantities, as well as tools for managing and creating reports.
- A graphic window with its own toolbar, located on the right-hand side, where the different elements of the job can be viewed.
- A specific area for structuring the bill of quantities, on the left-hand side.
Sequence of data input and output for the design and analysis of air-conditioning systems
Air-conditioning systems can be defined and analysed in the program using the following input and output sequence:
- Creating a new job (from "File", "New").
- (Optional) Linking to BIMserver.center, and importing floor plans and space layouts read from the BIM model, as well as the associated thermal load analysis results and the layout of thermal loads in the space.
- (Optional) If the project does not include the results of the heat load analysis, a heat load estimation is carried out in the process of creating a new job.
- Revising the general parameter settings (from "Project", "General options").
- Defining types of elements. This can be done in two additional ways:
- Loading manufacturers' catalogues (from “Project”, “Catalogue management”).
- Loading or manually entering the generic element libraries (from "Project", "Generic element library").
- Entering, arranging and interconnecting the elements of the system in the work area ("Condensing", "Water-based air conditioning", "DHW", "Air-source heat pump", "Water distribution", "Direct expansion" and "Air distribution" groups) in accordance with the permitted diagrams. Here are some examples:
- Boiler and radiator installation (from "Generators", "Boiler"; from "Emitters", "Radiator"; and from "Water distribution", "Water pipe").
- Heat pump and radiant floor installation (from "Generators", "Air-to-water heat pump, 2 pipes"; from "Emitters", "Radiant floor manifold"; and from "Water distribution", "Water pipes").
- Installation of ducted heat pumps and fan coils (from "Generators", "Air-to-water heat pump, 2-pipes"; from "Emitters", ‘Fan coils, 2-pipe’; from "Water distribution", "Water pipe"; from "Air distribution", "Rigid duct"; and from "Air distribution", "Grille").
- Direct expansion installation, VRF system ("VRF, Outdoor unit, heat pump (2 pipe)", "Indoor unit, wall mounted" and "Refrigerant pipe").
- Assigning thermal loads to devices (‘"Thermal loads" group). This assignment is automatic if both the reference points of the thermal loads and the units covering them are located inside the volumes formed by the spaces read from the geometrical model.
- Analysing the system, displaying the results on the screen and in the results reports ("Analysis" and "Results" groups).
- (Optional) Creating and managing the cost estimations and bills of quantities of the system ("Bill of quantities" tab).
- Obtaining reports and drawings (from "Results", "Reports"; and from "File", "Drawings").
- Exporting to BIMserver.center (from "BIMserver.center", "Share").
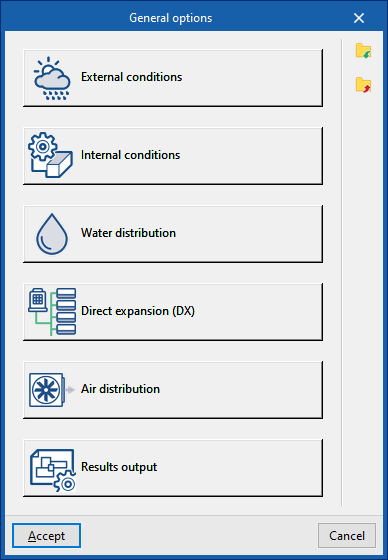
Defining the general project options
In the "Project" group of the main toolbar on the "Installation" tab, you can define the general options of the project:

The available options are as follows:
- External conditions
- Internal conditions
- Water distribution
- Direct expansion
- Air distribution
- Results output
These functions are detailed below.
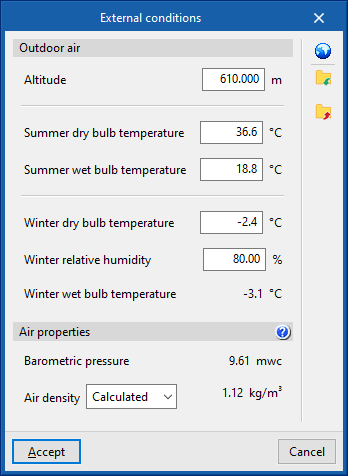
External conditions
Defines the external air conditions.
- Outdoor air
- Altitude (m)
- Dry-bulb temperature, summer (ºC)
- Wet-bulb temperature, summer (ºC)
- Dry-bulb temperature, winter (ºC)
- Relative humidity, winter (%)
- Wet-bulb temperature, winter (ºC)
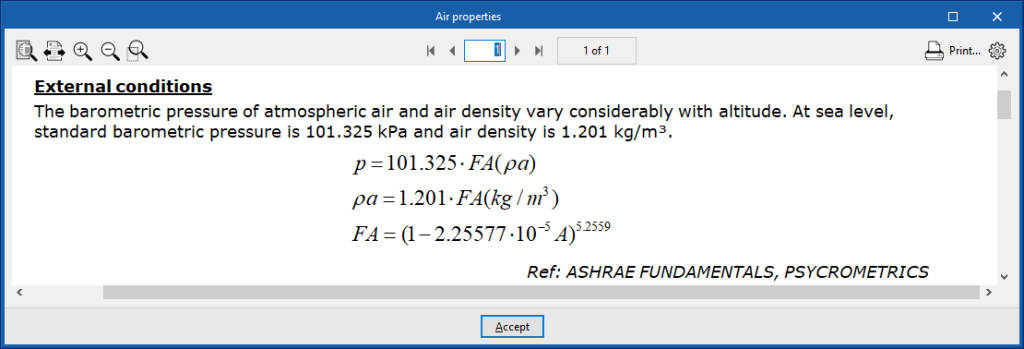
- Air properties
- Barometric pressure (mwc)
- Air density (Calculated/User-defined) (kg/m³)
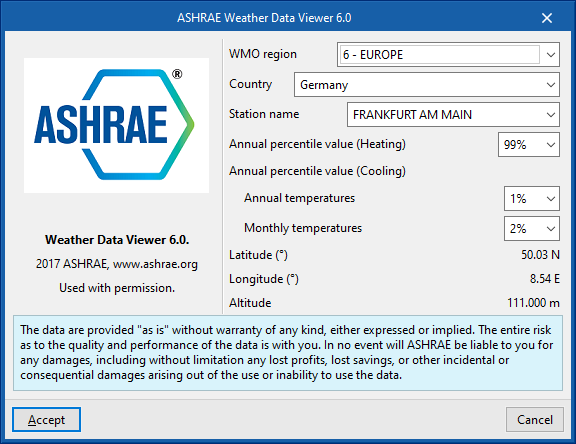
Climate data import
Outdoor condition data can be imported from the ASHRAE Weather Data Viewer 6.0 database using the button to the right of the "Outdoor conditions" window.
To import this data, the following parameters must be defined:
- WMO region
Defines the world region. - Country
Allows the country to be selected within the chosen region. - Station name
Allows the meteorological station to be selected within the chosen country.
From here, it is also possible to choose the percentile levels of the data to be imported:
- Annual percentile level (Heating)
Allows a level of 99.6% or 99% to be selected. - Annual percentile level (Cooling)
- Temperaturas anuales
Permite elegir un nivel de 0.4%, 1% o 2% para las temperaturas anuales. - Temperaturas mensuales
Permite elegir un nivel de 0.4%, 2% o 5% para las temperaturas mensuales.
- Temperaturas anuales
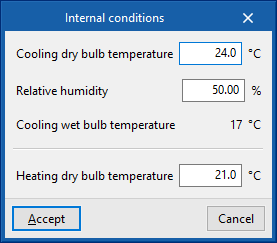
Internal conditions
Defines the indoor air conditions.
- Cooling dry-bulb temperature (ºC)
- Relative humidity (%)
- Cooling wet-bulb temperature (ºC)
- Heating dry-bulb temperature (ºC)
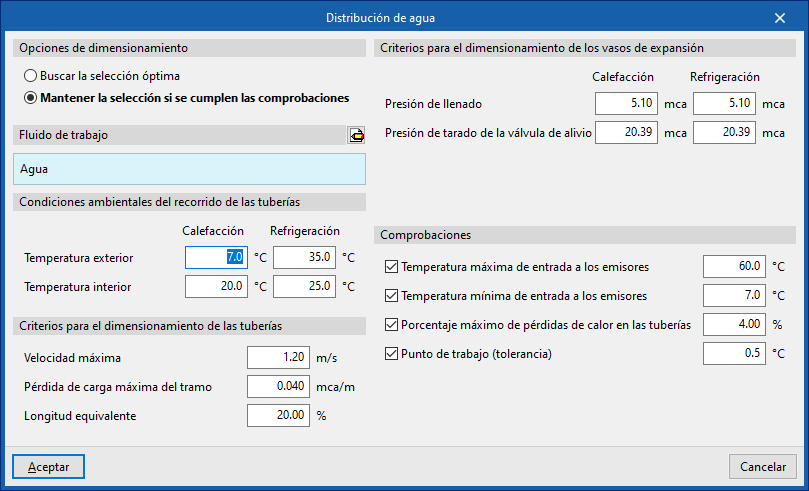
Water distribution
This section configures the sizing criteria for various elements of the water distribution system such as pipes and expansion vessels, and activates certain checks on them.
Design options
Allows the sizing process of the water distribution system elements to be adjusted:
- Search for the optimal selection
During the design process, the program will search for and select the smallest element in the series that meets all requirements. - Maintain the selection if checks are met
During the design process, the program will attempt to retain the element selected by the user. If the selected element meets the requirements, the program will not change it, even if there is a smaller one that also meets them. However, if the selected element does not comply, the program will replace it with the smallest element that does.
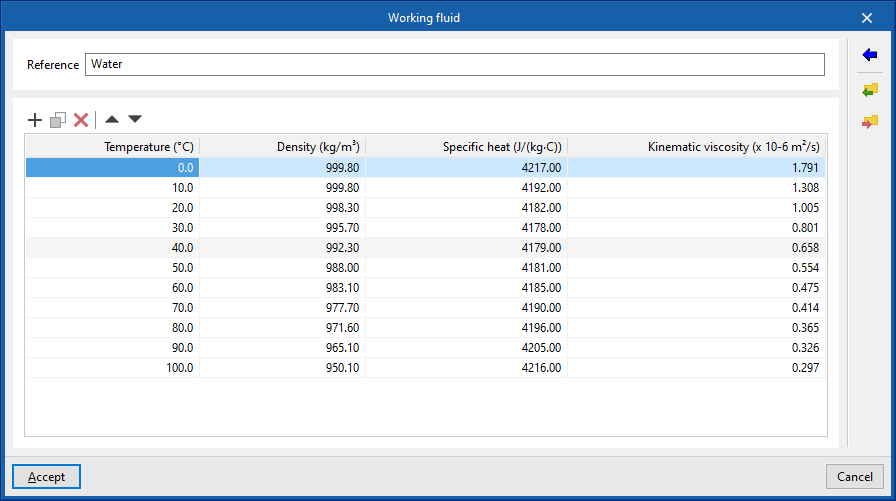
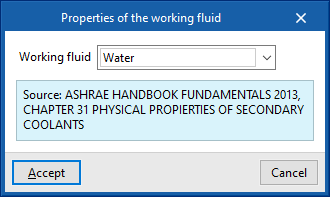
Working fluid
Defines the properties of the working fluid by reference and at different temperatures:
- Reference
- Working fluid properties table
- Temperature (ºC)
- Density (kg/m³)
- Specific heat (J/(kg·ºC))
- Kinematic viscosity (×10⁻⁶ m²/s)
It is possible to import predefined values for water and for water with additives using the assistant to the right:
- Working fluid properties
- Working fluid (Water / Water with ethylene glycol / Water with propylene glycol)
Environmental conditions along the pipe route
- Outdoor temperature (ºC) (Heating / Cooling)
- Indoor temperature (ºC) (Heating / Cooling)
Pipe design criteria
- Maximum velocity (m/s)
- Maximum head loss per section (mwc/m)
- Equivalent length (%)
Expansion vessel design criteria
- Filling pressure (mwc) (Heating / Cooling)
- Relief valve setting pressure (mwc) (Heating / Cooling)
Checks
- Maximum inlet temperature to emitters (ºC) (optional)
- Minimum inlet temperature to emitters (ºC) (optional)
- Maximum heat loss percentage in pipes (%)
- Operating point (tolerance) (ºC)
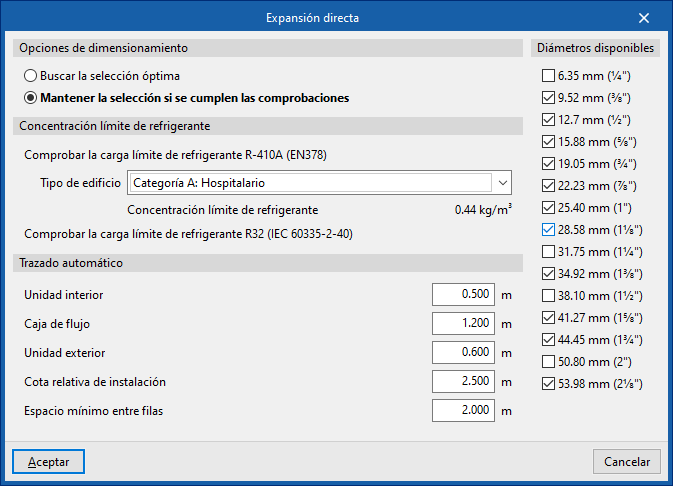
Direct expansion
Design options
Allows the design process of the direct expansion system elements to be adjusted:
- Search for the optimal selection
During the design process, the program will search for and select the smallest element in the series that meets all requirements. - Maintain the selection if checks are met
During the design process, the program will attempt to retain the element selected by the user. If the selected element meets the requirements, it will not be changed, even if there is a smaller one that also meets them. However, if it does not comply, the program will replace it with a suitable one.
Refrigerant charge limit concentration
This section allows the verification of the refrigerant charge limit.
To "Check the R-410A refrigerant charge limit (EN378)", select the "Building type" from the following:
- Category A: Hospital
- Category B: Residential, commercial, educational, public access
- Category C: Offices and administrative premises
- Category D: Industrial
Selecting a building type displays the associated "Refrigerant concentration limit".
It is also possible to "Check the R32 refrigerant charge limit (IEC60335-2-40)".
Automatic routing
Configures the distances used by the "Automatic routing (VRF)" option in the "Calculation" group.
- Indoor unit
- Flow box
- Outdoor unit
- Relative installation level
- Minimum spacing between rows
Available diameters
Allows you to define which refrigerant line diameters are available by activating or deactivating the corresponding boxes.
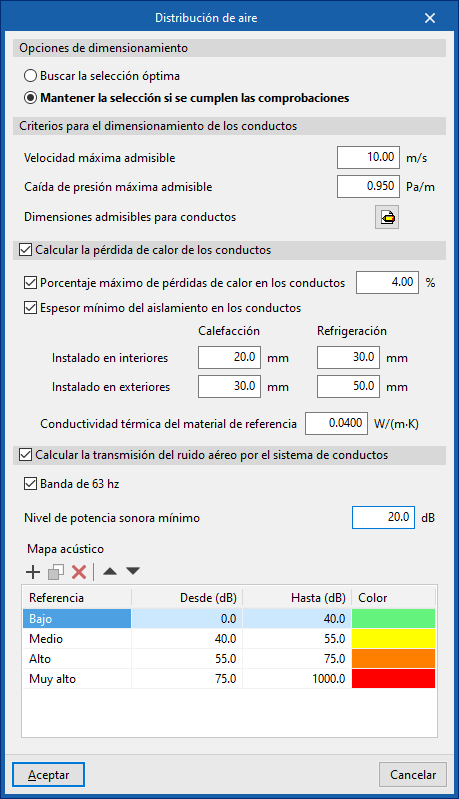
Air distribution
This section configures the design criteria for various air distribution system elements, such as ducts, and activates certain checks on them.
Design options
Allows the design process of the air distribution system elements to be adjusted:
- Search for the optimal selection
During the design process, the program will search for and select the smallest element in the series that meets all requirements. - Maintain the selection if checks are met
During the design process, the program will attempt to retain the element selected by the user. If it meets the requirements, it will not be changed. Otherwise, it will be replaced with a compliant one.
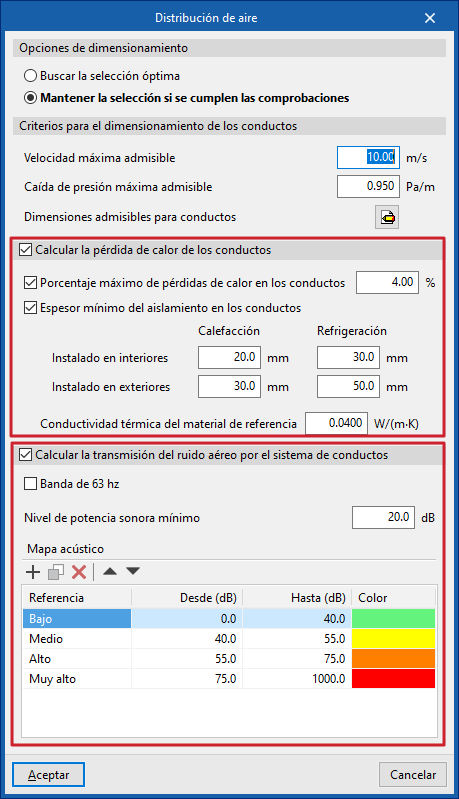
Duct design criteria
- Maximum allowable velocity (m/s)
- Maximum allowable pressure drop (Pa/m)
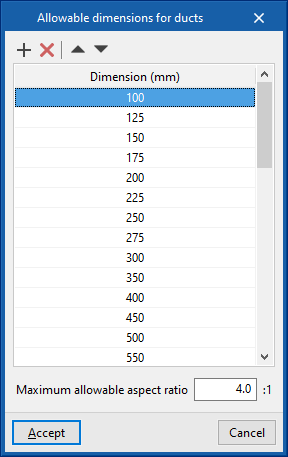
- Permissible duct dimensions
- Dimension (mm)
- Maximum allowable aspect ratio (n:1)
Calculate duct heat loss (optional)
Enables the thermal analysis of heat loss through air ducts when calculating or sizing the installation.
- Maximum percentage of heat losses in ducts (%)
- Minimum insulation thickness for ducts
- Defined for ducts in the following categories:
- Installed indoors (Heating, Cooling)
- Installed outdoors (Heating, Cooling)
- Further down, enter the "Thermal conductivity of reference material".
- Defined for ducts in the following categories:
Calculate airborne noise transmission through duct system
Enables acoustic calculation in air ducts when calculating or designing the installation.
- 63 Hz band (optional)
- Minimum sound power level
- Acoustic map
- Reference / From / To / Colour
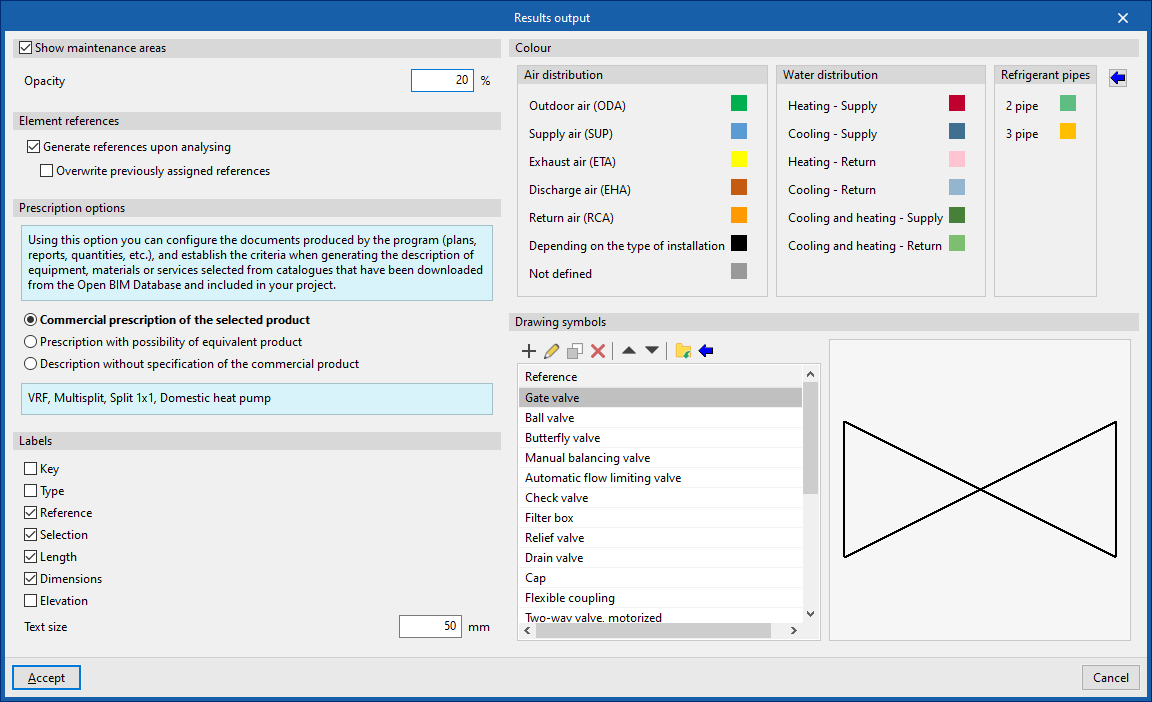
Results output
Allows you to configure different options related to the programme’s results output:
Show maintenance areas (optional)
Displays maintenance areas near equipment when this information is available.
- Opacity
Element references
Allows automatic generation of element references to be activated or deactivated.
- Generate references when calculating (optional)
- Overwrite previously assigned references (optional)
Specification options
Configures the documentation produced by the program (drawings, lists, measurements, etc.), establishing the criteria for generating descriptions of equipment, materials or services selected from the catalogues downloaded from Open BIM Database and included in the project.
- Commercial specification of the selected product
Descriptions will specify only the selected product. - Specification with equivalent product option
Descriptions will specify the selected product and indicate the possibility of using an equivalent. - Description without specifying a commercial product
LaDescriptions will not specify a particular commercial product.
Labels
Configures the information labels displayed over elements.
- Legend (optional)
- Type (optional)
- Reference (optional)
- Selection (optional)
- Length (optional)
- Dimensions (optional)
- Level (optional)
- Text size
- Colour
Colour
Allows modification of the display colour (on screen and in drawings) for elements of the following categories:
- Air distribution
- Outdoor air (ODA)
- Supply air (SUP)
- Extraction air (ETA)
- Exhaust air (EHA)
- Return air (RCA)
- According to the type of installation
- Undefined
- Water distribution
- Heating - Supply
- Cooling - Supply
- Heating - Return
- Cooling - Return
- Cooling and heating - Supply
- Cooling and heating - Return
- Refrigeration lines
- 2 pipes
- 3 pipes
The button on the right restores the "Default values".
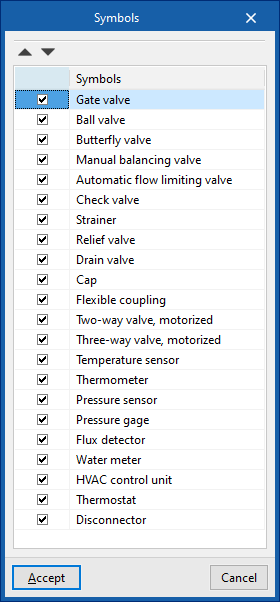
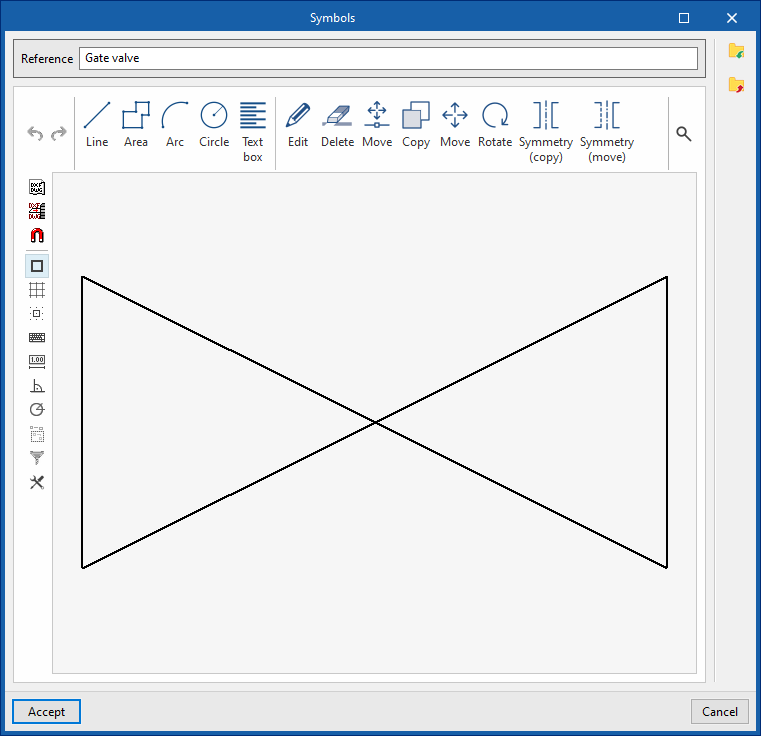
Symbols for drawings
Create symbols for different elements in the drawing using a graphic editor where you can insert lines, areas, arcs, circles and text boxes.
The program also offers the possibility of importing a series of predefined symbols using the wizard in the top toolbar.
Tools for managing manufacturers' catalogues
In the "Project" group of the main toolbar of the "Installation" tab, there is an option for managing the manufacturer's product catalogues in order to incorporate them into the project:

Catalogue management
This allows manufacturers' catalogues to be downloaded using the connection to the Open BIM Database, making it easier to enter data into the program for project development.
Clicking on this option opens a window with the available manufacturer catalogues.
Using the "Filters applied" option, filters can be applied by element "Category", "Language" and "Country" so that only manufacturers offering product catalogues with these characteristics are displayed.
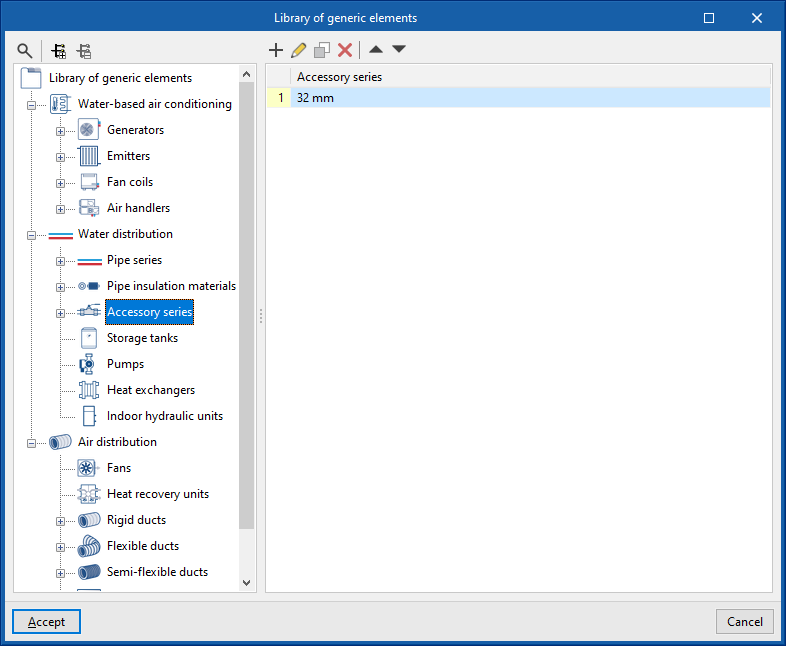
Catalogue download
The following options are shown for each manufacturer:
- Download
Downloads the manufacturer's catalogue. The products in the catalogue will be available in the project. - Update
Updates the selected manufacturer's catalogue to the latest version, deleting the version downloaded in the project. - Delete
Deletes the selected manufacturer's catalogue. The products in the catalogue will no longer be available in the project.
Connection to Open BIM Database
At the bottom of this dialogue box, the program allows users to log in with their Open BIM Database account and password.
| Note: |
|---|
| The products from the downloaded catalogues can be selected when entering the elements in the system. |
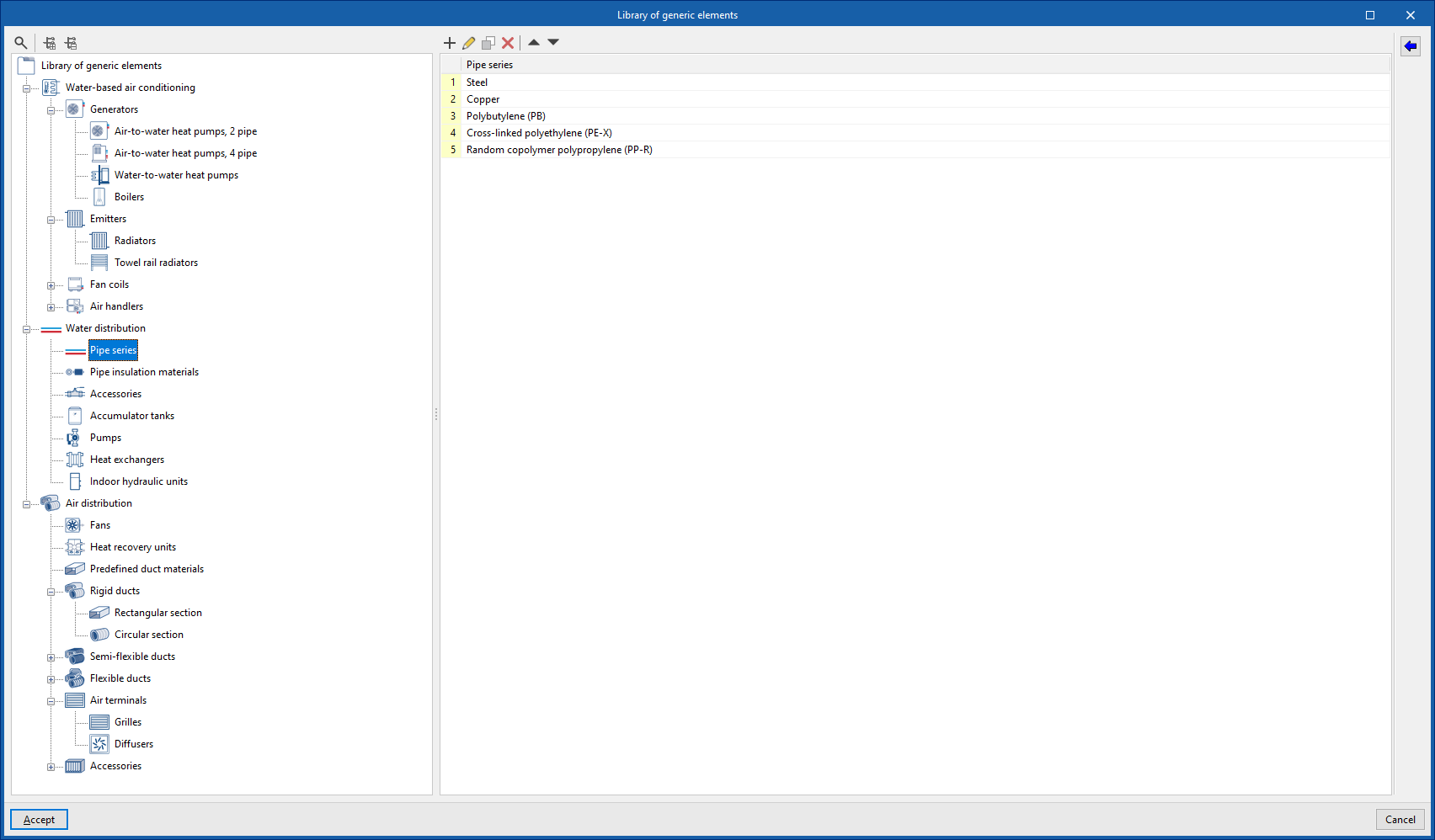
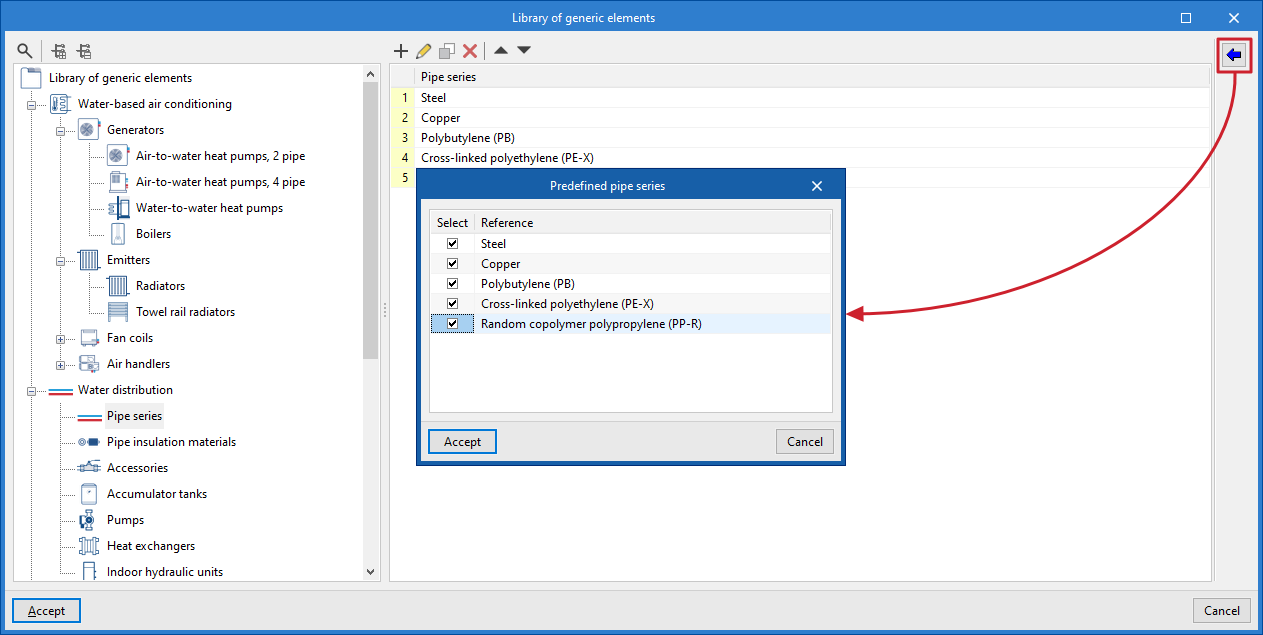
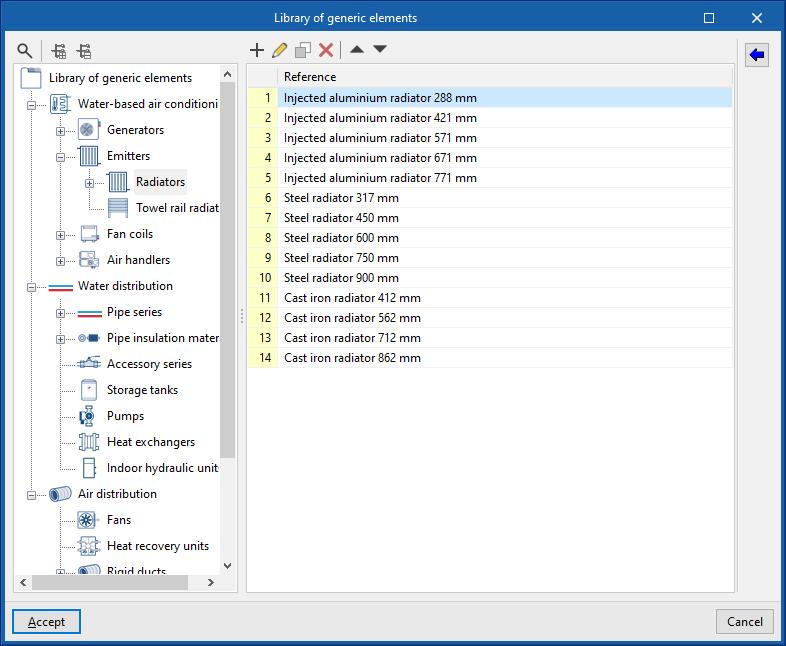
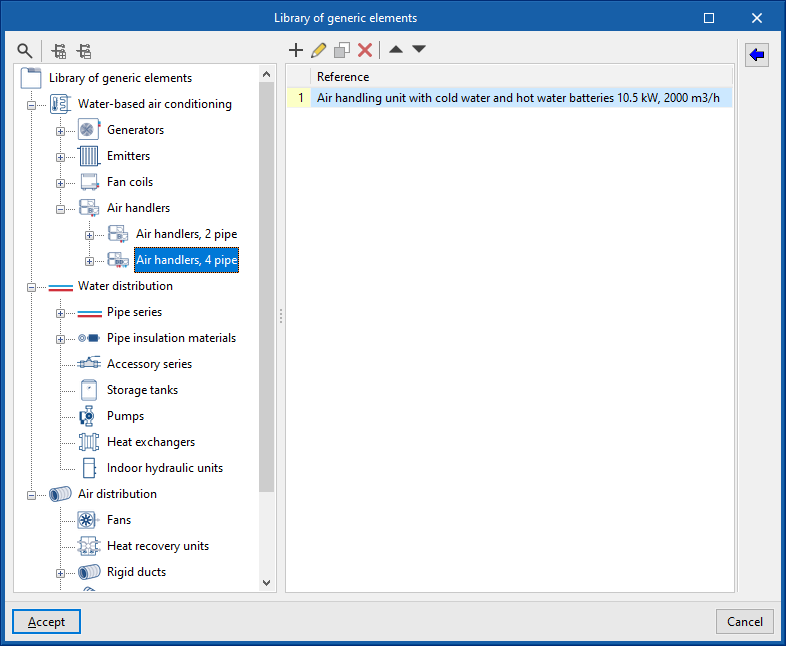
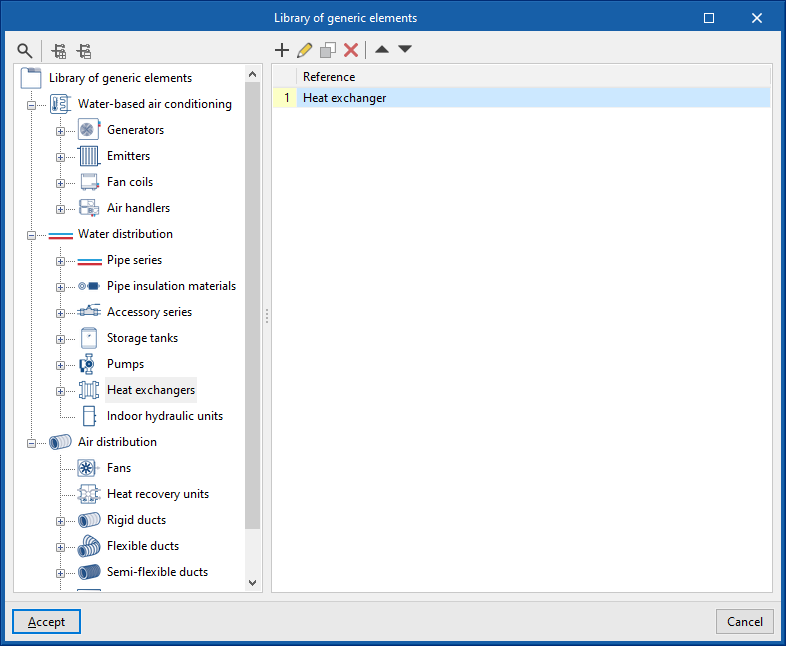
Management of the project's generic elements library
In the "Project" group of the main toolbar on the "Installation" tab, you will find the option to manage the project's generic element library:

Generic elements library
You can create and manage libraries of generic types of the following elements:
- Water-based air conditioning
- Generators (Air-water heat pumps, 2 pipes; Air-water heat pumps, 4 pipes; Water-water heat pumps; Boilers)
- Emitters (Radiators; Towel radiators)
- Fan coils (Fan coils, 2 pipes; Fan coils, 4 pipes)
- Air conditioners (Air conditioners, 2 pipes; Air conditioners, 4 pipes)
- Water distribution
- Pipe series
- Insulation for pipes
- Fittings
- Accumulators
- Pumps
- Exchangers
- Hydraulic indoor units
- Air distribution
- Fans
- Heat recovery units
- Predefined materials for ducts
- Rigid ducts (rectangular section; circular section)
- Semi-flexible ducts (rectangular section; circular section)
- Flexible ducts (rectangular section; circular section)
- Air terminals (grilles; diffusers)
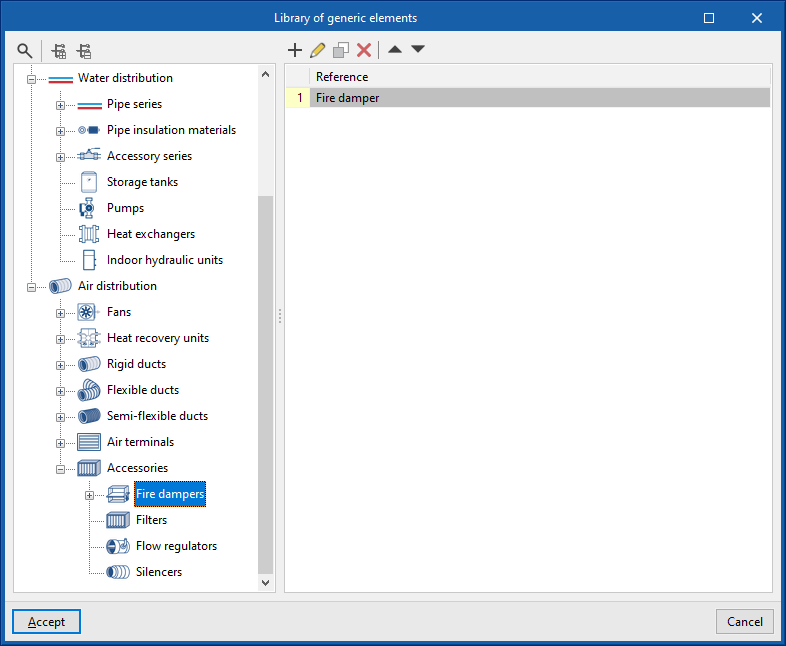
- Accessories (Fire dampers; Filters; Flow regulators; Silencers)
Entering condensing circuit elements
In the "Installation" tab, in the "Condensation" group of the main toolbar, the following elements can be defined and entered:

These elements are used to integrate the design of condensation circuits for water-to-water heat pumps. Based on their power and performance data, the program calculates the thermal power in the external heat exchanger of the heat pumps and allows the hydraulic circuit to be defined down to the equipment responsible for dissipating this power.
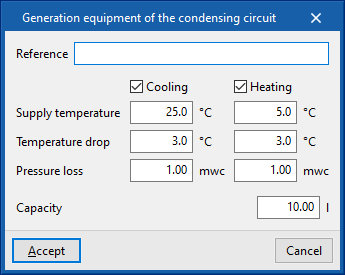
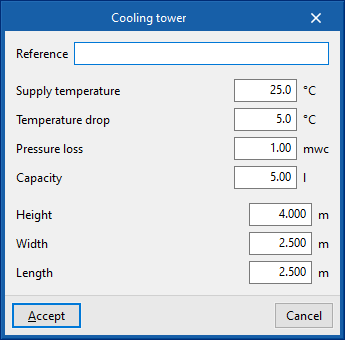
Generation equipment of the condensing circuit
Enters a condensing circuit generation unit. This unit represents a heat source, such as a geothermal collector field.
When entering a generating set, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Design conditions
- Supply temperature (Cooling (optional) / Heating (optional))
- Temperature drop (Cooling (optional) / Heating (optional))
- Pressure loss (Cooling (optional) / Heating (optional))
- Capacity
Entering emitters (water-based air conditioning)
Within the "Installation" tab, the following elements can be defined and entered in the "Emitters" menu of the "Water-based climate control" group in the main toolbar:

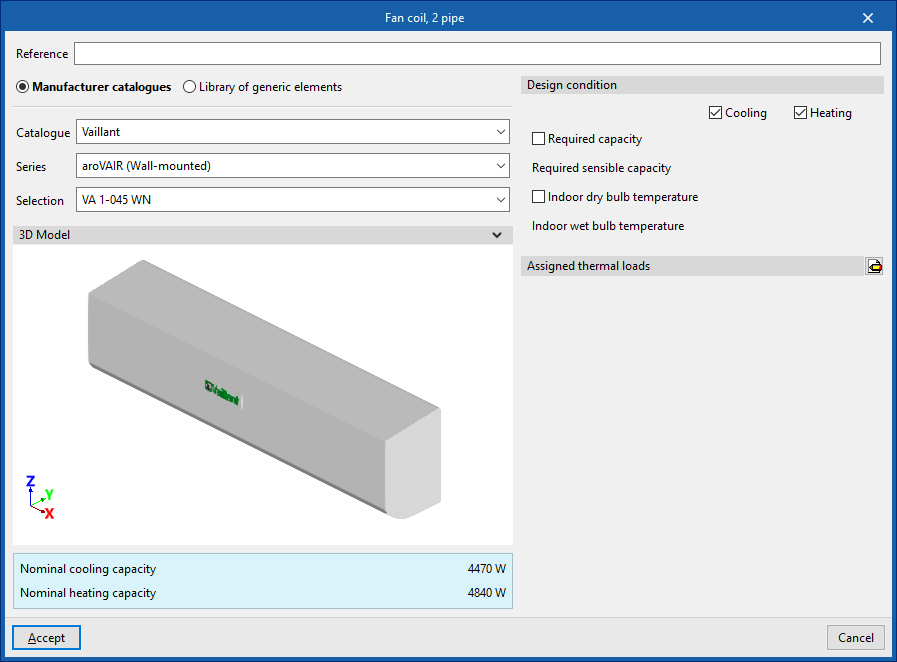
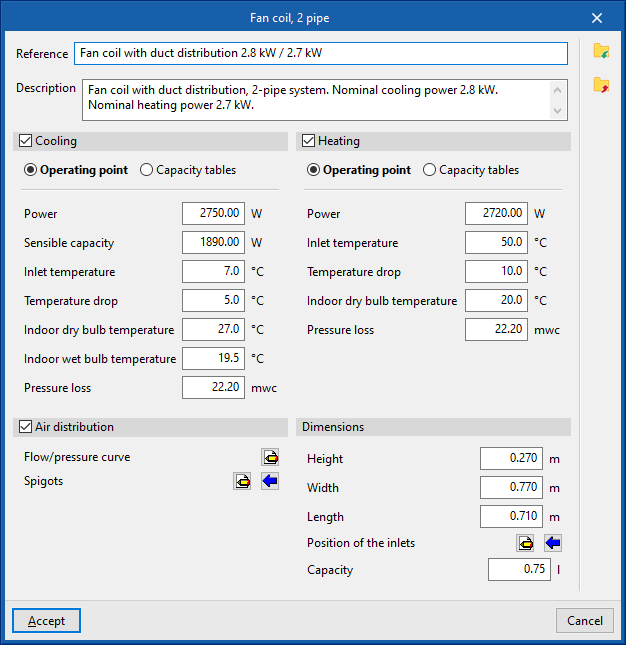
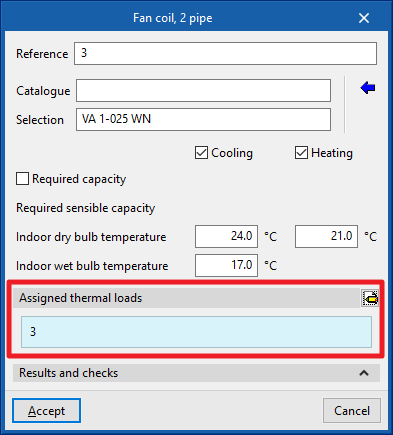
Fan coil
Inserts fan coils (with direct discharge or ducted distribution) for a two-pipe or four-pipe system:
- Fan coil, 2 pipe
- Fan coil, 4 pipe
When inserting a fancoil, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Catalogue / Selection
The program selects and imports data from "Manufacturer catalogues", if available, or from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard available on the right. - Design conditions
- Required capacity (optional) (Heating (optional) / Cooling (optional))
- Required sensible capacity (Cooling (optional))
- Indoor dry bulb temperature (Heating (optional) / Cooling (optional))
- Indoor wet bulb temperature (Cooling (optional))
- Assigned thermal loads
Defines the following percentages on the values of the thermal loads for heating and/or cooling of the project. The program automatically assigns loads according to the arrangement of the terminal elements in the model.- % Assigned heating capacity
- % Assigned total cooling capacity
- % Assigned sensible cooling capacity
- % Required heating load
- % Required total cooling load
- % Required sensible cooling load
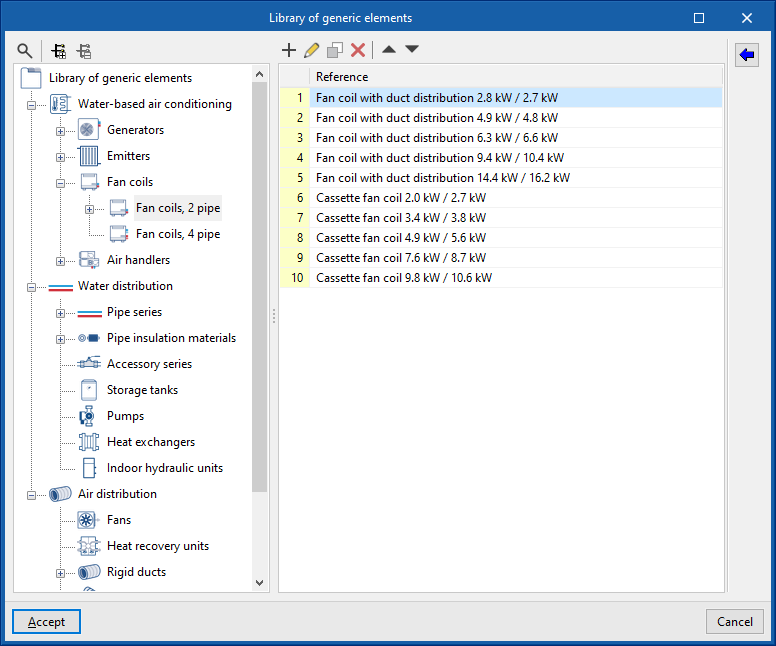
Library of generic fan coils
Within the "Project" group, in the "Library of generic elements" option, the libraries of available 2-pipe and 4-pipe generic fan coil types can be created and edited.
The data associated with each type of 2-pipe or 4-pipe fan coil is as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Refrigeration (optional)
- Operating point (Power; Sensible capacity; Inlet temperature; Temperature drop; Indoor dry bulb temperature; Indoor wet bulb temperature; Pressure loss)
- Capacity tables (Power; Sensible capacity; Pressure loss)
- Heating (optional)
- Operating point (Power; Inlet temperature; Temperature drop; Indoor dry bulb temperature; Pressure ^loss)
- Capacity tables (Power; Pressure loss)
- Air distribution (optional)
- If this option is checked, the program considers the fancoil to be a ducted distribution fancoil.
- Flow/pressure curve
- Midpoint (Flow rate; Pressure)
- Point (Flow rate; Pressure)
- Outlets
- Inlets
- Installation
- Air flow type (Outside air (ODA) / Supply air (SUP))
- Inlet can be disconnected (optional)
- Geometry
- Type (Rectangular / Circular)
- Width x Height / Diameter
- Installation
- Inlets
- Flow/pressure curve
- Dimensions (Height; Width; Length; Position of inlets; Capacity)
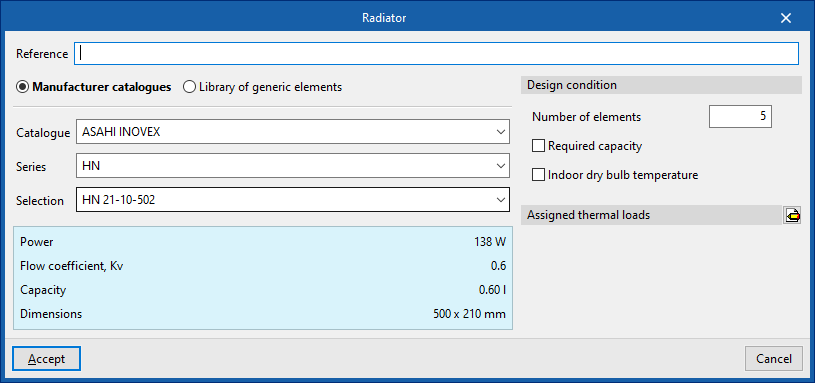
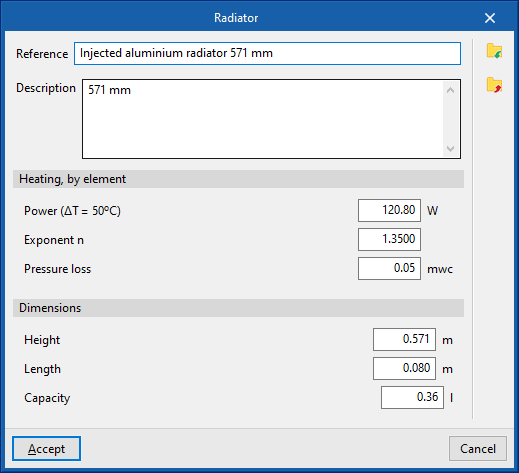
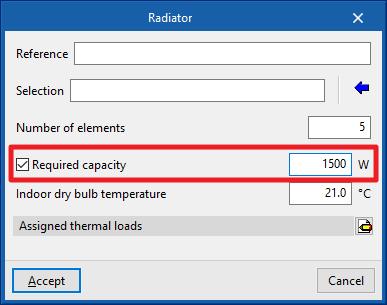
Radiator
Enters radiators.
When entering a radiator, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Selection
- The program can select and import data from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right-hand side.
- Number of elements
- Design conditions
- Required capacity (optional)
- Indoor dry bulb temperature
- Assigned thermal loads
- Defines the following percentages on the values of the heating thermal loads of the project. The program automatically locates loads according to the arrangement of the terminal elements in the model.
- % Assigned heating capacity
- % Required cooling load
Library of generic radiators
Within the "Library of generic elements" option, in the "Project" group, the available libraries of generic radiator types can be created and edited.
The data associated with each type of radiator is as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Heating, by element
- Power (ΔT=50ºC)
- Exponent n
- Pressure loss
- Dimensions (Height; Length; Capacity)
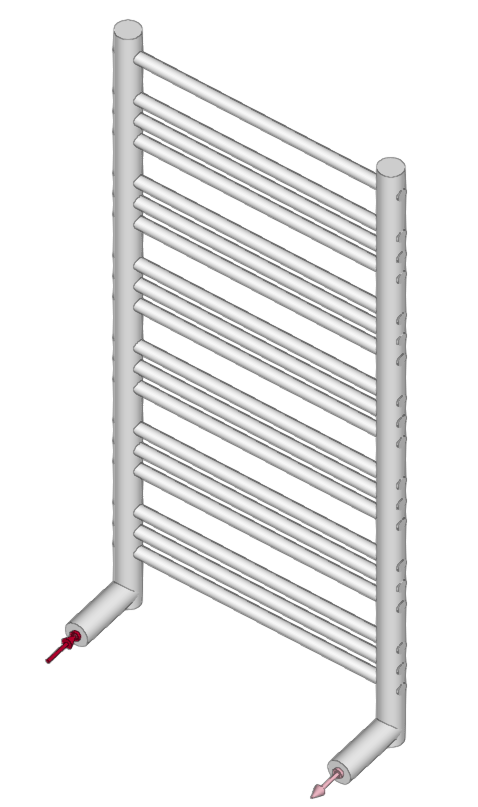
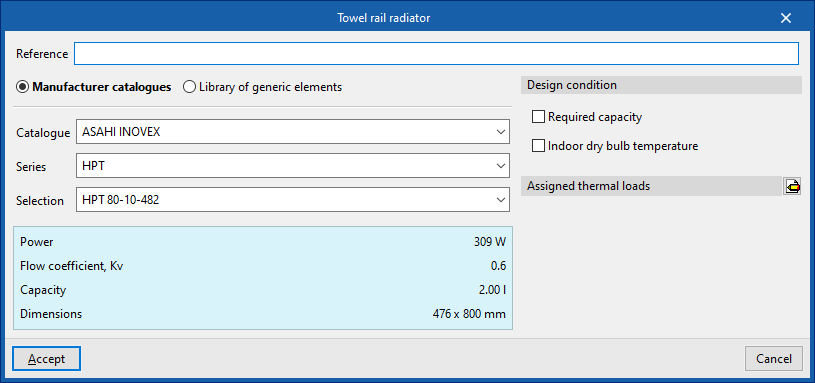
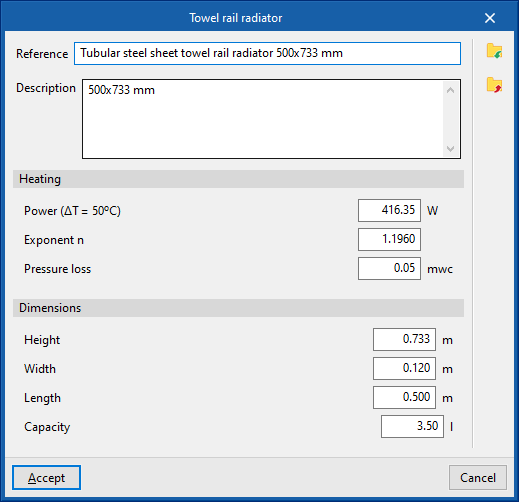
Towel rail radiator
Enters towel rail radiators.
To enter a towel rail radiator, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Selection
- The program can select and import data from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right-hand side.
- Number of elements
- Design conditions
- Required capacity (optional)
- Indoor dry bulb temperature
- Assigned thermal loads
- Defines the following percentages on the values of the heating thermal loads of the project. The program automatically locates loads according to the arrangement of the terminal elements in the model.
- % Assigned heating capacity
- % Required cooling load
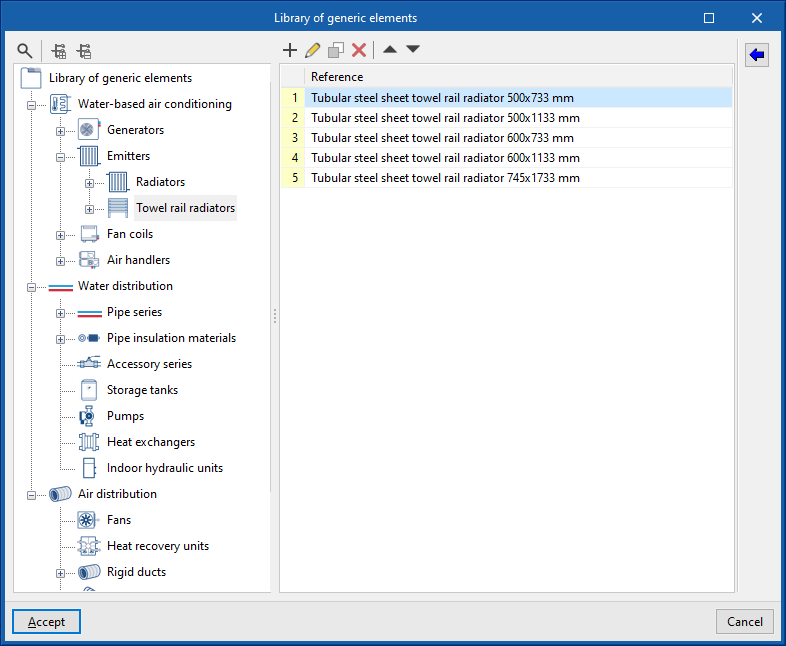
Library of generic towel rail radiators
Within the "Library of generic elements" option, in the "Project" group, the available libraries of generic towel rail radiator types can be created and edited.
The data associated with each type of towel rail radiator is as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Heating, by element
- Power (ΔT=50ºC)
- Exponent n
- Pressure loss
- Dimensions (Height; Length; Capacity)
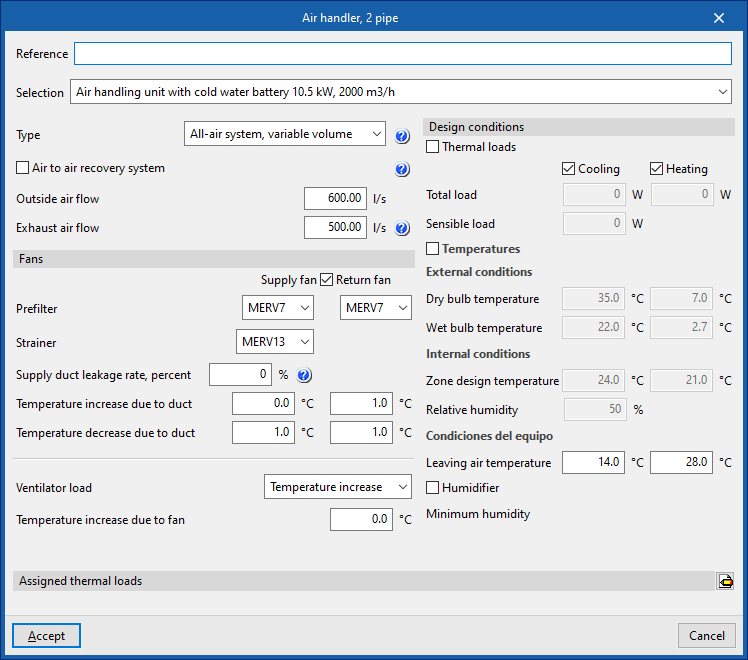
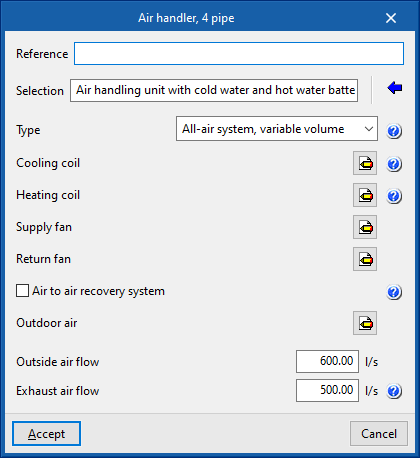
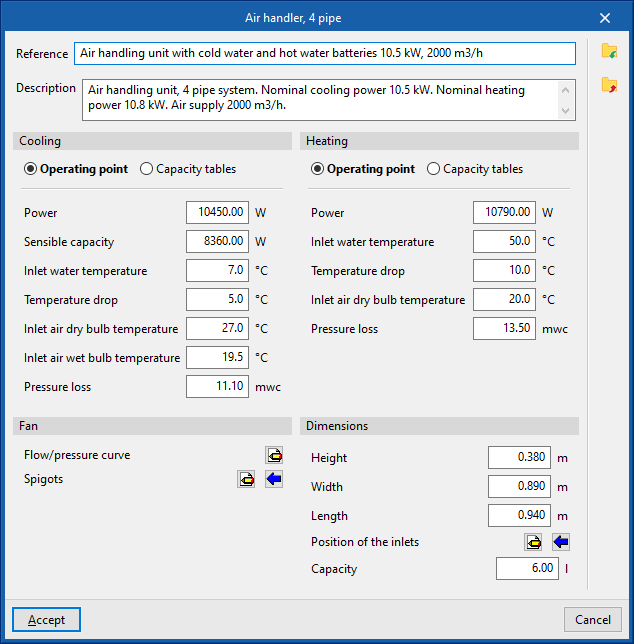
Air handler
Enters air conditioners for a two-pipe or four-pipe system:
- Air handler, 2 pipe
- Air handler, 4 pipe
When entering an air handler, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Selection
- The program selects and imports data from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard available on the right hand side.
- Description
- Type (All air system, constant volume / All air system, variable volume)
- Cooling coil (optional in "Air handling unit, 2-pipe")
- Heating coil (optional for "Air handling unit, 2-pipe")
- Supply fan
- Return fan
- Air to air recovery system (optional)
- Type (Sensible / enthalpy)
- Efficiency (%)
- Outdoor air
- Pre-filter
- Design parameters
- Outside air flow
- Exhaust air flow
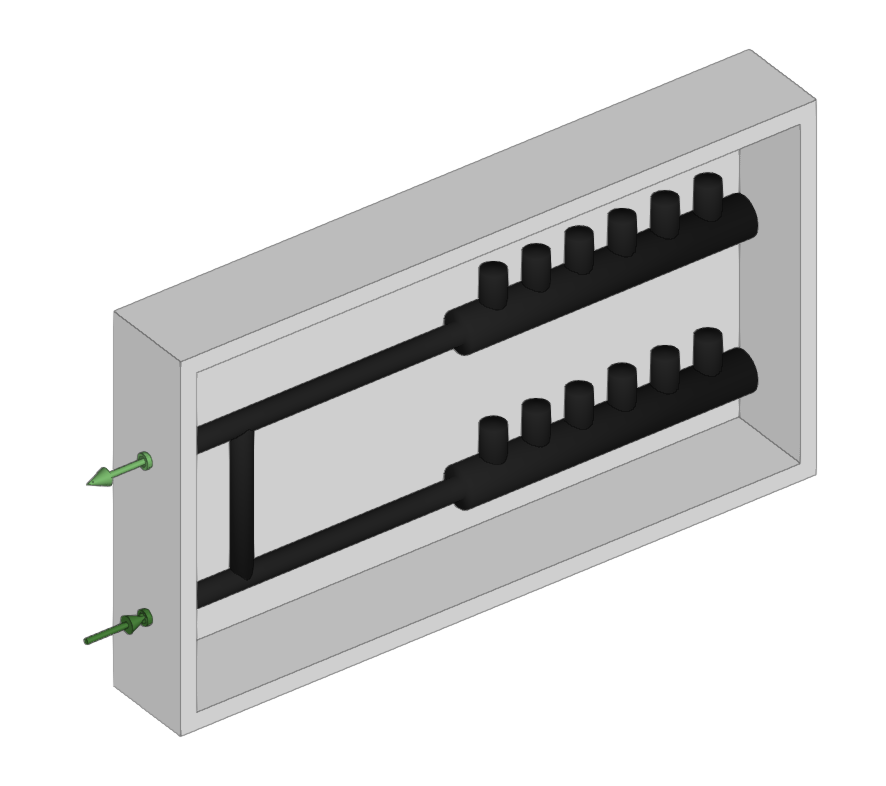
Library of generic air handlers
In the "Library of generic elements" option, within the "Project" group, the libraries of available generic 2-pipe and 4-pipe air conditioning unit types can be created and edited.
The data associated with each type of 2-pipe or 4-pipe air conditioner are as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Cooling (optional for "Air handler, 2 pipe")
- Operating point (Power; Sensible power; Inlet water temperature; Temperature drop; Inlet air dry bulb temperature; Inlet air wet bulb temperature; Pressure loss)
- Capacity tables (Power; Sensible capacity; Pressure loss)
- Heating (optional on "Air conditioner, 2 pipes")
- Operating point (Power; Inlet water temperature; Temperature drop; Inlet air dry bulb temperature; Pressure loss)
- Capacity tables (Power; Power output; Pressure drop)
- Fan
- Flow/pressure curve
- Midpoint (Flow; Pressure)
- Point (Flow; Pressure)
- Outlets
- Inlets
- Installation
- Type of air flow (Outside air (ODA) / Supply air (SUP) / Extract air (ETA) / Exhaust air (EHA))
- Inlet can be disconnected (optional)
- Geometry
- Type (Rectangular / Circular)
- Width x Height / Diameter
- Flow/pressure curve
- Dimensions (Height; Width; Length; Position of inlets; Capacity)
The program will display warnings for the connections in the system that has not been completed, without hindering the analysis of the other system.
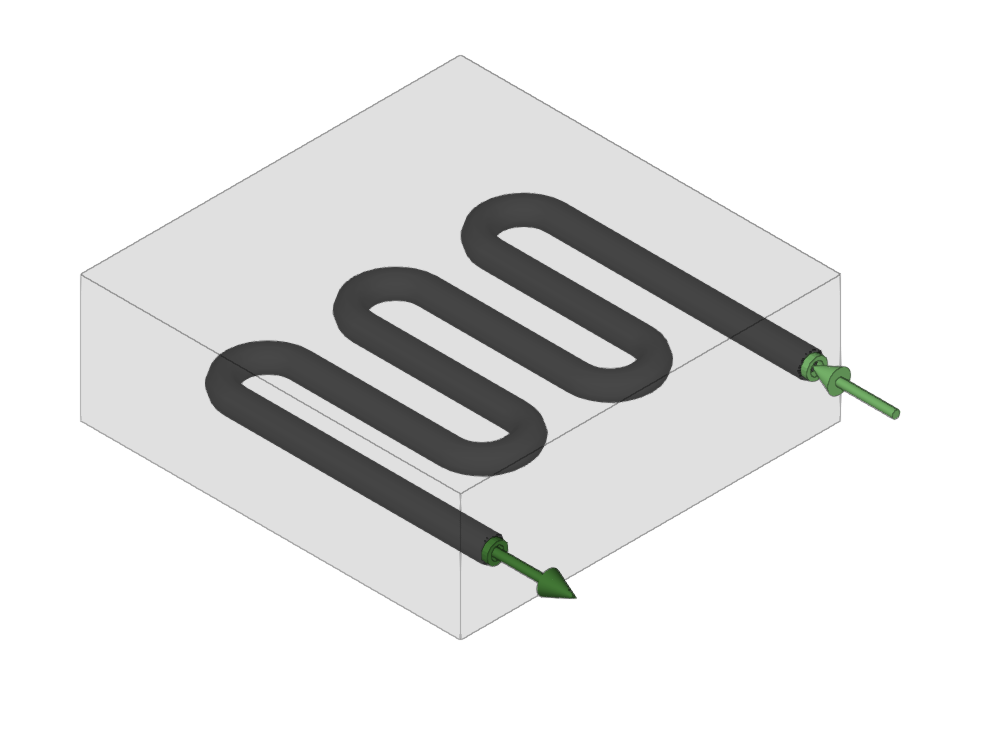
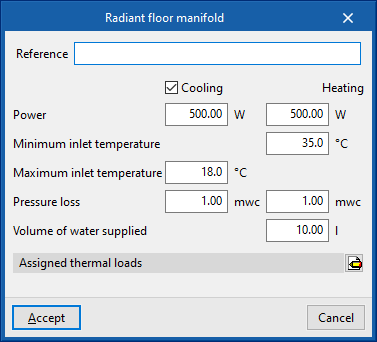
Radiant floor manifold
Enters radiant floor manifolds.
When entering a radiant floor manifold, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Design conditions
- Power (Cooling (optional) / Heating)
- Minimum inlet temperature (Heating)
- Maximum inlet temperature (Cooling (optional))
- Pressure loss (Cooling (optional) / Heating)
- Volume of water supplied (Heating)
- Thermal loads assigned
- Defines the percentages assigned to the equipment on the values of the thermal loads of the project. The program automatically assigns loads according to the arrangement of the terminal elements in the model.
These manifolds will reach CYPEHVAC as requirements, which can be viewed if the corresponding layer in "Imported requirements" in the left-hand side panel "Own elements" is activated.
When using the "Radiant floor manifold" option, the program asks the user if they want to automatically generate manifolds at the position of the requirements. If accepted, it will automatically arrange the manifolds in the model and fill in their data by taking them from the imported requirements.
If not, users can enter the manifolds freely by snapping the requirements individually. When entering them, the program will ask users once again whether they wish to fill in their values by taking them from the requirement. If the user decides to enter the values manually and they do not cover the values required by the requirement, a non-compliance error will remain visible.
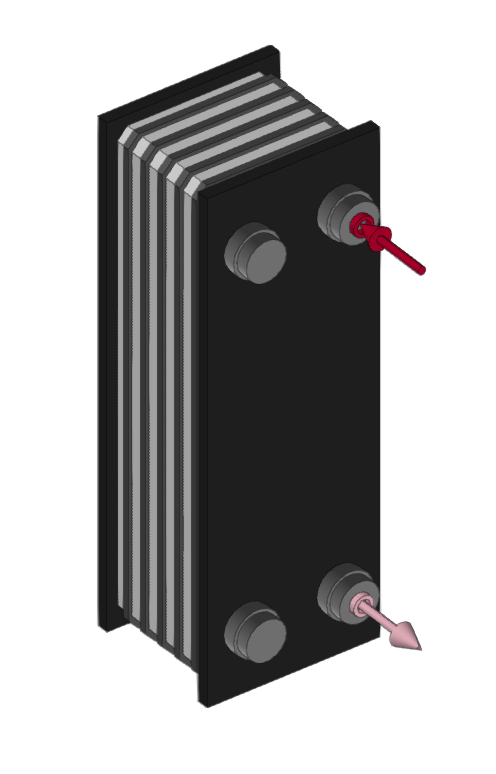
Entering DHW exchangers and cylinders
In the "Installation" tab, in the "DHW" menu of the "Water Heating" group in the main toolbar, the following elements can be defined and entered:

These elements link the air-conditioning system to the domestic hot water system.
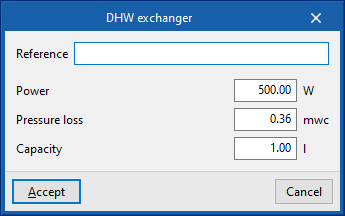
DHW exchanger
Enters DHW heat exchangers.
When entering a DHW heat exchanger, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Design conditions
- Power
- Pressure loss
- Capacity
Entering domestic heat pump systems
Within the "System" tab, in the "Domestic heat pump" group of the main toolbar, there are options for defining and entering the following elements, which make up the different domestic heat pump systems covered by the program:

- Equipment
- Compact unit, monobloc domestic heat pump system
- Outdoor unit, bibloc domestic heat pump system
- Indoor unit with DHW tank, bibloc domestic heat pump system
- Indoor wall unit, bibloc domestic heat pump system
- Outdoor unit, hydraulic bibloc domestic heat pump system
- Indoor unit with DHW tank, hydraulic bibloc domestic heat pump system
- Indoor wall unit, hydraulic bibloc domestic heat pump system
- Refrigerant pipe
The following domestic heat pump systems are available:
Monobloc domestic heat pump system
A monobloc domestic heat pump system consists only of the following compact unit, available in the "Equipment" menu:
- Compact unit, monobloc domestic heat pump system
This unit is equipped with two connection sockets with water distribution pipes.
When entering a compact unit of a monobloc domestic heat pump system, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Catalogue / Series / Selection
Selects and imports data from previously uploaded manufacturer catalogues via the "Catalogue management" option. - 3D Model
3D view of the selected unit. - Nominal heating capacity / Nominal cooling capacity
Nominal capacities of the selected unit. - Design condition
- Supply temperature (Cooling (optional) / Heating (optional))
Temperature difference (Cooling (optional) / Heating (optional))
This figure is set by the program.
Bibloc domestic heat pump system
A bibloc domestic heat pump system consists of two elements, the outdoor unit and the indoor unit, available in the "Equipment" menu, connected by a refrigerant pipe:
- Outdoor unit
- Outdoor unit, bibloc domestic heat pump system
- Indoor unit
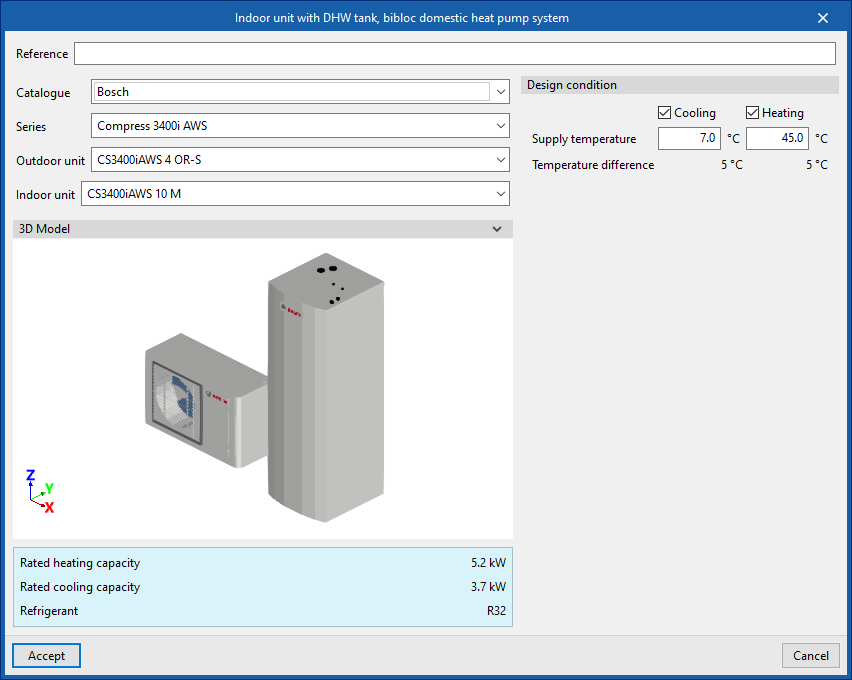
One of the following must be selected:- Indoor unit with DHW tank, bibloc domestic heat pump system
- Indoor wall unit, bibloc domestic heat pump system
The outdoor unit and the indoor unit must be connected to a "Refrigerant pipe" via the corresponding option in the "Domestic heat pump" group.
The indoor unit also has two connection sockets with water distribution pipes.
When the indoor unit is entered, the corresponding outdoor unit is simultaneously selected in the same editing panel, depending on the system. In this way, there is no need to enter any data for the outdoor unit when it is entered and only its layout in the space needs to be defined.
Therefore, when entering an outdoor unit of a bibloc domestic heat pump system, only the following parameter needs to be entered:
- Reference

When entering an indoor unit of a bibloc domestic heat pump system, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Catalogue / Series / Outdoor unit / Indoor unit
Selects and imports data from previously uploaded manufacturer catalogues via the "Catalogue management" option. - 3D Model
3D view of the selected unit. - Nominal heating capacity / Nominal cooling capacity / Refrigerant
Nominal capacities and type of refrigerant of the selected unit. - Design conditions
- Supply temperature (Cooling (optional) / Heating (optional))
Temperature difference (Cooling (optional) / Heating (optional))
This figure is set by the program.
Hydraulic bibloc domestic heat pump system
A bibloc domestic heat pump system consists of two elements, the outdoor unit and the indoor unit, available in the "Equipment" menu, connected by water distribution pipes:
- Outdoor unit
- Outdoor unit, hydraulic bibloc domestic heat pump system
- Indoor unit
One of the following must be selected:- Outdoor unit, hydraulic bibloc domestic heat pump system
- Indoor wall unit, hydraulic bibloc domestic heat pump system
The primary circuit can be laid by connecting the outdoor unit and the indoor unit with "Water distribution" pipes, which are available in the corresponding group. In this case, the pipe length limits, the difference in dimensions and the pipe diameter established by the manufacturer for the primary circuit must be checked.
The indoor unit also has two further connection sockets with water distribution pipes.
When the indoor unit is entered, the corresponding outdoor unit is simultaneously selected in the same editing panel, depending on the system. This way, there is no need to enter any data for the outdoor unit at the time of entry and only its layout in the space needs to be defined.
When inserting an outdoor unit of a hydronic bibloc domestic heat pump system, only the following parameter needs to be entered:
- Reference
When inserting an outdoor unit of a hydraulic bibloc domestic heat pump system, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Catalogue / Series / Outdoor unit / Indoor unit
Selects and imports data from previously uploaded manufacturer catalogues via the "Catalogue management" option. - 3D model
3D view of the selected unit. - Nominal heating capacity / Nominal cooling capacity
Nominal capacities of the selected unit. - Design conditions
- Supply temperature (Cooling (optional) / Heating (optional))
- Temperature difference (Cooling (optional) / Heating (optional))
This figure is set by the program.
Entering equipment (water distribution)
In the "Installation" tab, in the "Equipment" menu of the "Water distribution" group in the main toolbar, the following elements can be defined and entered:

Fittings
Enters fittings for the water distribution system.
When entering fittings, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Selection
The program selects and imports data from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right-hand side.
Library of generic fittings
The "Library of generic elements" option, within the "Project" group, is used to create and edit the libraries of available generic fitting types.
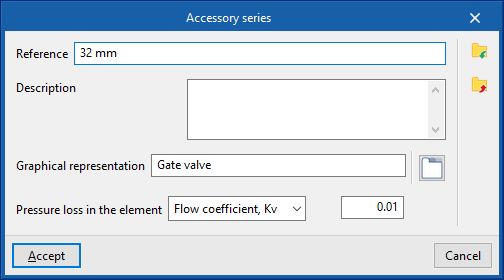
The data associated with each type of fitting is as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Graphical representation
Accesses the symbol library available from "General options" via "Symbols for drawings" in the "Project" group of the general interface. - Element pressure drop (Flow coefficient, Kv / Localised pressure loss)
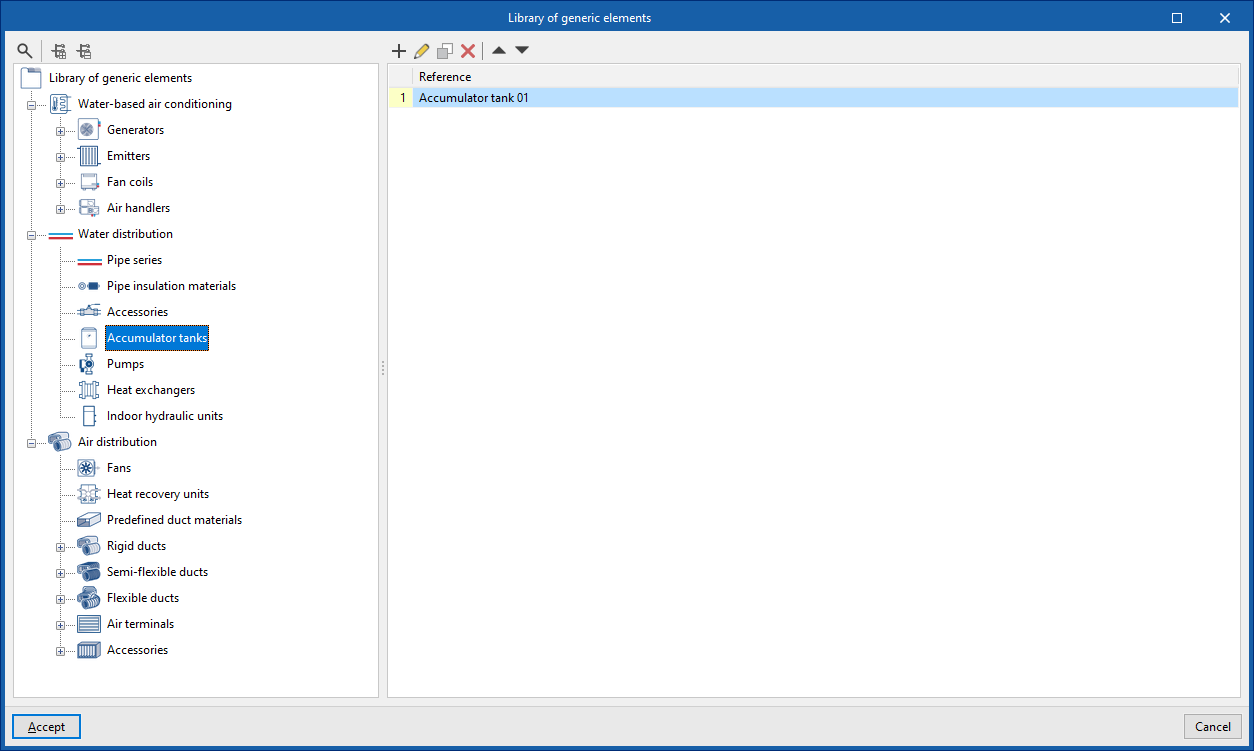
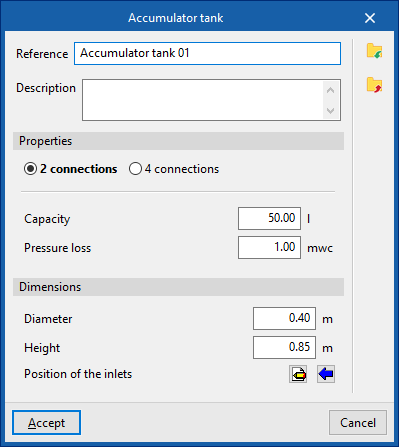
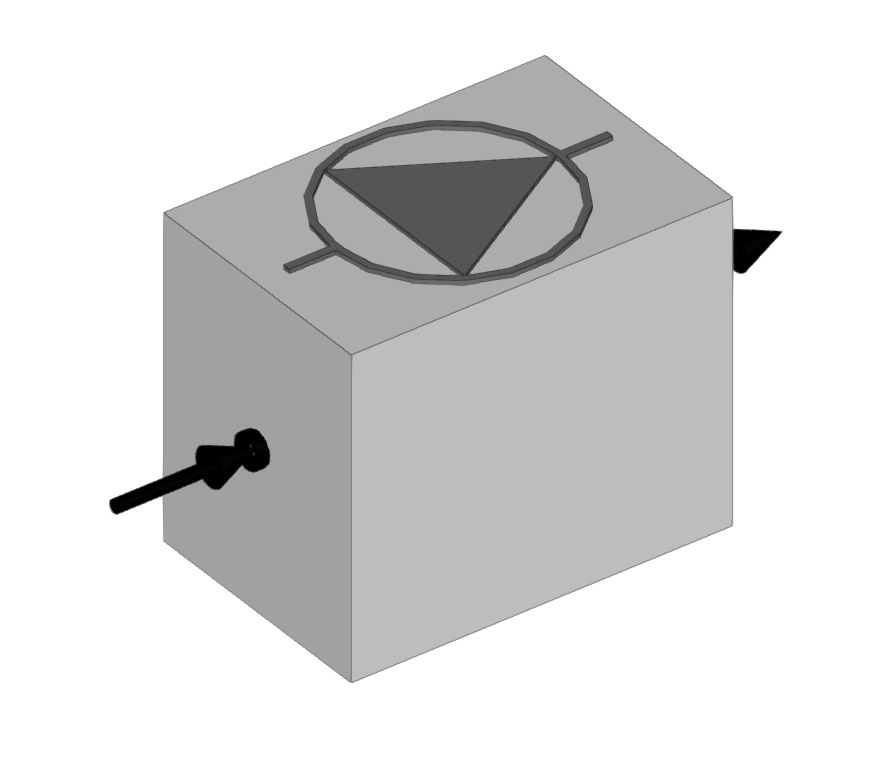
Accumulator tank
Inserts accumulator tanks.
When entering accumulator tanks the following parameters must be indicated:
- Reference
- Selection
The program selects and imports data from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right-hand side.
Library of generic accumulator tanks
The "Library of generic elements" option, within the "Project" group, is used to create and edit the libraries of available generic accumulator tank types.
The data associated with each type of accumulator tank is as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Characteristics
- 2 outlets (Capacity; Pressure loss)
- 4 outlets (Capacity; Pressure loss, primary circuit; Pressure loss, secondary circuit)
- Dimensions (Diameter; Height; Inlet position)
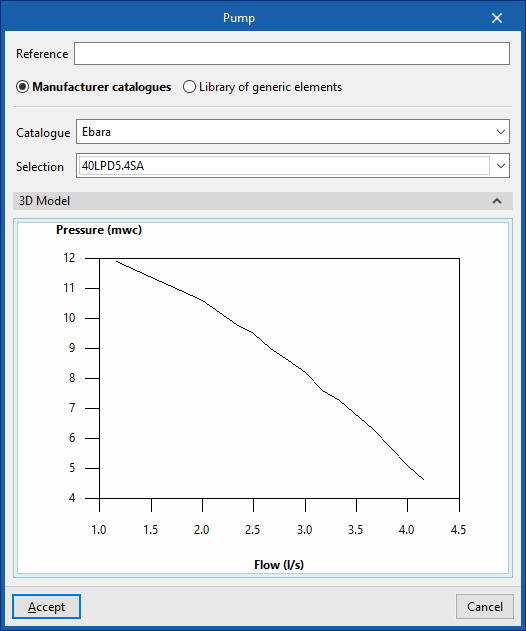
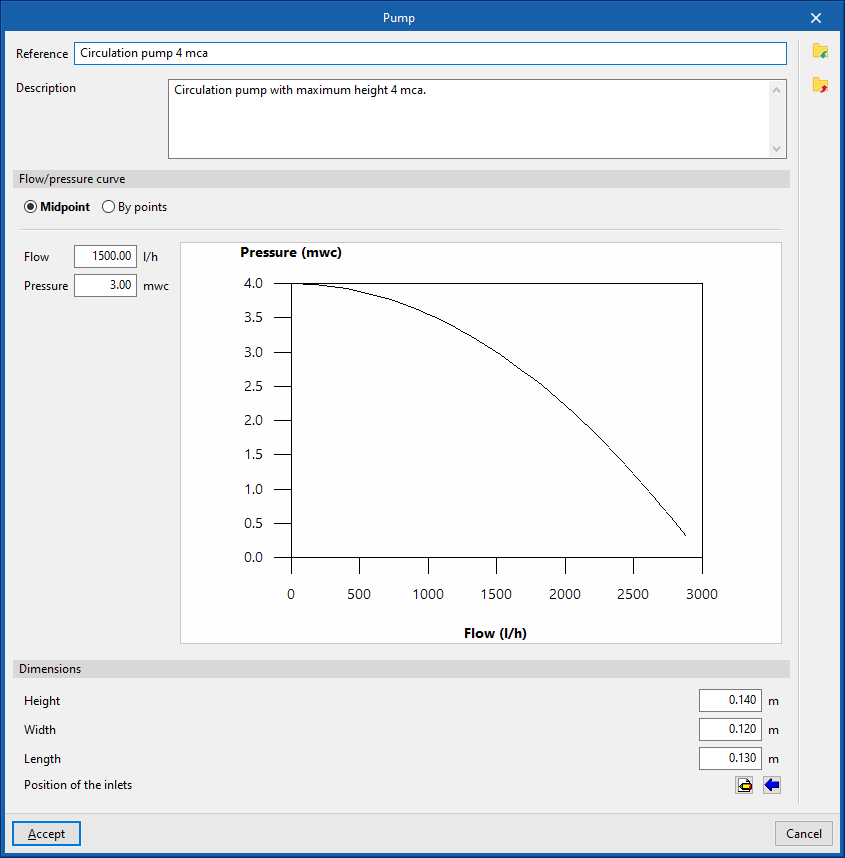
Pump
Inserts circulation pumps.
When entering a pump, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Selection
The program selects and imports data from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right-hand side.
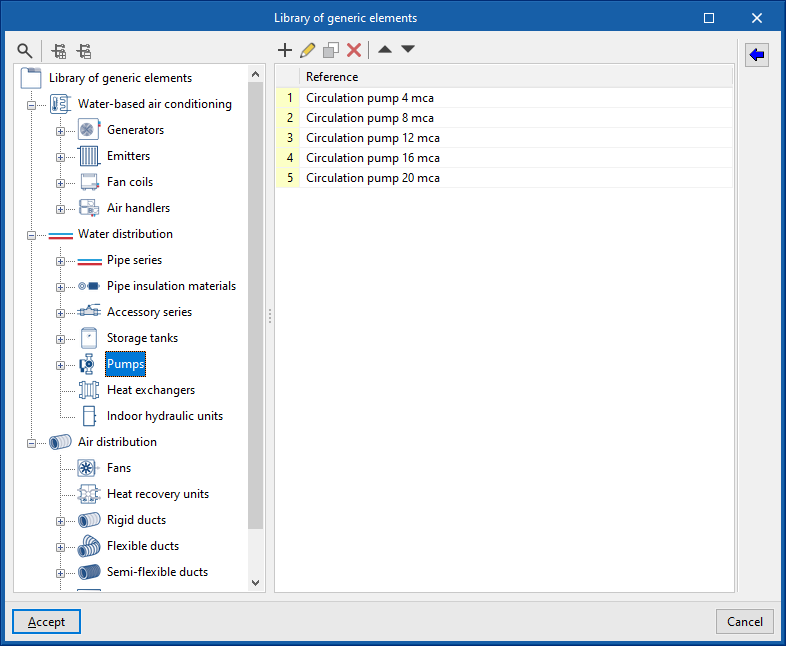
Library of generic pumps
The "Library of generic elements" option, within the "Project" group, is used to create and edit the libraries of available generic fitting types.
The data associated with each type of pump is as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Flow/pressure curve
- Midpoint (Flow; Pressure)
- Dotted (Flow; Pressure)
- Dimensions (Height; Width; Length; Inlet position)
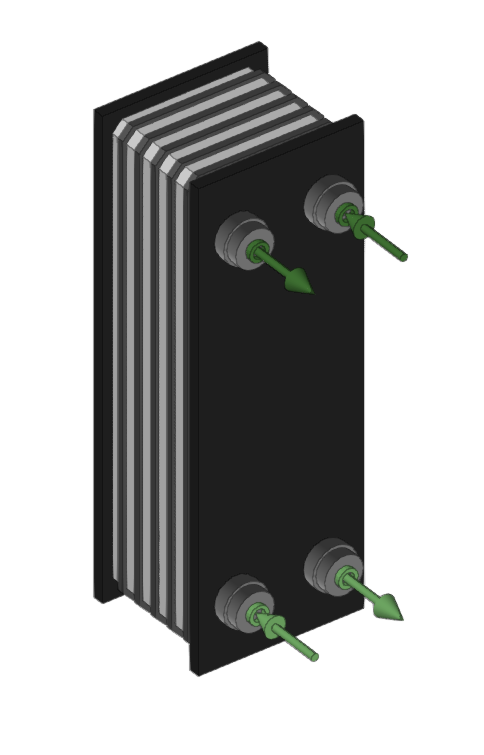
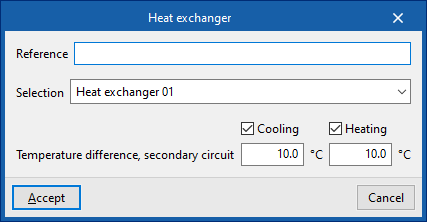
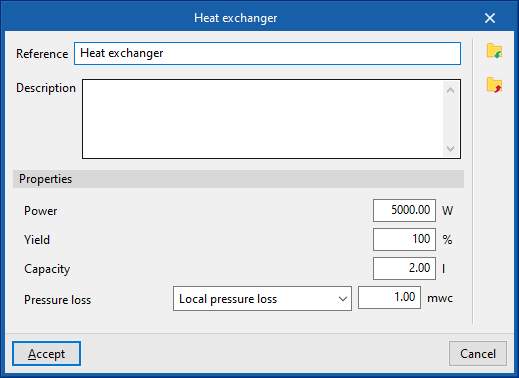
Heat exchanger
Inserts heat exchangers for the water distribution system.
When entering a heat exchanger, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Selection
The program selects and imports data from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right-hand side. - Temperature drop, secondary circuit (Cooling (optional); Heating (optional))
Library of generic heat exchangers
The "Library of generic elements" option, within the "Project" group, is used to create and edit the libraries of available generic fitting types.
The data associated with each type of heat exchanger is as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Characteristics
- Power
- Performance
- Capacity
- Pressure loss (Localised pressure loss / Flow coefficient, Kv / Depending on the flow rate)
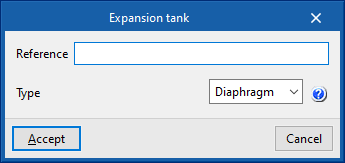
Expansion tank
Inserts expansion tanks.
When entering an expansion tank, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Type
- Open
Tank expansion vessel open to atmosphere. - Closed
Closed tank expansion vessel, containing a volume of air and water in contact with each other.
- Open
- Diaphragm
A diaphragm tank expansion vessel, which has a flexible inner membrane separating air and water.
By clicking on "Calculate", the program collects the minimum and maximum temperature and the volume of fluid in the system from the associated installation and provides the required capacity of the expansion tank according to its type.
Indoor hydraulic unit
Enters indoor hydraulic units.
A hydronic indoor unit is a commercially available unit that brings together all the hydraulic fittings required in domestic aerothermal systems, such as the circulation pump, expansion tank or storage tank, under the same housing.
This means that to use these fittings, only this unit needs to be connected between the air-to-water heat pump and the circuit inside the building.
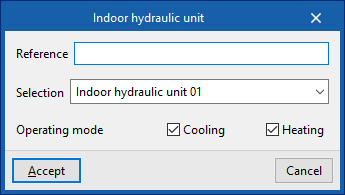
When entering a hydraulic indoor unit, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Selection
The program selects and imports data from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right-hand side. - Operating mode (Cooling (optional); Heating (optional))
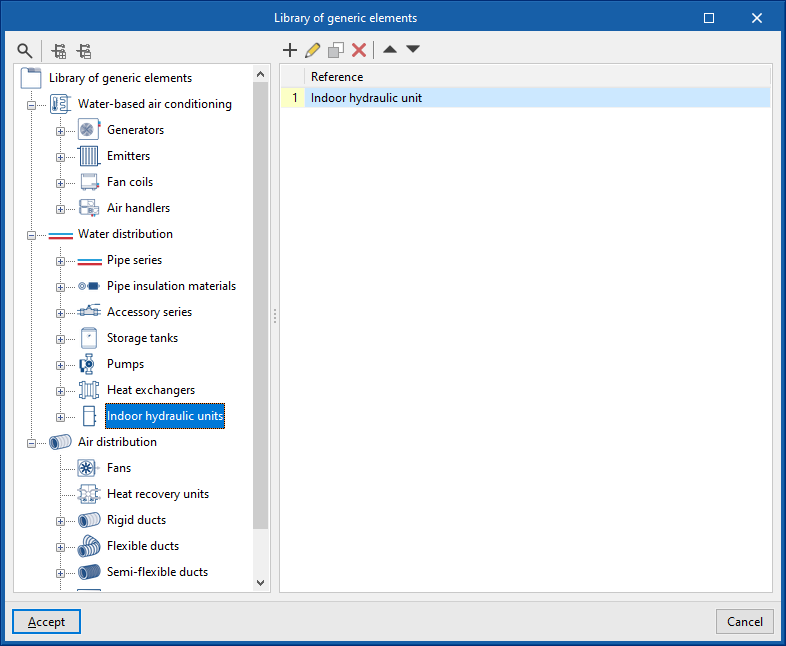
Library of generic hydraulic indoor units
The "Library of generic elements" option, within the "Project" group, is used to create and edit the libraries of available generic fitting types.
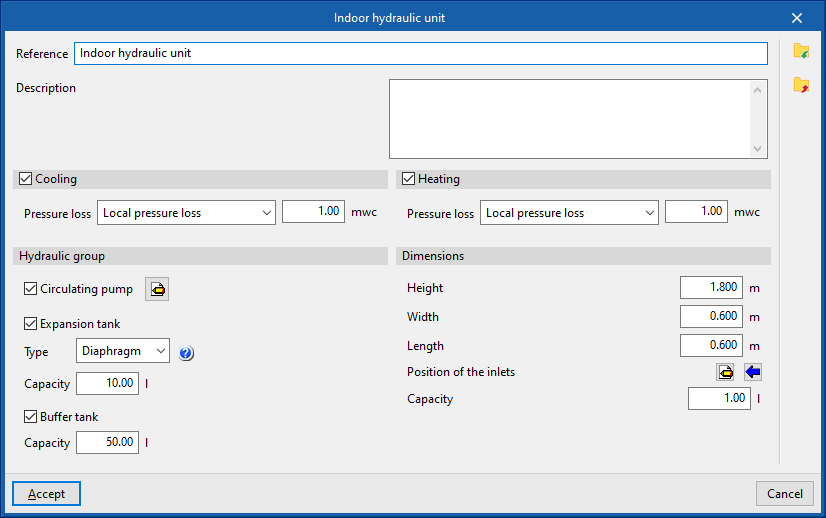
The data associated with each type of hydraulic indoor unit are as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Cooling (optional)
- Pressure drop (Localised pressure loss / Flow coefficient, Kv / Depending on the flow rate)
- Heating (optional)
- Pressure drop (Localised pressure loss / flow coefficient, Kv / Depending on the flow rate)
- Hydraulic unit
- Circulation pump (optional)
- Midpoint (Flow rate; Pressure)
- Point (Flow rate; Pressure)
- Expansion vessel (optional)
- Type (Open / Closed / Diaphragm)
- Capacity
- Inertia Accumulator (optional)
- Capacity
- Circulation pump (optional)
- Dimensions (Height; Width; Length; Position of inlets; Capacity)
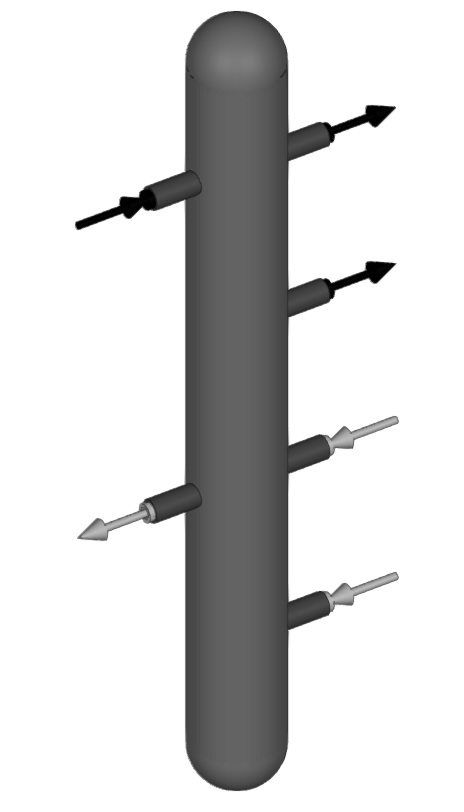
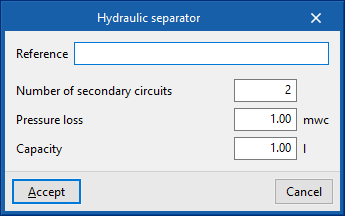
Hydraulic separator
Inserts hydraulic separators. This element allows the installation to be divided into independent circuits. The program calculates the pressure losses in each of these circuits separately.
When entering a hydraulic separator, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Number of secondary circuits
- Pressure loss
- Capacity
Entering pipes (water distribution)
Within the "Installation" tab, in the "Water distribution" group of the main toolbar, the following options are available to enter the pipes of the system:

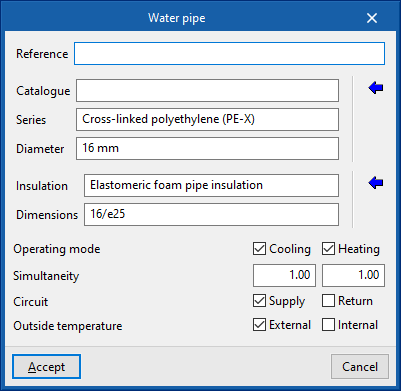
Water pipe
Water pipes can be entered in any direction by drawing them freely in any view of the model.
When entering a pipe, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Pipe selection
- The program selects and imports data from "Manufacturer catalogues" or from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right-hand side.
- Catalogue
- Series
- Diameter
- Selection of pipe insulation
- The program selects and imports data from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right.
- Insulation
- Dimensions
- Design conditions
- Operating mode (Cooling (optional); Heating (optional))
- Simultaneity (Cooling; Heating)
- Circuit (Supply (optional) / Return (optional))
- Outside temperature (Outdoor (optional) / Indoor (optional))
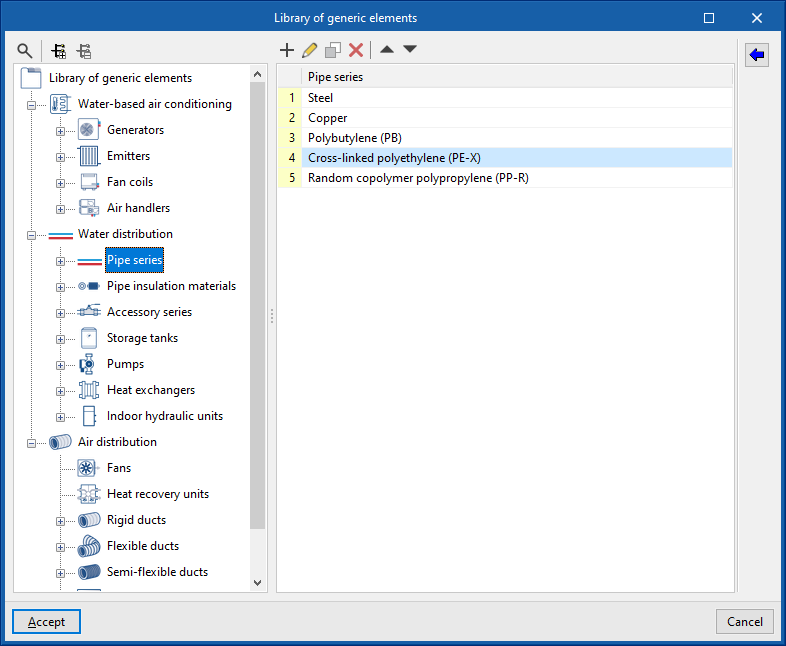
In the "Library of generic elements" option, within the "Project" group, the available generic pipe and insulation libraries can be created and edited.
Pipe library
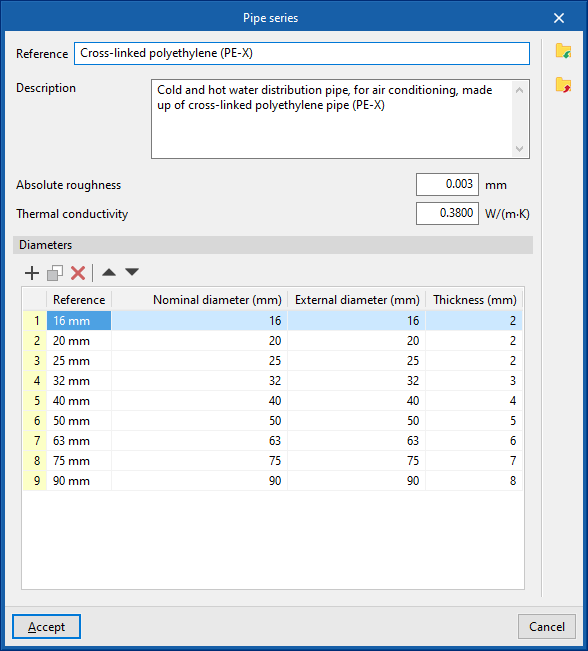
The data associated with each type of pipe is as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Material
- Absolute roughness
- Thermal conductivity
- Diameters (Reference; Nominal diameter; External diameter; Thickness)
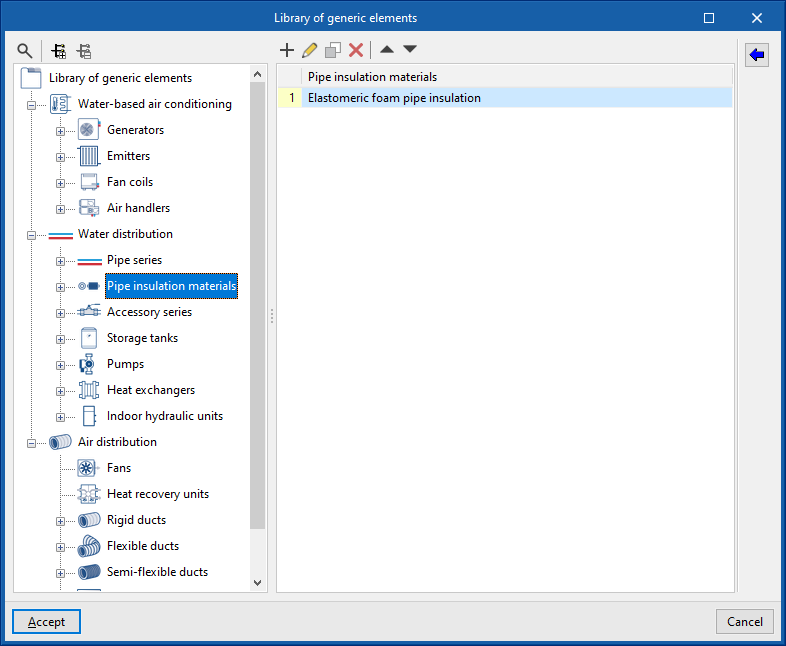
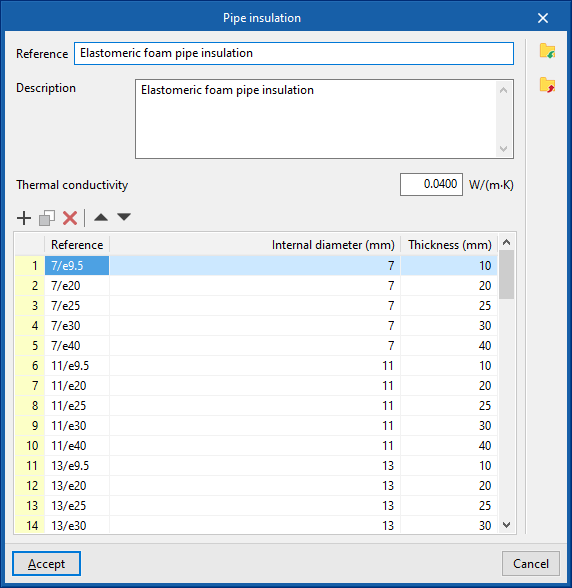
Insulation library
The data associated with each type of insulation is as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Material
- Thermal conductivity
- Diameters (Reference; Internal diameter; Thickness)
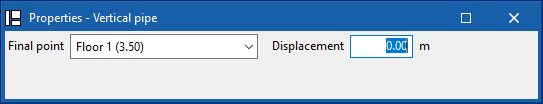
Vertical pipe
Inserts vertical pipes using the elevation of the plan views of the model as a support.
By clicking on this option, the program defines the characteristics of the pipe by means of an editing panel identical to the one that appears when using the "Pipe" option.
Then, in the "Properties - Vertical pipe" dialogue box, the level associated with the "End point" of the pipe is defined, together with a "Displacement" above the indicated level, expressed in positive or negative values. The starting point of the pipe is marked with the cursor on a point in the work area.
The pipe is then laid out from the working plane elevation of the active view, where the starting point has been marked, to the elevation defined by the selected level and the offset indicated in the dialogue box.
Pipe based on the existing pipe
This option inserts new pipes by taking the data from an existing pipe in the model.
To do this, first select the pipe from which the information will be extracted and accept the editing panel. The new pipe is then inserted into the model at the desired position.
Entering direct expansion systems (multisplit and split 1x1)
Within the "Installation" tab, in the "Multisplit" and "Split" menus of the "Direct expansion" group in the main toolbar, there are options for defining and entering the elements of the multisplit and split 1x1 direct expansion systems covered by the program:

- Multisplit
- Outdoor multi-split unit
- Indoor unit, wall-mounted
- Indoor unit, with distribution using ducts
- Split
- Outdoor 1x1 unit
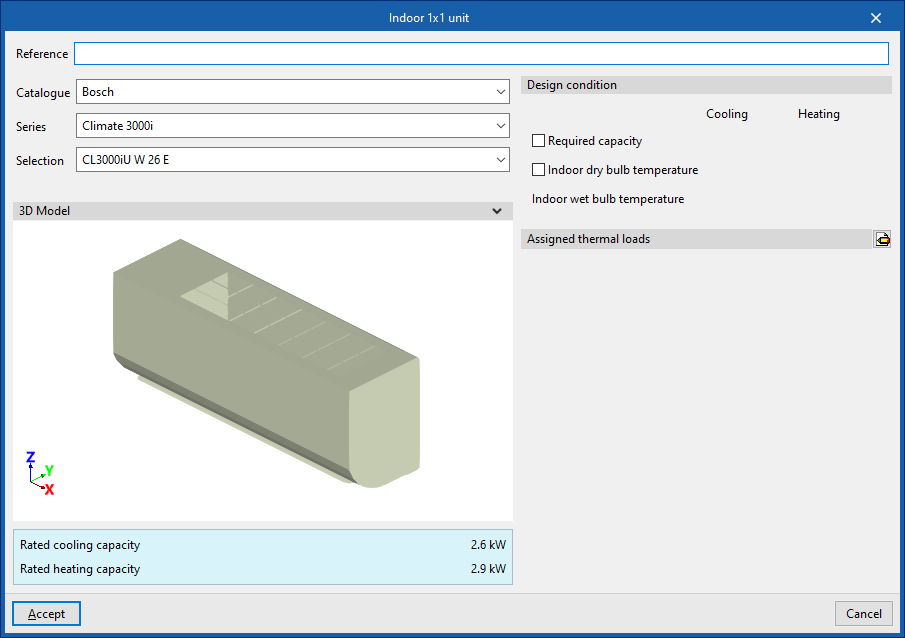
- Indoor 1x1 unit
The following systems are available:
Direct expansion multi-split system
This system consists of an outdoor unit connected to several indoor units.
Outdoor unit (multisplit)
The option to enter the outdoor unit of a multi-split direct expansion system is as follows:
- Multi-split outdoor unit
When entering an outdoor unit for a multi-split system, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Catalogue / Series / Selection
Selects and imports data from manufacturer catalogues previously uploaded using the "Catalogue management" option. - 3D model
3D view of the selected unit. - Nominal heating capacity / Nominal cooling capacity / Connected indoor units / Refrigerant
Nominal power ratings, connected indoor units, and refrigerant type of the selected unit.
Indoor units (multisplit)
The options for installing indoor units in multi-split systems are as follows:
- Multi-split indoor unit, wall-mounted
- Multi-split indoor unit, with duct distribution
When entering an indoor unit for a multi-split system, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Catalogue / Series / Selection
Selects and imports data from previously loaded manufacturer catalogues using the"Catalogue management" option. - 3D model
3D view of the selected unit. - Nominal heating capacity / Nominal cooling capacity / Capacity index
Properties of the selected unit. - Design conditions
- Power required (Cooling/Heating) (optional)
- Indoor dry bulb temperature (Cooling/Heating) (optional)
- Indoor wet bulb temperature (Cooling) (optional)
- Assigned thermal loads
Defines the following percentages on the values of the thermal loads for heating and/or cooling of the project. The program automatically assigns loads according to the layout of the terminal elements in the model.- % Assigned heating capacity
- % Assigned total cooling capacity
- % Assigned sensible cooling capacity
- % Required heating load
- % Required total cooling load
- % Required sensible cooling load
Direct expansion split system 1x1
This system consists of an outdoor unit and an indoor unit.
The options for installing the outdoor unit and indoor unit of a 1x1 direct expansion split system are as follows:
- 1x1 outdoor unit
- 1x1 indoor unit
When entering an outdoor unit for a 1x1 split system, only the following parameter needs to be specified:
- Reference
When entering an indoor unit for a 1x1 split system, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Catalogue / Series / Selection
Selects and imports data from previously loaded manufacturer catalogues using the"Catalogue management" option. - 3D model
3D view of the selected unit. - Nominal heating capacity / Nominal cooling capacity
Properties of the selected unit. - Design conditions
- Power required (Cooling/Heating) (optional)
- Indoor dry bulb temperature (Cooling/Heating) (optional)
- Indoor wet bulb temperature (Cooling) (optional)
- Assigned thermal loads
Defines the following percentages on the values of the thermal loads for heating and/or cooling of the project. The program automatically assigns loads according to the layout of the terminal elements in the model.- % Assigned heating capacity
- % Assigned total cooling capacity
- % Assigned sensible cooling capacity
- % Required heating load
- % Required total cooling load
- % Required sensible cooling load
Entering equipment (air distribution)
Within the "Installation" tab, in the "Equipment" menu of the "Air distribution" group in the main toolbar, the following elements can be defined and entered:

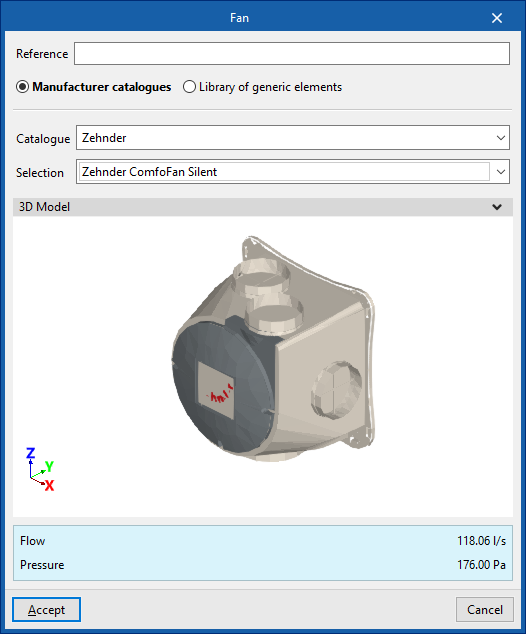
Fan
Enters fans.
When entering a fan, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Catalogue / Selection
The program can select and import data from "Manufacturer catalogues" or from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right-hand side.
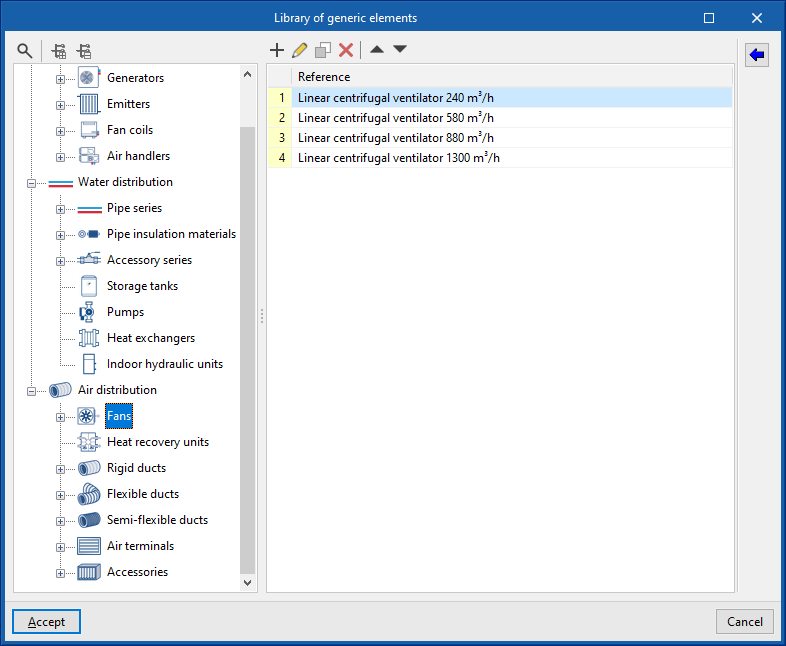
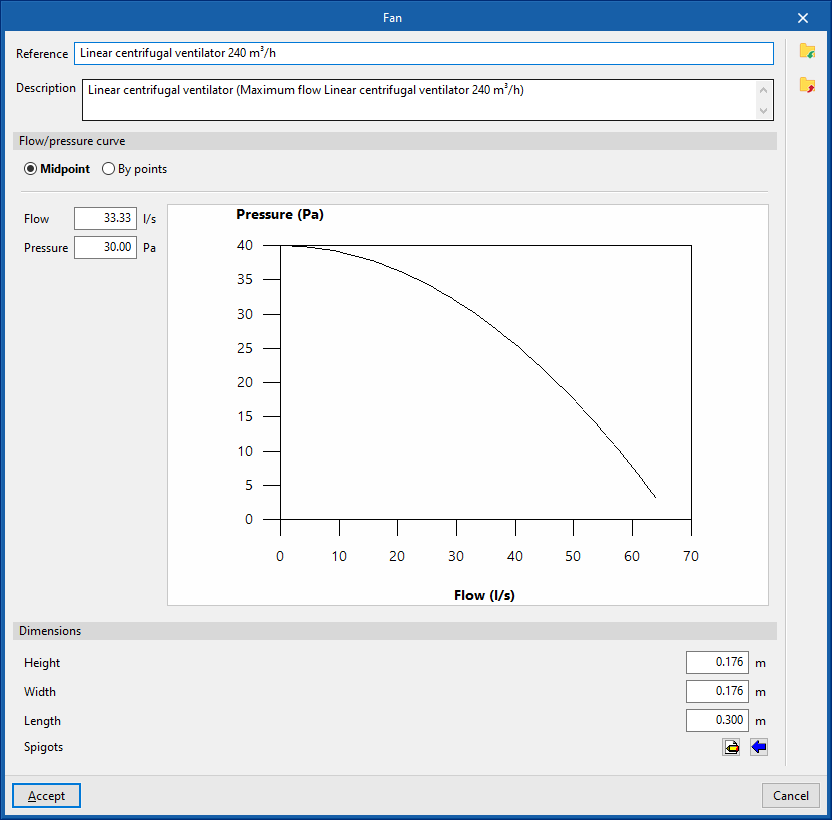
Library of generic fans
In the "Library of generic elements" option, within the "Project" group, the available library of generic fans can be created and edited.
The data associated with each type of fan is as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Flow/pressure curve
- Midpoint (Flow; Pressure)
- By points (Flow; Pressure)
- Dimensions
- Height
- Width
- Length
- Spigots
- Connections
- Installation
- Type of air flow (Outside air (ODA) / Supply air (SUP) / Exhaust air (ETA) / Discharge air (EHA) / Depending on the type of installation)
- The spigot can remain disconnected (optional)
- Geometry
- Type (Rectangular / Circular)
- Width x Height / Diameter
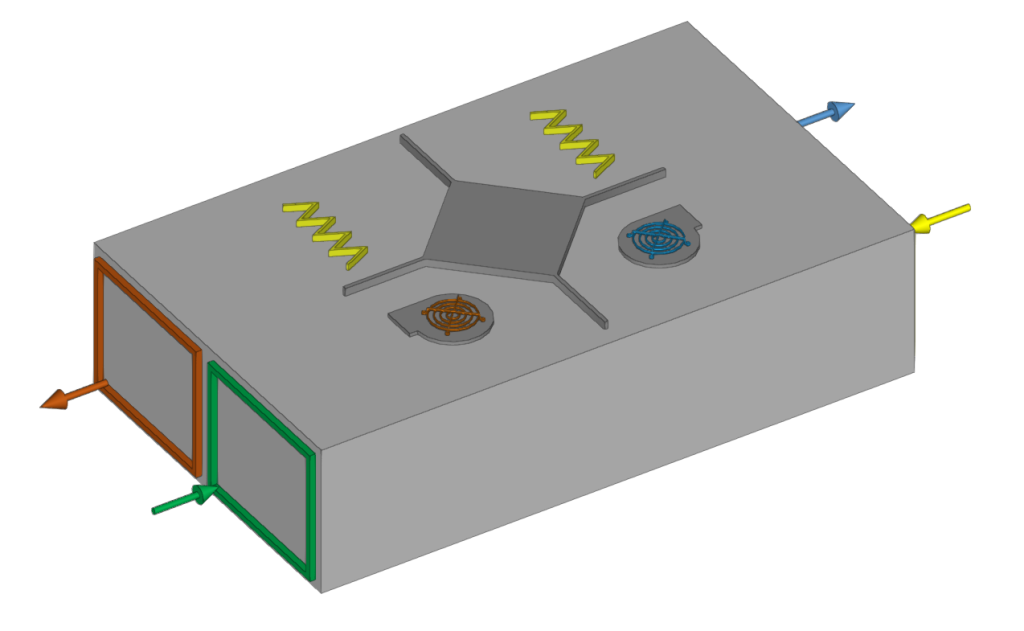
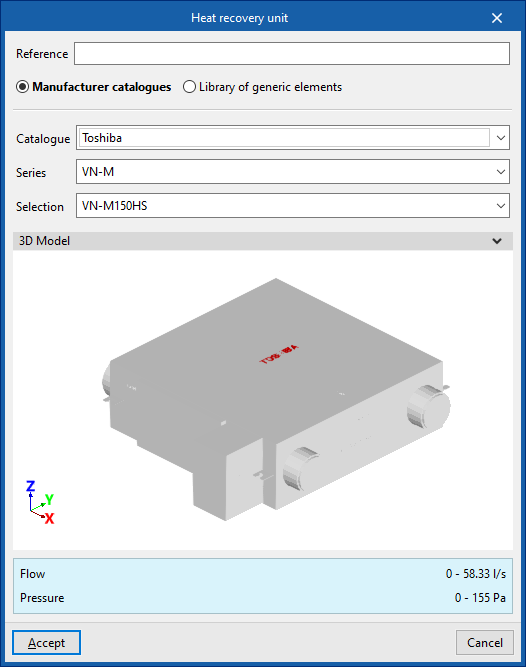
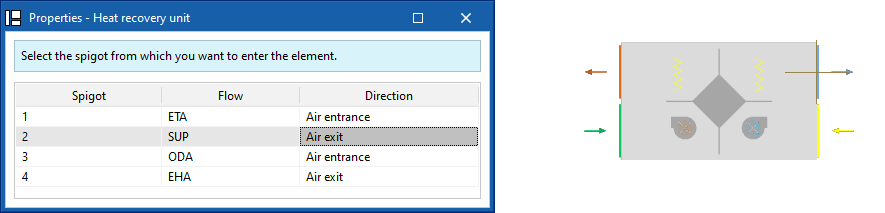
Heat recovery unit
Enters heat recovery units.
When entering a heat recovery unit, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Catalogue / Selection
The program can select and import data from "Manufacturer catalogues" or from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right-hand side.
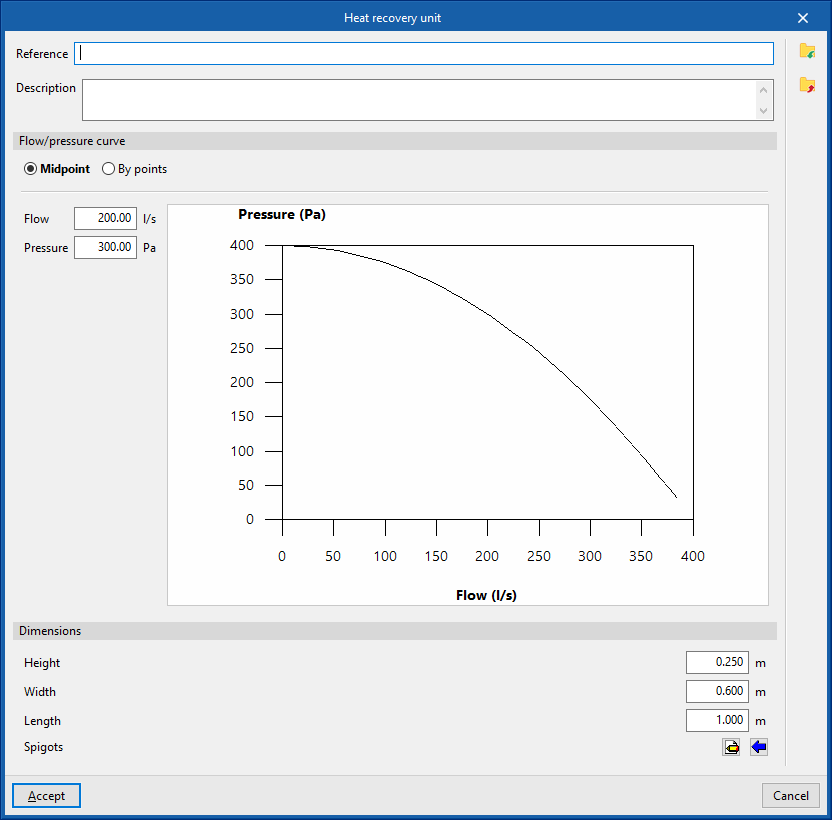
Library of generic heat recovery units
In the "Library of generic elements" option, within the "Project" group, the available library of generic heat recovery units can be created and edited.
The data associated with each type of heat recovery unit are as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Flow/pressure curve
- Midpoint (Flow; Pressure)
- By points (Flow; Pressure)
- Dimensions
- Height
- Width
- Length
- Spigots
- Connections
- Installation
- Type of air flow (Outside air (ODA) / Supply air (SUP) / Exhaust air (ETA) / Discharge air (EHA) / Depending on the type of installation)
- The spigot can remain disconnected (optional)
- Geometry
- Type (Rectangular / Circular)
- Width x Height / Diameter
Fire damper
Inserts fire dampers.
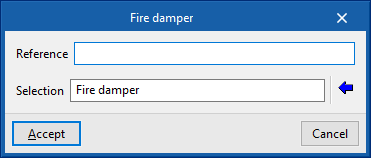
When entering a fire damper, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Selection
The program can select and import data from "Manufacturer catalogues" or from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right-hand side.
Library of generic fire damper
In the "Library of generic elements" option, within the "Project" group, the available library of generic fire dampers can be created and edited.
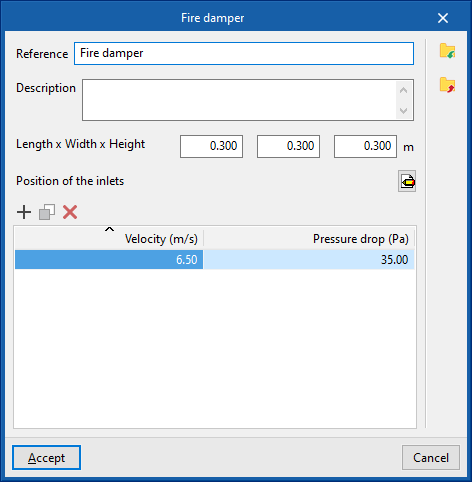
The data associated with each type of fire damper is as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Dimensions
- Length x Width x Height
- Position of the inlets
- Sockets
- Type (Rectangular / Circular)
- Width x Height / Diameter
- Sockets
- Design values, depending on the flow
- Velocity; Pressure loss
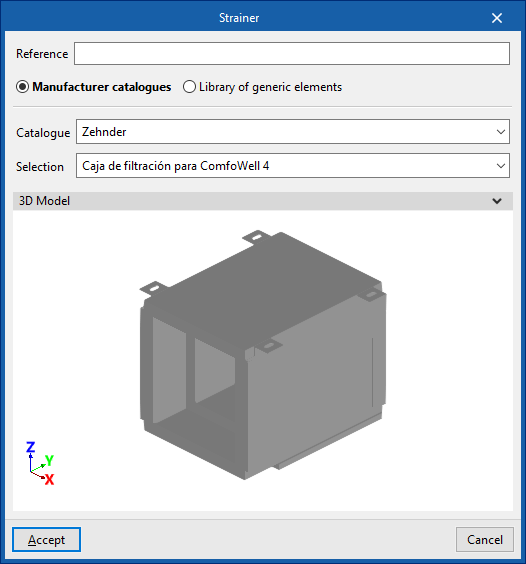
Strainer
Enters strainers.
When entering a strainer, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Catalogue / Selection
The program can select and import data from "Manufacturer catalogues" or from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right-hand side.
Library of generic strainers
In the "Library of generic elements" option, within the "Project" group, the available library of generic strainers can be created and edited.
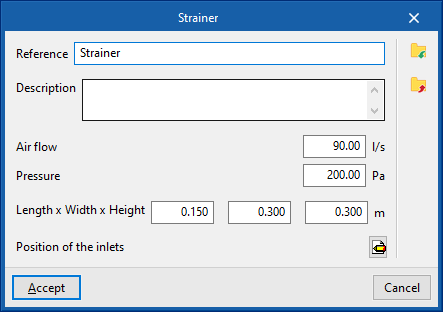
The data associated with each type of filter is as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Air flow rate
- Pressure
- Dimensions
- Length x Width x Height
- Position of inlets
- Inlets
- Type (Rectangular / Circular)
- Width x Height / Diameter
- Inlets
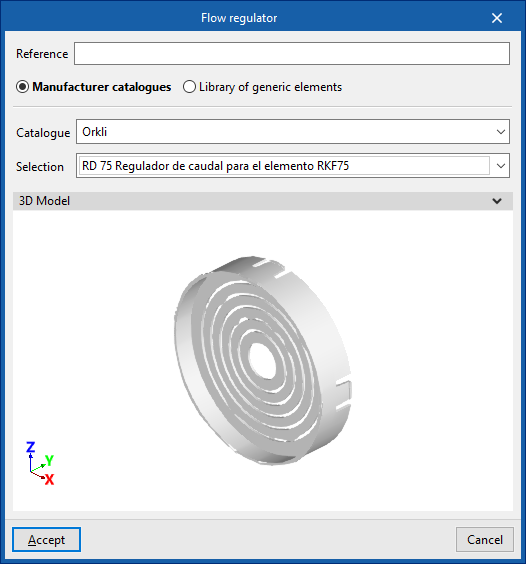
Flow regulators
Enters flow regulators.
When entering a flow regulator, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Catalogue / Selection
The program can select and import data from "Manufacturer catalogues" or from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right-hand side.
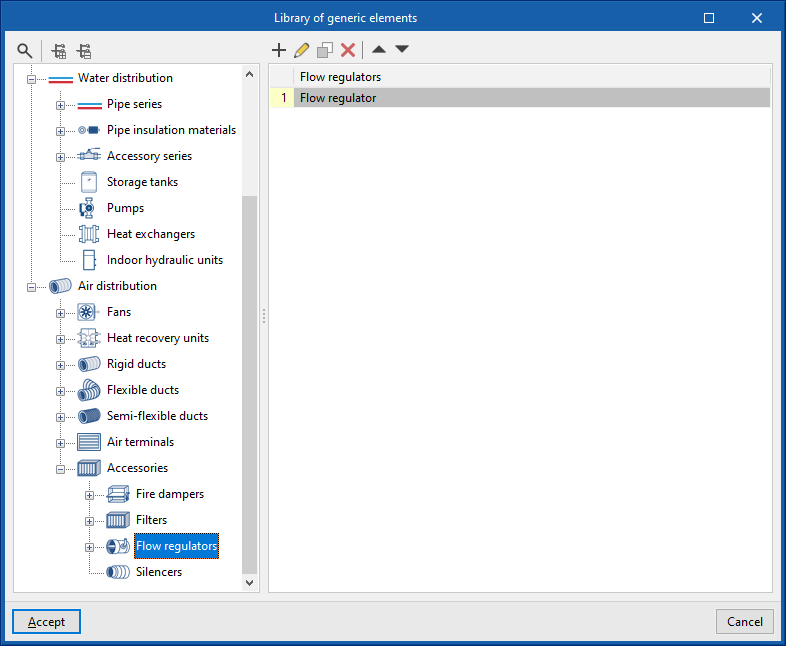
Library of generic flow regulators
In the "Library of generic elements" option, within the "Project" group, the available library of generic flow regulators can be created and edited.
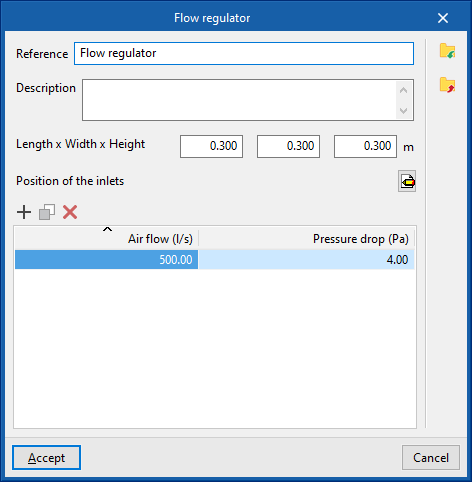
The data associated with each type of flow regulator is as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Dimensions
- Length x Width x Height (m)
- Position of inlets
- Inlets
- Type (Rectangular / Circular)
- Width x Height / Diameter
- Inlets
- Design values, depending on the flow
- Air flow rate; Pressure loss
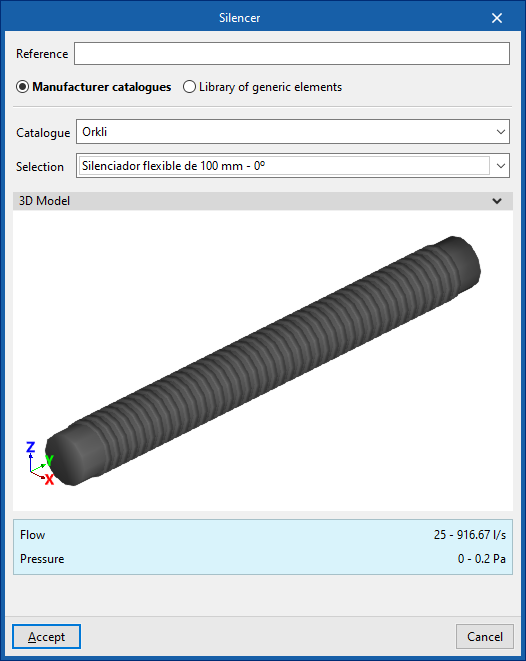
Silencer
Enters silencers.
When entering a silencer, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Catalogue / Selection
The program can select and import data from "Manufacturer catalogues" or from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right-hand side.
Library of generic silencers
In the "Library of generic elements" option, within the "Project" group, the available library of generic silencers can be created and edited.
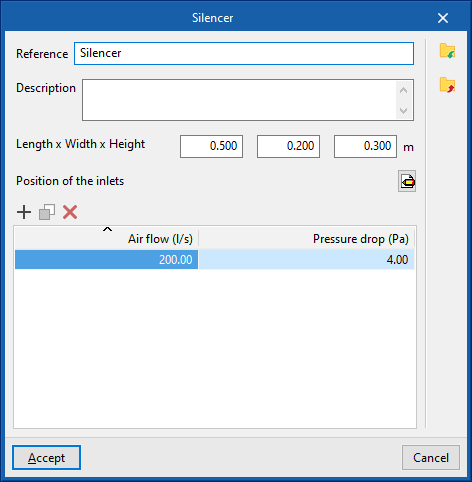
The data associated with each type of silencer is as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Dimensions
- Length x Width x Height (m)
- Position of inlets
- Inlets
- Type (Rectangular / Circular)
- Width x Height / Diameter
- Inlets
- Design values, depending on the flow
- Air flow rate; Pressure loss
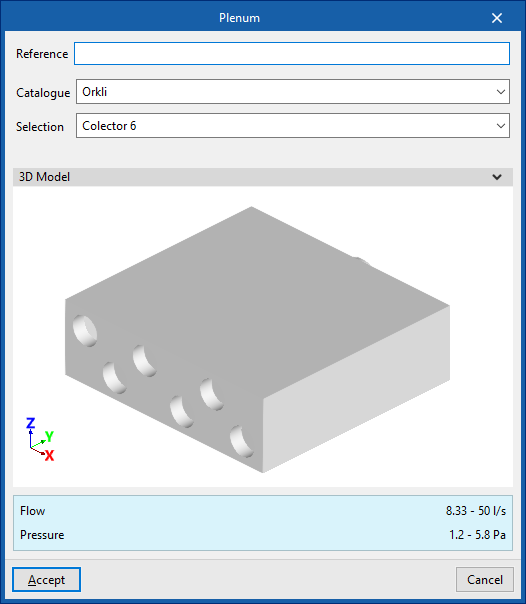
Plenum
Inserts plenums in duct systems.
When entering a plenum, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Catalogue / Selection
Selects and imports data from previously loaded manufacturer's catalogues using the "Catalogue management" option. - 3D Model
- Three-dimensional visualisation of the selected equipment.
Entering ducts (air distribution)
Within the "Installation" tab, in the "Ducts" menu of the "Air distribution" group in the main toolbar, there are options for entering the air duct spans in the installation:

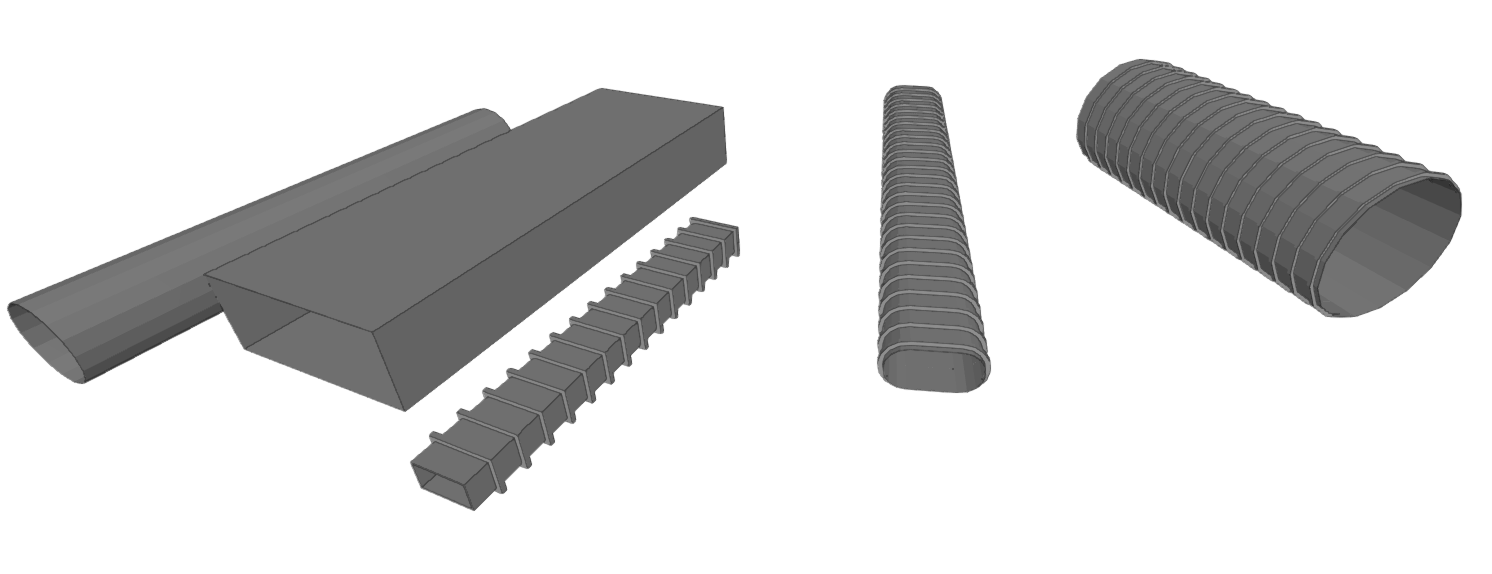
- Rigid conduit
- Semi-flexible conduit
- Flexible duct
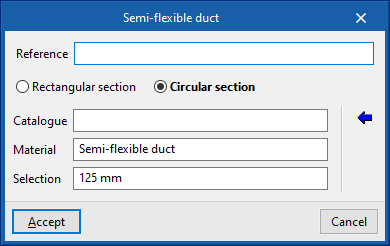
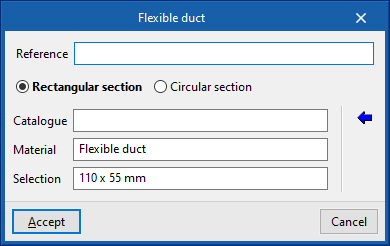
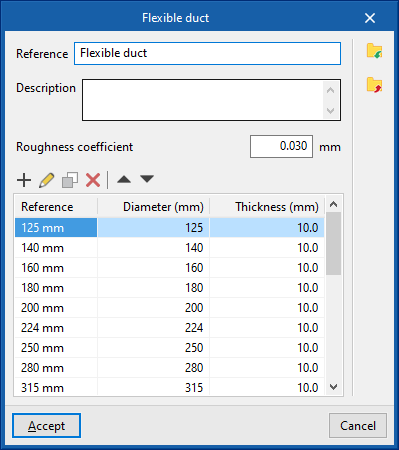
Rigid duct / Semi-flexible duct / Flexible duct
These options allow the insertion of rigid, semi-flexible and flexible air ducts, respectively.
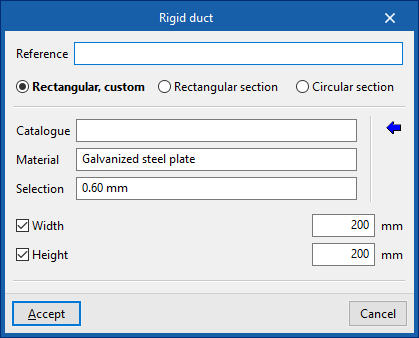
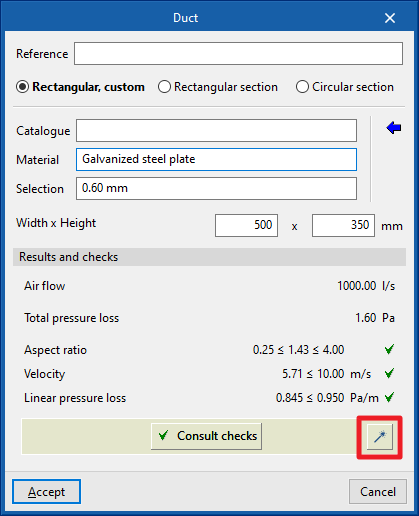
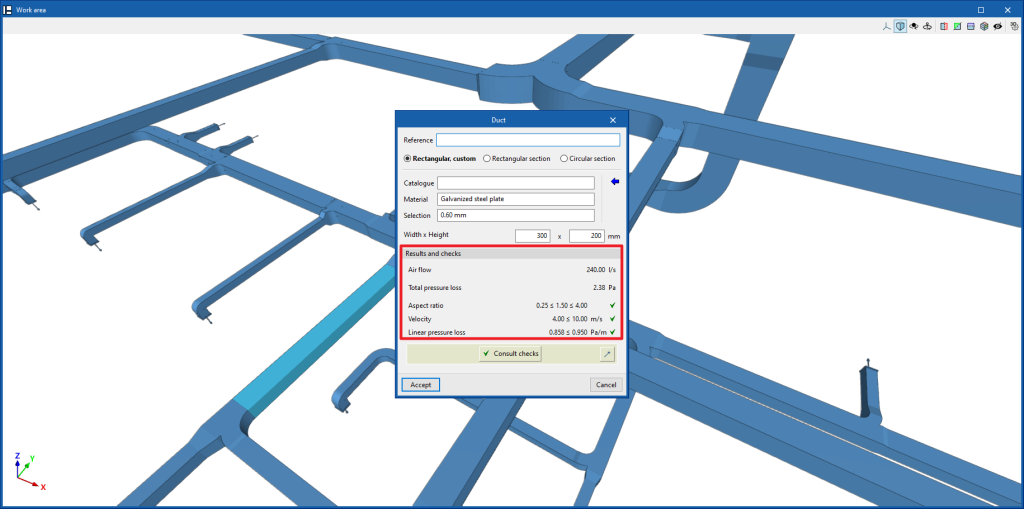
When entering a duct, the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Type of duct
- Rectangular, custom (only for “Rigid ducts”) / Rectangular section / Circular section
- Catalogue selection
- Catalogue
- Material
- Selection
- Duct dimensions
- Width / Height (only for “Rectangular, custom”)
By activating the "Width" and/or "Height" checkboxes, the dimensions of the air ducts can be forced so that they are not modified by the program during the analysis.
- Width / Height (only for “Rectangular, custom”)
Data can be selected and imported from the "Manufacturer catalogues" or the "Library of generic elements" using the assistant available on the right-hand side of the program.
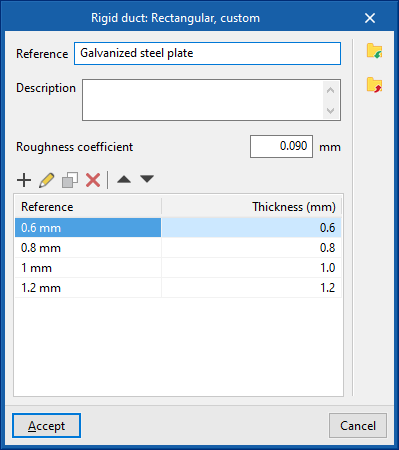
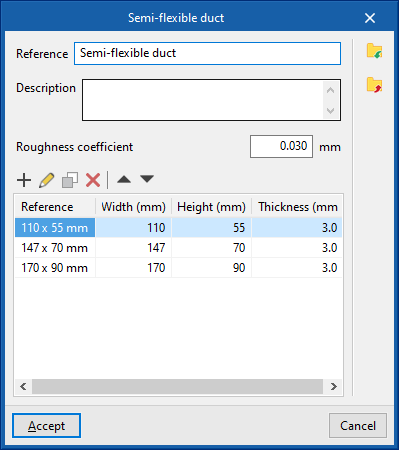
Library of generic elements
In the "Library of generic elements" option, in the "Project" group, generic duct libraries can be created and edited.
The data associated with each type of duct, regardless of whether they are rigid, semi-flexible or flexible, is as follows:
- Reference
- Description
- Roughness coefficient
- Rectangular ducts, custom
- Reference
- Thickness
- Rectangular ducts
- Reference
- Height
- Width
- Thickness
- Circular ducts
- Reference
- Diameter
- Thickness
Duct ends must be connected to other ducts, or ventilation unit or air terminal must be incorporated into the ducts.
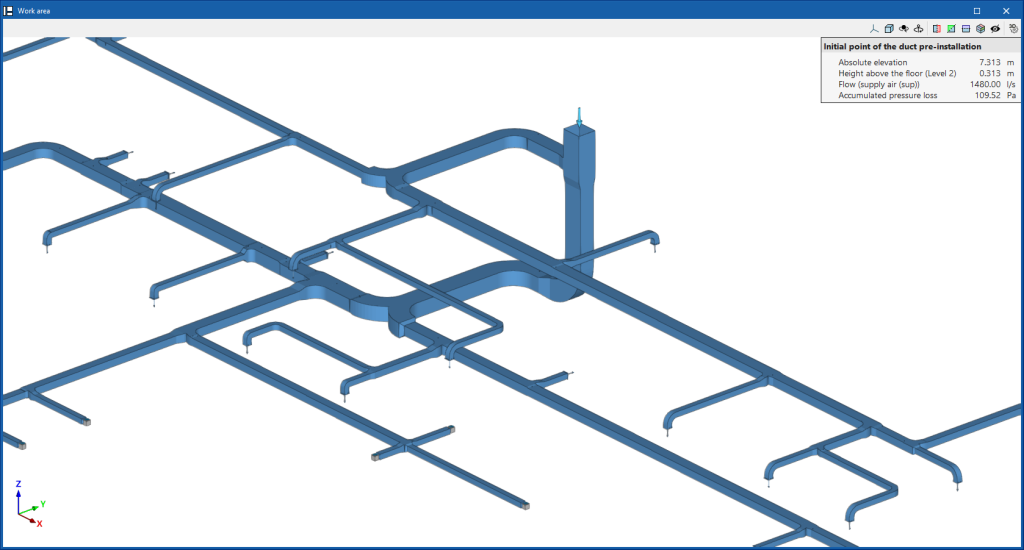
If the entire ductwork system has terminal elements and is closed at all ends except one, a "Initial point of the duct pre-installation" must be provided at that end (available in the "Equipment" menu of the "Air distribution" group) so that the program interprets this situation and does not require the addition of a supply air machine.
In the design process, the program analyses the layout and connections of the installation. It categorises the ducts as "Supply air (SUP)" (blue), "Discharge air (EHA)" (red), "Exhaust air (ETA)" (yellow) or "Outdoor air (ODA)" (green) and displays them with the colour that determines their category. This category can also be seen in the information text that appears when hovering over each duct.
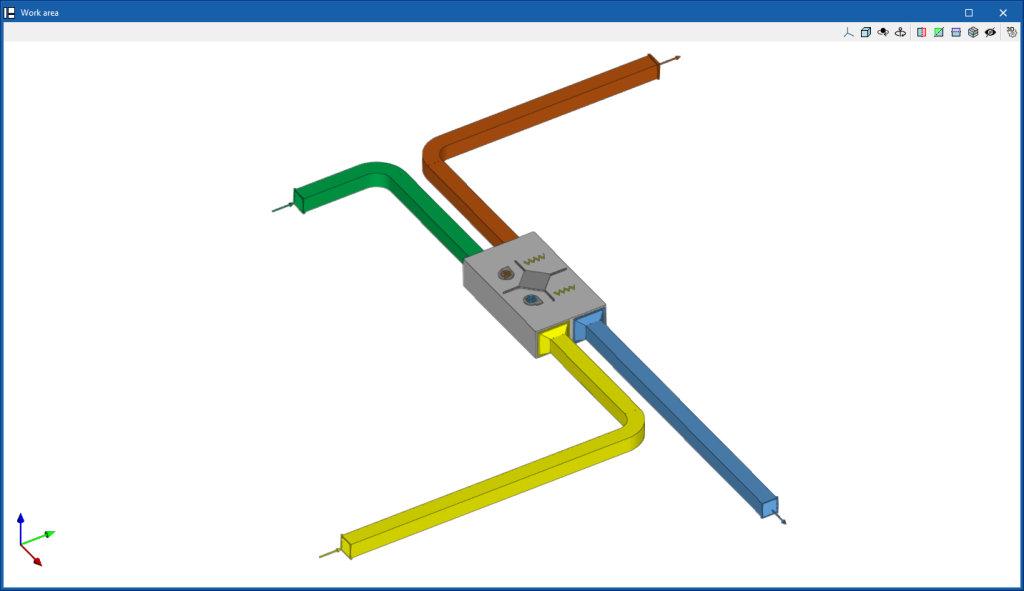
Inserting and generating fittings (air distribution)
In the "Installation" tab, in the "Air distribution" group of the main toolbar, there is a "Fittings" menu:

The options in this menu allow users to enter air duct connections by hand or to generate them automatically. The program includes the ASHRAE catalogue of elbows, transitions and branches as well as manufacturer catalogue fittings. These options are:
Generate fittings
Automatically generates the fittings in the air ducts. In doing so, the length of the duct sections reaching each fitting is adjusted.
For this purpose, the most appropriate type of fitting, whether elbows, transitions or branches, is sought and arranged according to the situation.
The generation of fittings is also integrated in the process that launches the "Design" option.
Delete fitting
This deletes the fittings. In doing so, the duct sections are lengthened so that they are not disconnected, thus taking the place of each eliminated connection.
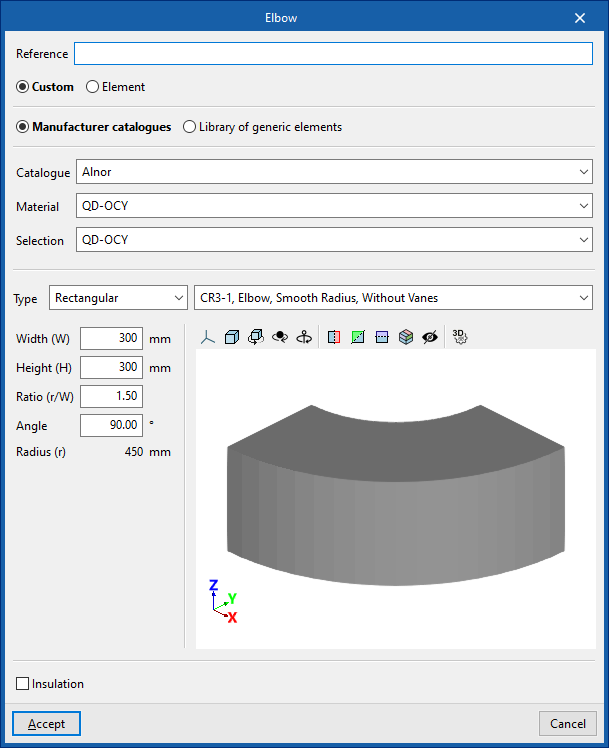
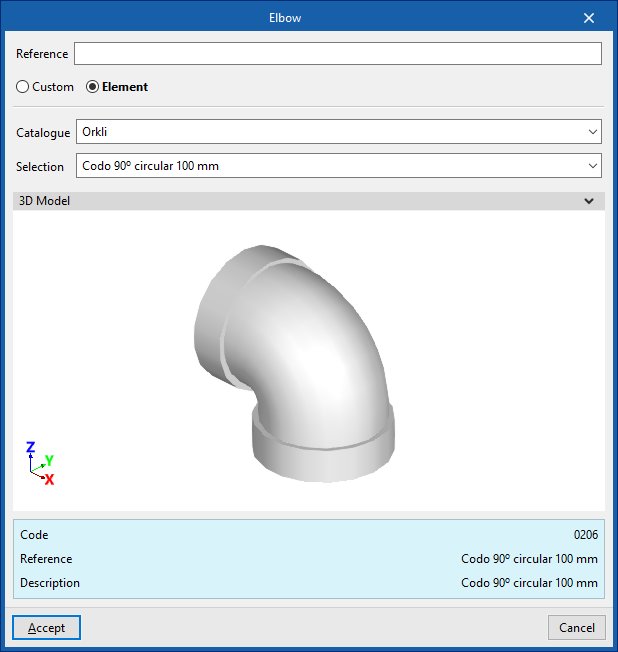
Elbow
Enters an elbow.
When entering an elbow the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Generic
Defines a generic connection.- Catalogue / Material / Selection
Selects and imports duct data from "Manufacturer catalogues" or from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right. - Type
- Rectangular
- Circular
- Catalogue / Material / Selection
- Manufacturer catalogues
Selects and imports fittings from manufacturer catalogues using the wizard on the right.- Catalogue / Selection
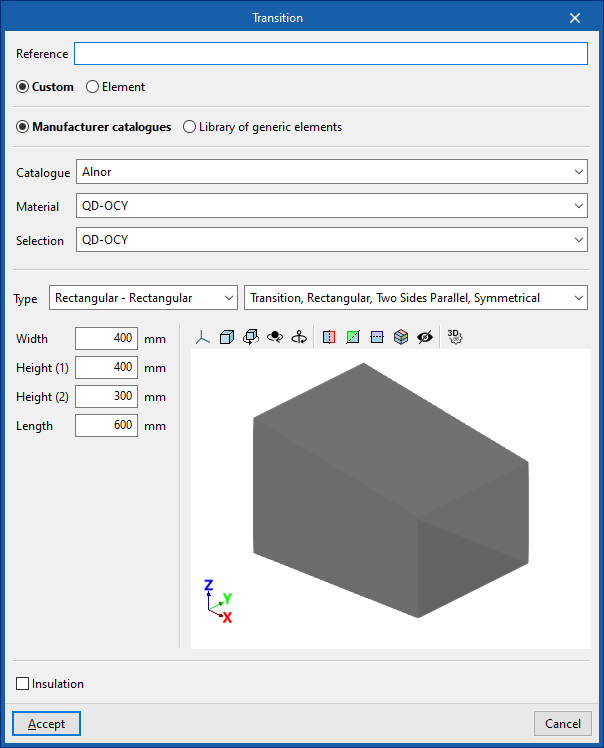
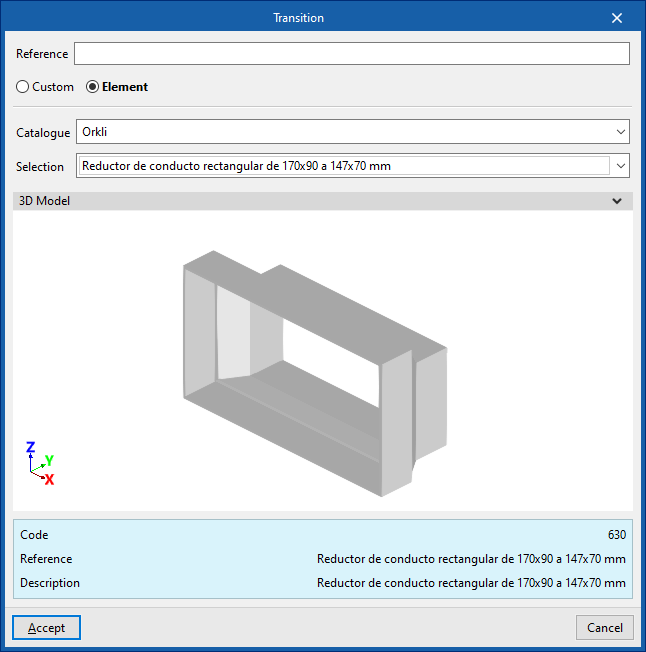
Transition
Enters a transition.
When entering a transition the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Generic
Defines a generic connection.- Catalogue / Material / Selection
Selects and imports duct data from "Manufacturer catalogues" or from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right. - Type
- Rectangular - Rectangular
- Rectangular - Circular
- Circular - Rectangular
- Circular - Circular
- Catalogue / Material / Selection
- Manufacturer catalogues
Selects and imports fittings from manufacturer catalogues using the wizard on the right.- Catalogue / Selection
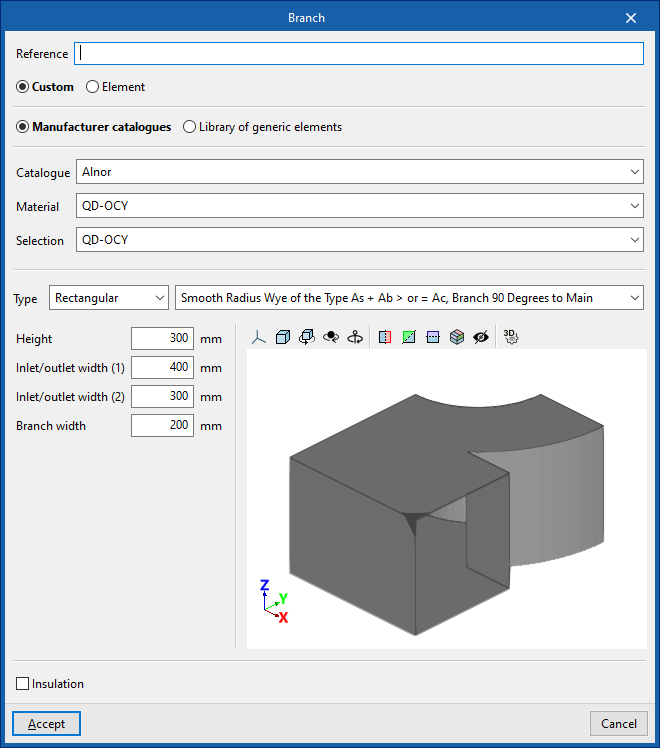
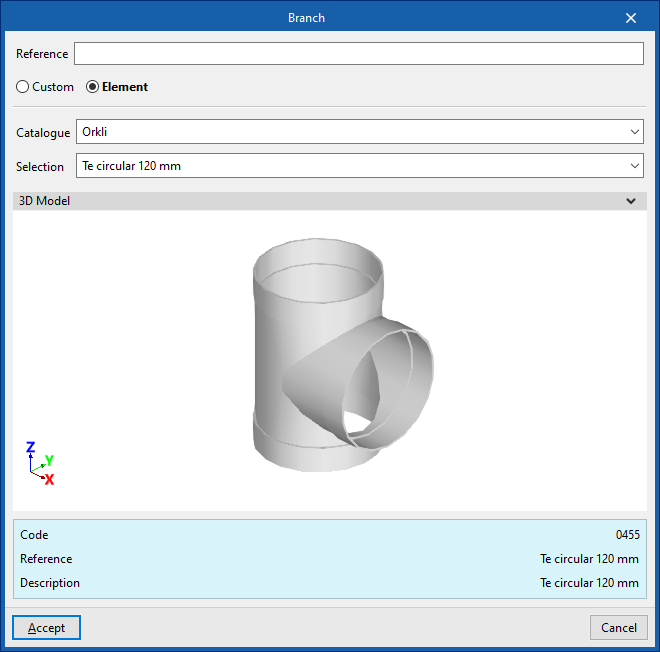
Branch
Enters a branch.
When entering a branch the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Generic
- Defines a generic connection.
- Catalogue / Material / Selection
Selects and imports duct data from "Manufacturer catalogues" or from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right. - Type
- Rectangular
- Circular
- Catalogue / Material / Selection
- Manufacturer catalogues
Selects and imports fittings from manufacturer catalogues using the wizard on the right.- Catalogue / Selection
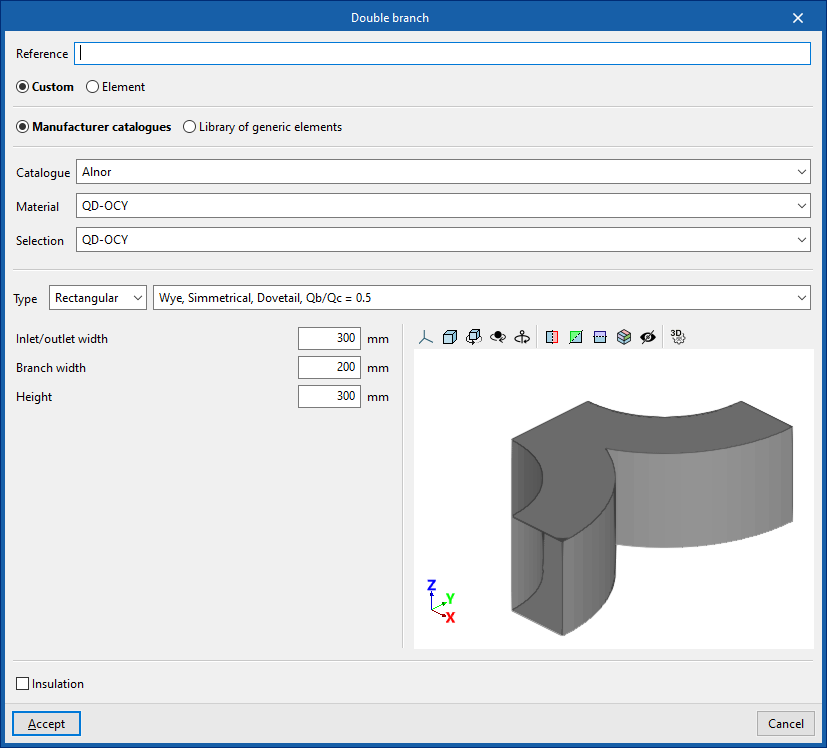
Double branch
Enters a double branch.
When entering a branch the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Generic
- Defines a generic connection.
- Catalogue / Material / Selection
Selects and imports duct data from "Manufacturer catalogues" or from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right. - Type
- Rectangular
- Circular
- Catalogue / Material / Selection
- Manufacturer catalogues
Selects and imports fittings from manufacturer catalogues using the wizard on the right.- Catalogue / Selection
Triple branch
Enters a triple branch.
When entering a branch the following parameters must be specified:
- Reference
- Generic
Defines a generic connection.- Catalogue / Material / Selection
Selects and imports duct data from "Manufacturer catalogues" or from the "Library of generic elements" using the wizard on the right. - Type
- Rectangular
- Circular
- Catalogue / Material / Selection
- Manufacturer catalogues
Selects and imports fittings from manufacturer catalogues using the wizard on the right.- Catalogue / Selection
Editing tools
In the "Edit" group of the main toolbar, under the "Installation" tab, there are several tools for editing the installation:

The tool area of this group allows the following operations to be performed:
| Edit | Edit the parametric properties of the element selected in the model. | |
| Delete | Delete a previously entered element. | |
| Modify height position | Modify the height position of an element by specifying a relative displacement or absolute elevation. | |
| Move | Move an element or an element’s node. | |
| Move a group of elements | Move a group of elements. | |
| Measure length | Measure lengths between defined points on the model. If a closed contour is selected, it also indicates the area. | |
| Copy onto another floor plan | Create a copy of the selected elements in the desired floor plans. This feature is only available on floor plans. | |
| Rotate | Rotate an element about the "x", "y" or "z" axis. | |
| Rotate a group of elements | Rotate a group of elements. | |
| Copy | Create a copy of one or more elements. | |
| Assign | Assign the parametric properties of the selected element to other elements. | |
| Symmetry (copy) | Copy a selection of elements with symmetry with respect to a vertical plane defined by two points. | |
| Symmetry (move) | Move a selection of elements with symmetry about a vertical plane defined by two points. | |
| Divide | Divide pipes or air ducts into several sections. | |
| Extend/trim element | Extend or trim an element (pipe, refrigeration line, or duct) relative to another reference element. The first element acts as the reference, while the second is either extended or trimmed after the option is used. | |
| Extend/Trim to Intersection | Extends or trims two selected elements (pipes, refrigeration lines, or ducts) to their point of intersection. | |
| Join | Joins the selected ducts into a single segment. | |
| Annotations | Inserts a free annotation. |
Importing and assigning thermal loads
The "Thermal loads" group in the main toolbar, under the "Installation" tab, contains the tools for managing the thermal loads of the model:

Importing thermal loads from the BIM mode
CYPEHVAC can import the thermal loads per space calculated in programs such as CYPETHERM LOADS from the BIMserver.center project information.
These loads are represented in the model view by specific symbols, which are visible if the corresponding layer is activated in the "Own elements" panel, located by default on the left-hand side (by accessing "Imported requirements" and "Thermal loads").
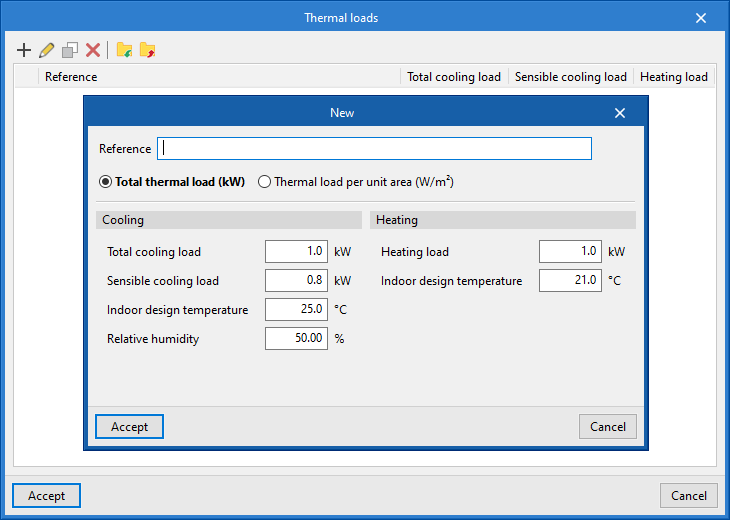
Entering and editing thermal loads
Thermal loads can be entered and edited directly in CYPEHVAC using the table accessible from the "Assign" or "Edit" icons in the "Thermal loads" group in the upper toolbar.
Loads can be defined with a total value or by their value per unit area:
- Total thermal load (kW)
- Thermal load per unit area (W/m2)
- Area
The following parameters can be defined for cooling loads and heating loads:
- Cooling
- Total cooling load
- Sensible cooling load
- Indoor design temperature
- Relative humidity
- Heating
- Heating load
- Indoor design temperature
Assigning thermal loads
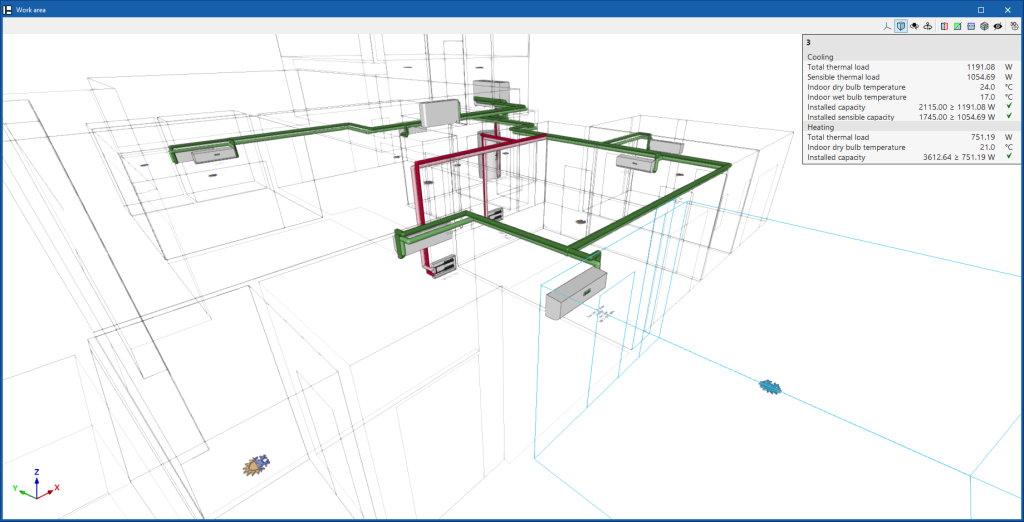
Automatically assigning heat loads
If a thermal load is imported into a space defined in the BIM model and there are one or more terminal elements in that space (e.g. radiators), the program performs the load assignment automatically.
The combined power of these elements will appear as "Installed power" in the thermal load of the space, so the program can check if it is enough to cover the load.
Manually assigning heat loads
If necessary, a percentage of the thermal loads of the spaces (either loads read from the BIM model or loads entered directly into the program) can also be manually assigned to the desired equipment using the "Assign" icon in the "Thermal loads" group in the upper toolbar or by editing each element and using the options in the "Assigned thermal loads" section.
This option is useful if the terminal elements in each space are not entered, e.g. if in a ducted fan coil or air conditioning system the air distribution system is not modelled.
Required capacity
If the "Required capacity" option in the equipment editing panel is activated, the power required to be covered by the equipment is defined directly. This power requirement can be entered in such a way that it is equivalent to the thermal load of the space and can be different from the nominal power of the equipment.
If the "Power requirement" option is deactivated, the system is sized at rated power.
This affects the flow rate of the water pipes leading to the equipment, and also affects the requirements of the generating equipment, such as heat pumps or boilers.
Calculations, checks and designs
In the "Calculation" group of the main toolbar, under the "Installation" tab, there are options for calculating, checking and designing the elements of the model:

Update results
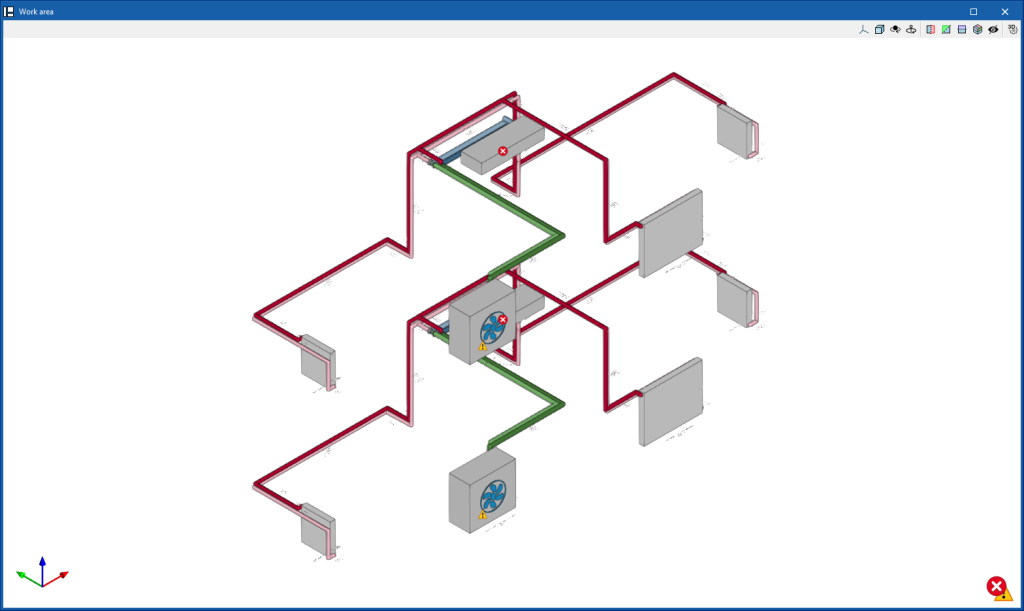
Checks whether the parameters that have been entered to analyse the system are within the allowed ranges.
The result is a direct display with error or warning messages on the elements that present a problem in the check, in addition to the results and reports available after the analysis in the "Results and checks" section of the edit panel of each element.
Design
Designs the system, i.e. it automatically selects the size of the elements.
The design algorithm of the terminal elements keeps the selection made by the user if all the checks carried out on the equipment are fulfilled.
In the editing panel of some elements, the program also allows the partial design with the corresponding tool in the lower right-hand area.
For previously defined fittings, these fittings are deleted during the design process (extending the ducts so that they are not disconnected) and are automatically generated again (positioning the fitting and adjusting the length of the ducts).
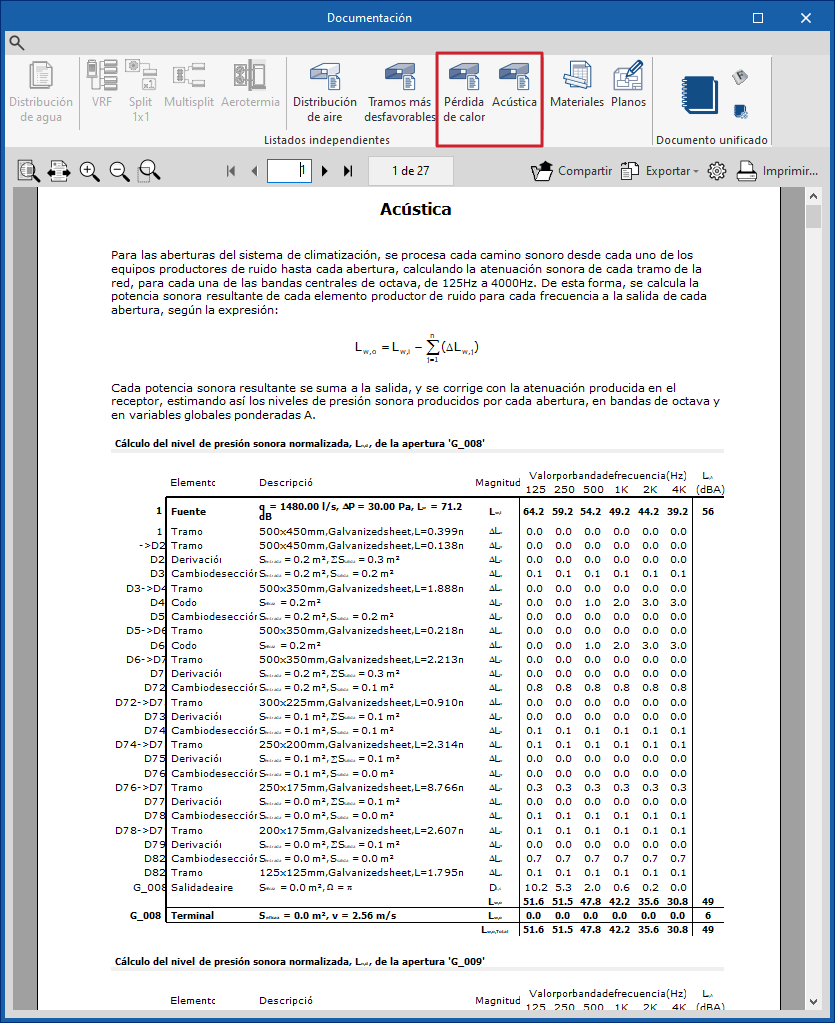
Thermal and acoustic analysis in ducts
The program can carry out the thermal and/or acoustic analysis of air duct networks. To do this, follow the steps below.
Activation of thermal and acoustic analysis in ducts
Thermal and/or acoustic analyses are activated in the "General options" of the "Project" group, in "Air distribution".
In this window, you can activate the boxes "Calculate heat loss from ducts" and/or "Calculate airborne noise transmission through the duct system".
Entering data for equipment or starting points in the duct installation
Data for equipment or starting points in the duct system can be entered in the following ways to perform thermal and/or acoustic analyses.
Entering acoustic data for generic equipment
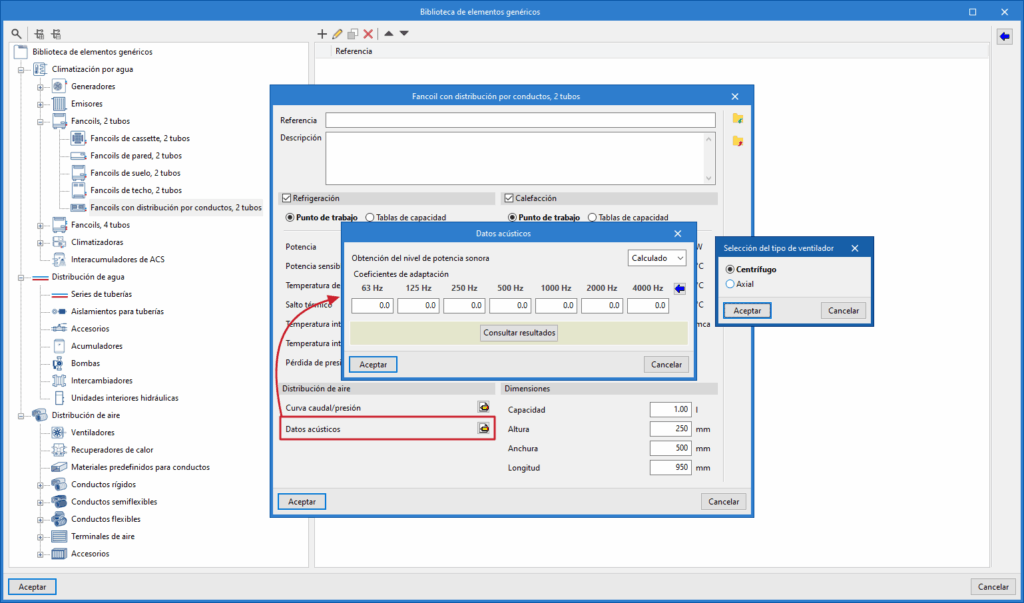
Acoustic data is entered into generic equipment by accessing its editing panel in the "Generic elements library" and then clicking on the option available next to the "Acoustic data" label (or "Acoustic data (supply)" and "Acoustic data (Return/Extraction)" in equipment with two associated networks).
This option is available for ventilation and air conditioning equipment with air distribution, such as fan coils with duct distribution, air conditioners, fans and heat recovery units.
The "Sound power level" of the equipment can be "Manual" or "Calculated":
- If "Manual" is selected, the "Sound power level (dB)" must be defined for each of the following frequencies: 63, 125, 250, 500, 1000, 2000 and 4000 hertz.
- If "Calculated" is selected, the "Adaptation coefficients" for these same frequencies are defined using the wizard on the right, which allows the necessary values to be imported by selecting the "Fan type" from "Centrifugal" or "Axial".
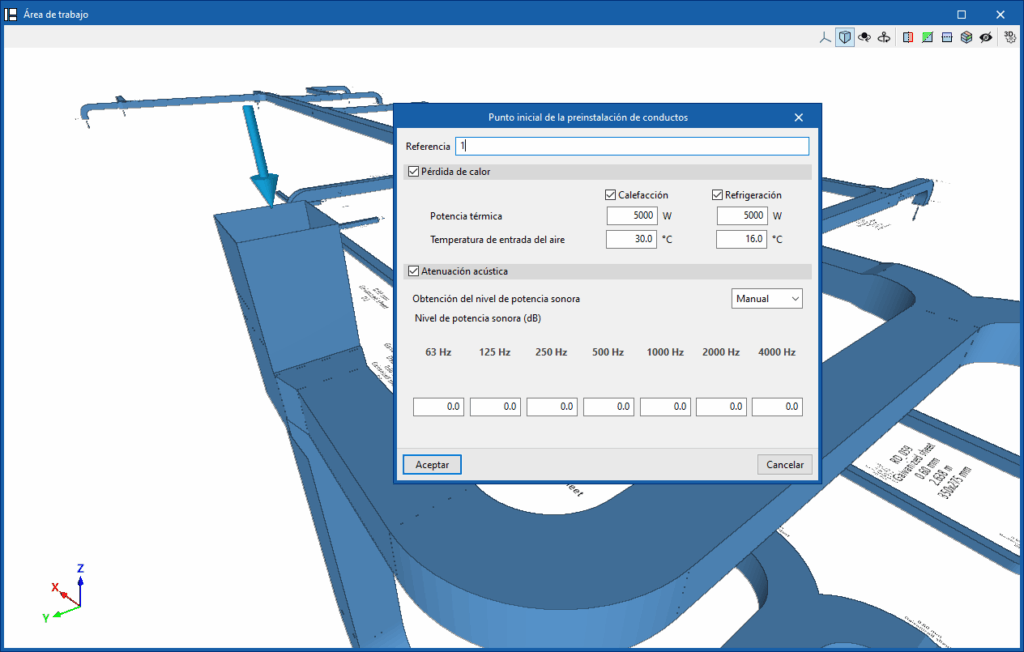
Entering thermal and acoustic data at the starting points of duct pre-installations
In the case of duct pre-installations without equipment installed, the "Heat loss" and "Acoustic attenuation" boxes are activated in the "Starting point of the duct pre-installation" editing window.
When the "Heat loss" option is activated, the "Thermal power" and "Air inlet temperature" are defined for "Heating" and/or "Cooling".
When the "Sound attenuation" option is activated, the "Sound power level" is defined in the same way as explained for generic library equipment.
Entering acoustic data in manufacturer equipment
Acoustic data is included alongside other technical characteristics in the equipment listed in the manufacturer catalogues of the Open BIM Database. Therefore, simply download and update the catalogue and select the desired equipment to load this data.
Consulting thermal and acoustic analysis results
If the options indicated above have been selected, the thermal and/or acoustic analysis in ducts is performed in a combined manner when the model analysis is launched, using the options in the "Analysis" group. The results obtained can then be consulted in the following ways.
Consulting results for specific elements
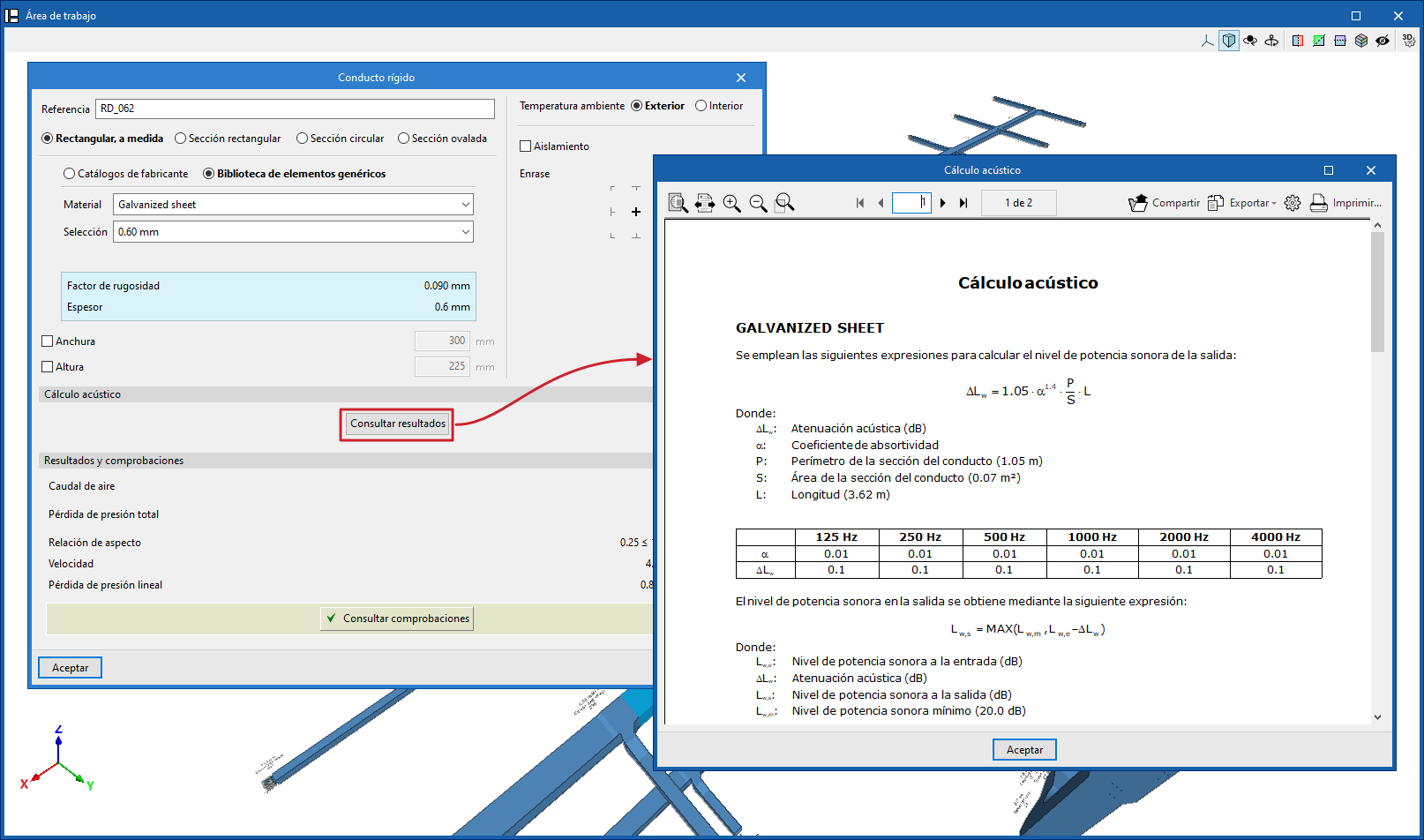
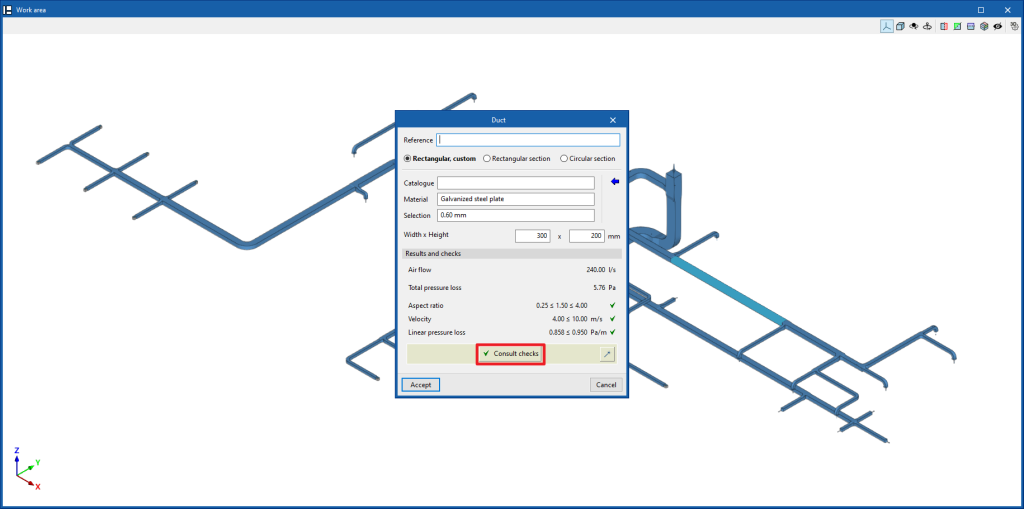
The programme allows you to consult the lists of acoustic analysis results from the editing panel for each piece of equipment or section of duct, in the "Acoustic analysis" section, by clicking on "Check results".
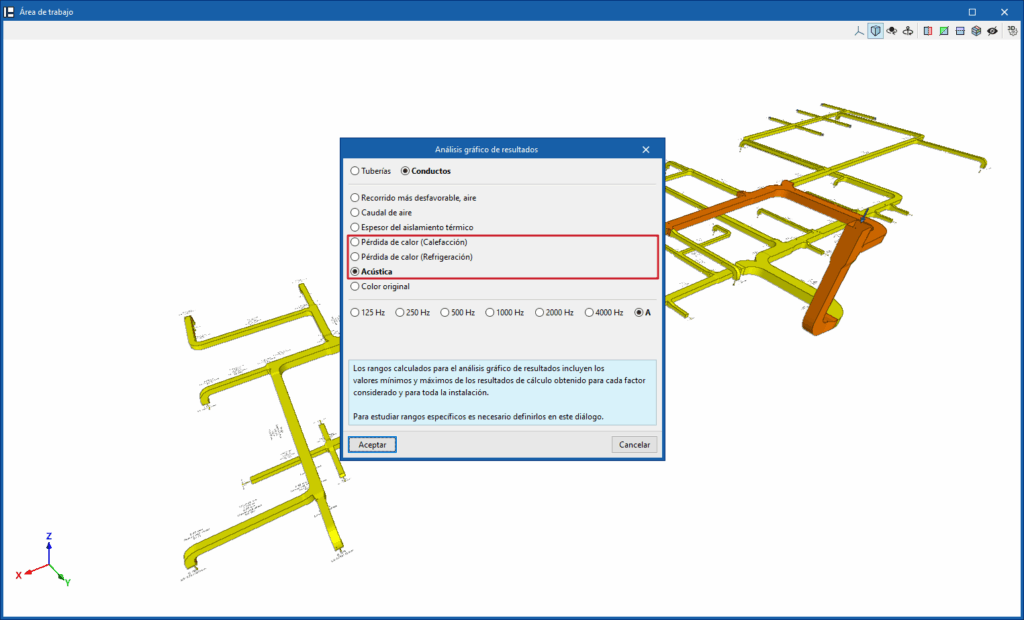
Graphical analysis of thermal and acoustic analysis results
It is also possible to view the results graphically by colouring the duct sections in the model using the "Graphical analysis of results" option, selecting the "Heat loss (Heating)", "Heat loss (Cooling)" or "Acoustics" options in its settings.
Results output
In the "Results" group of the main toolbar, under the "Installation" tab, there are options for obtaining information on the analysis results of the installation:

Analysis results can also be obtained in the following ways:
Checking the results on screen
After the analysis, CYPEHVAC displays the results in the tooltip or information text that appears when the cursor is positioned on an element in the system, and the compliance of the checks carried out on it. To do this, the "Show information texts" option in the top right-hand toolbar must be checked.
Results and checks
The program also displays the "Results and checks" of the last analysis carried out in the corresponding section of the edit panel of each element, as well as its compliance status.
Graphical analysis of results
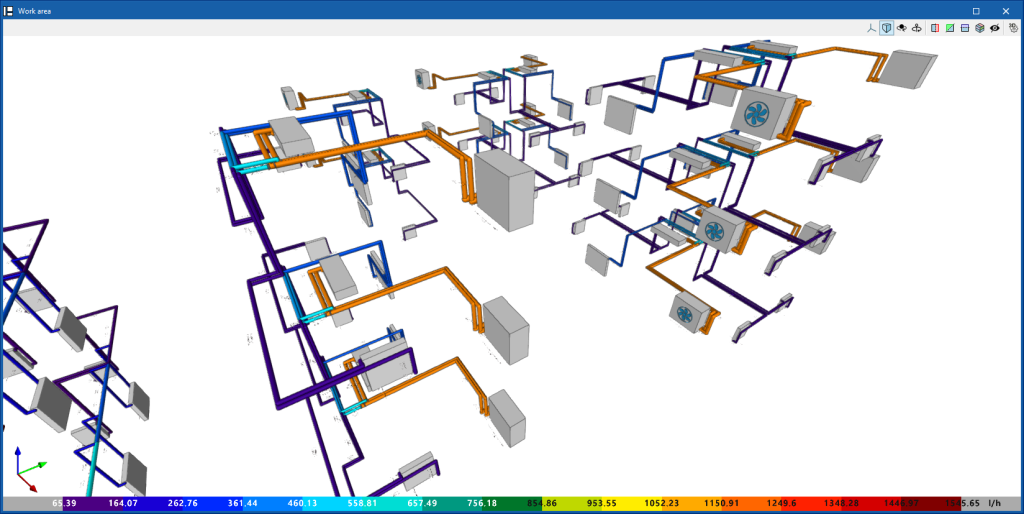
By means of the "Graphical analysis of results" option in the "Results" group of the main toolbar, the analysed values of different magnitudes are displayed by colouring the sections of the water distribution system.
By default, the program displays the minimum and maximum values of each factor obtained in the analysis for the entire system. However, the colour scale can be adjusted according to the specific ranges of minimum and maximum values defined in the corresponding dialogue box.
The results available in the graphical analysis of results are as follows:
- Worst case path, cold water
- Worst case path, hot water
- Flow
- Pressure loss of the span
- Velocity
- Thermal insulation thickness
- Linear heat flow
- Hot water temperature
- Cold water temperature
Show/Hide incidents
If this option is activated, the elements in which an error has occurred are highlighted. By positioning the cursor on these elements, the message describing the error can be displayed.
Job reports
The program can print the reports directly or generate HTML, PDF, TXT, RTF or DOCX files.
Reports are obtained via the "Reports" option in the "Results" group of the main toolbar.
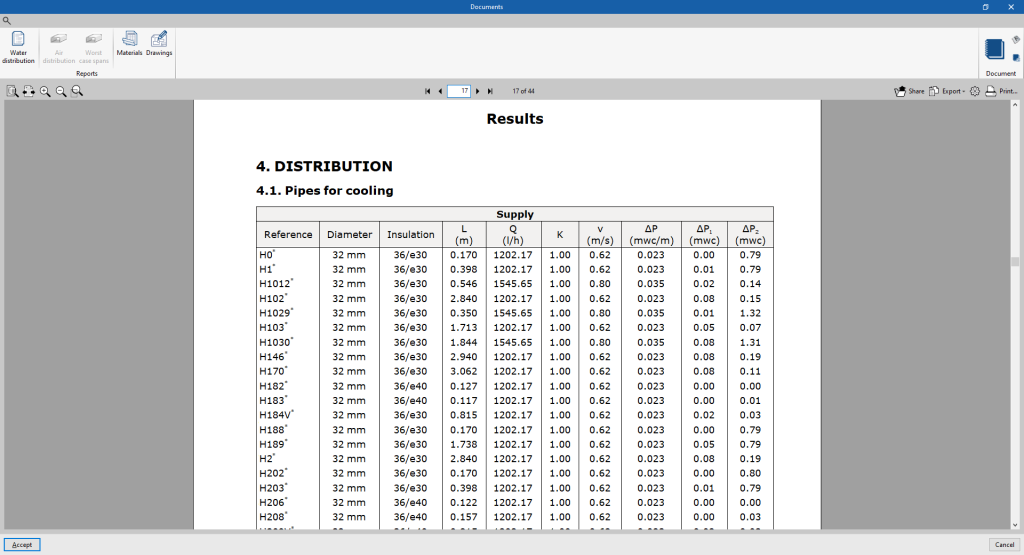
- Water distribution
Displays a report with the analysis results of the water distribution system. The data for the following elements are included:- Generators
- Emitters
- Fittings
- Distribution
- System-specific reports
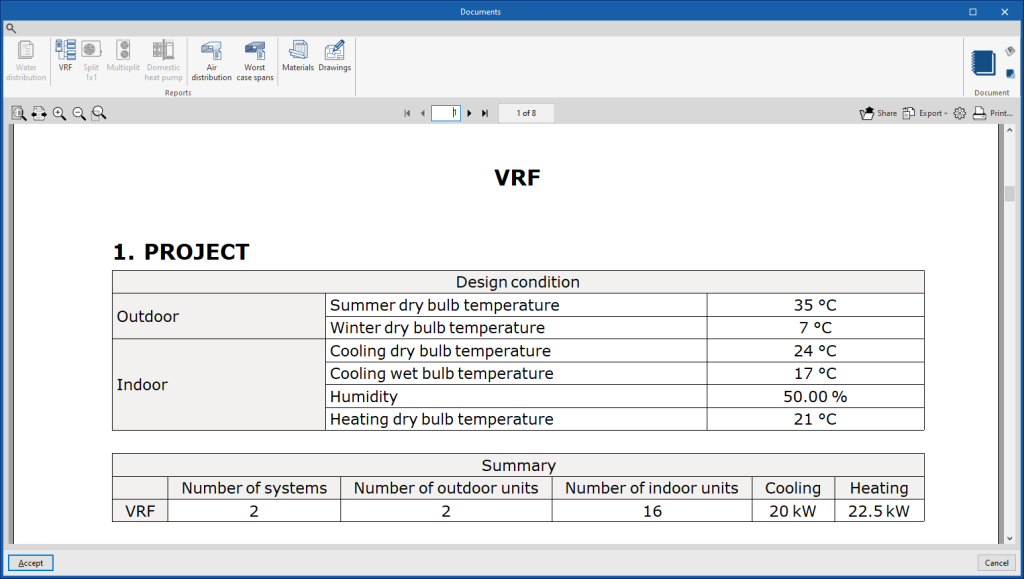
Each of these reports shows specific information on the following systems entered in the model:- VRF
- Split 1x1
- Multisplit
- Air-source heat pump
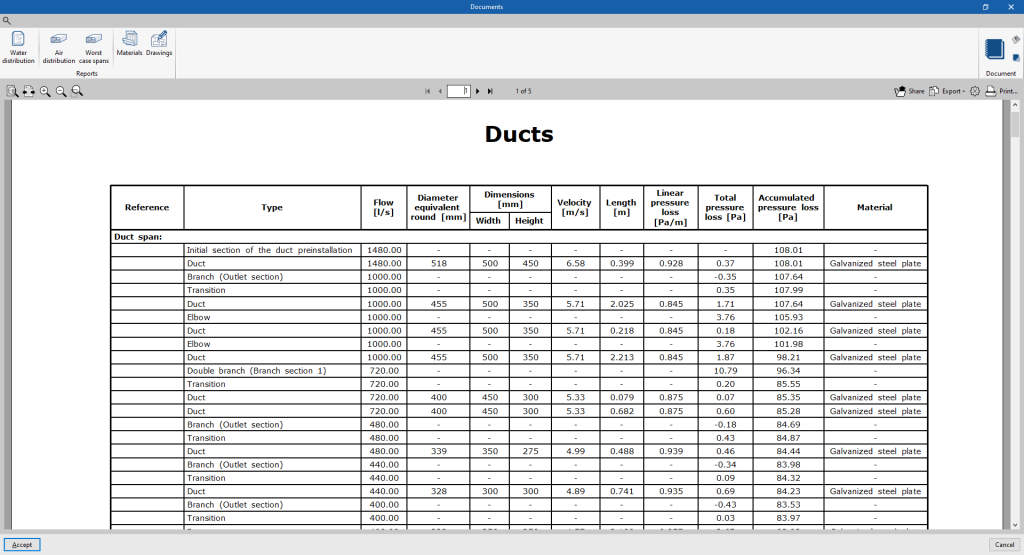
- Air distribution
Displays a report with the analysis results of the air distribution system. The data for all ducts and nodes are organised by air duct sections in a table including the following information:- Reference
- Type
- Flow
- Diameter equivalent
- Dimensions (Width, Height)
- Velocity
- Length
- Linear pressure loss
- Total pressure loss
- Accumulated pressure loss
- Material
- Most unfavourable sections
Displays a specific report of the most unfavourable air duct runs for each independent tree in the system.
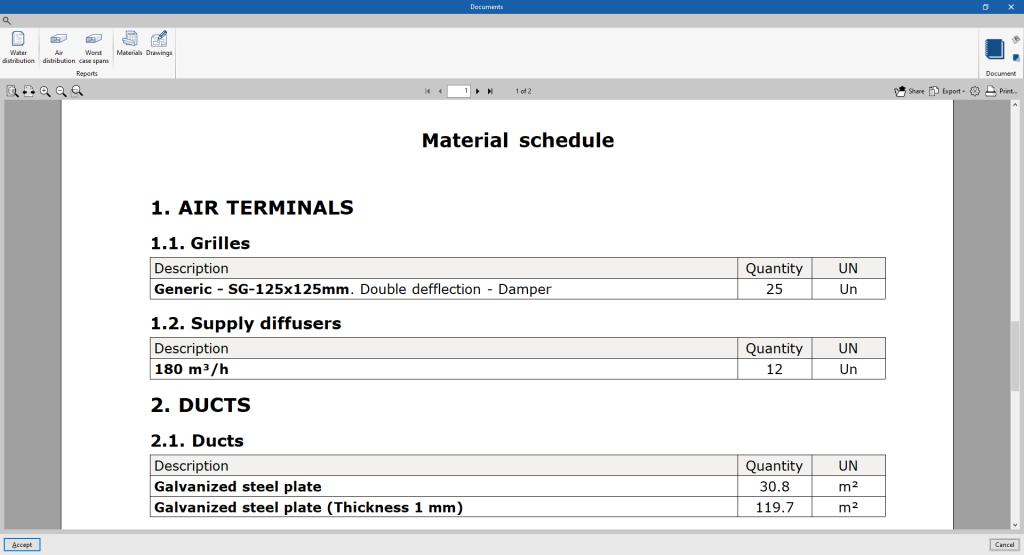
- Materials
Displays the table of materials with the measurement of the elements arranged in the system.
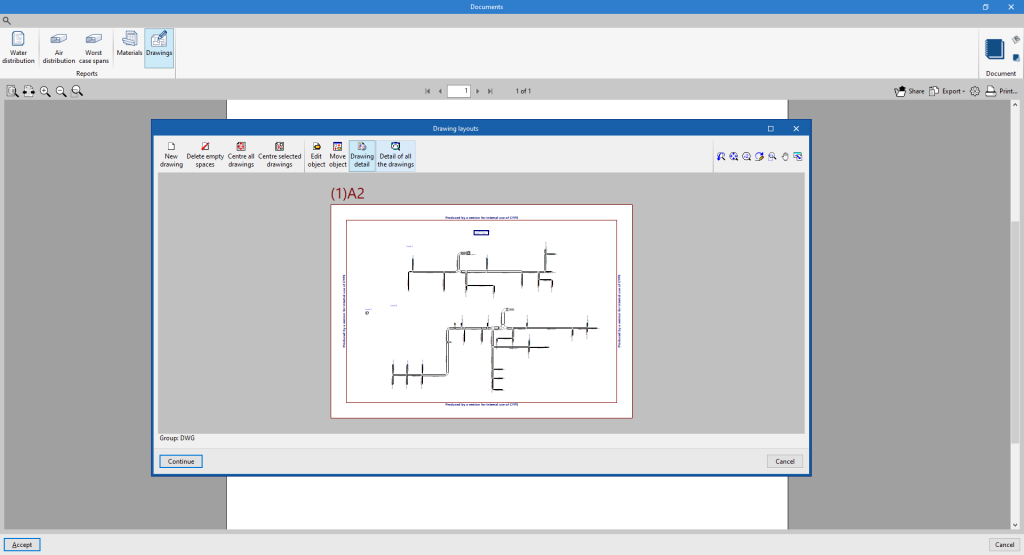
- Drawings
With this option, the program can print drawings as reports, so they can be integrated and exported as another document.
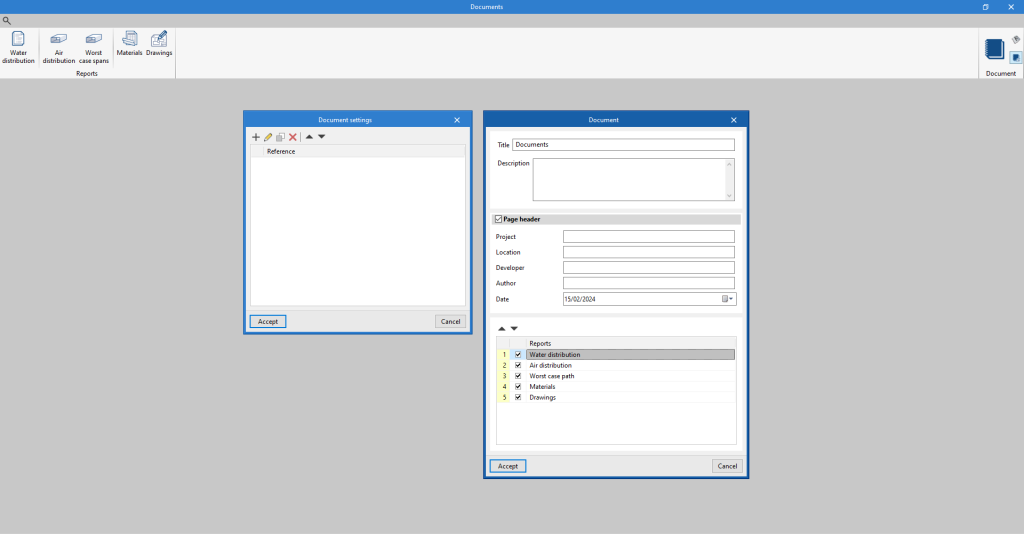
Document configuration
To create documents that incorporate the information of several selected reports together, the "Document configuration" option is used. It allows the following data to be configured:
- Title
- Description
- Page header (optional)
- Project; Location; Developer; Author; Date
- Reports to be included
The document created is printed using the "Document" option.
The "Document styles" can also be modified using the corresponding option.
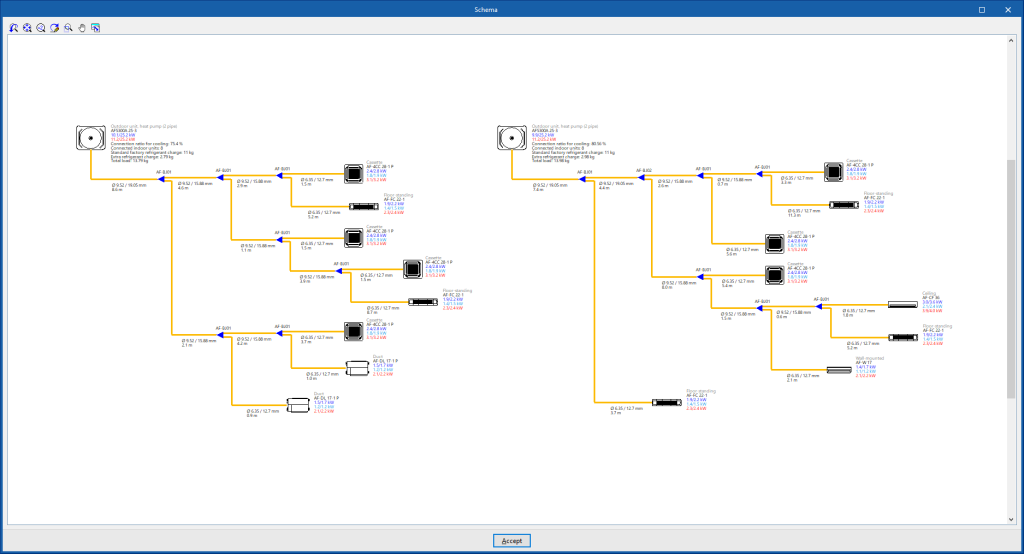
System diagram
By using the "Diagram" option in the "Results" group of the main toolbar, the program generates and displays the diagram of the direct expansion systems.
These diagrams can be incorporated into the job drawings.
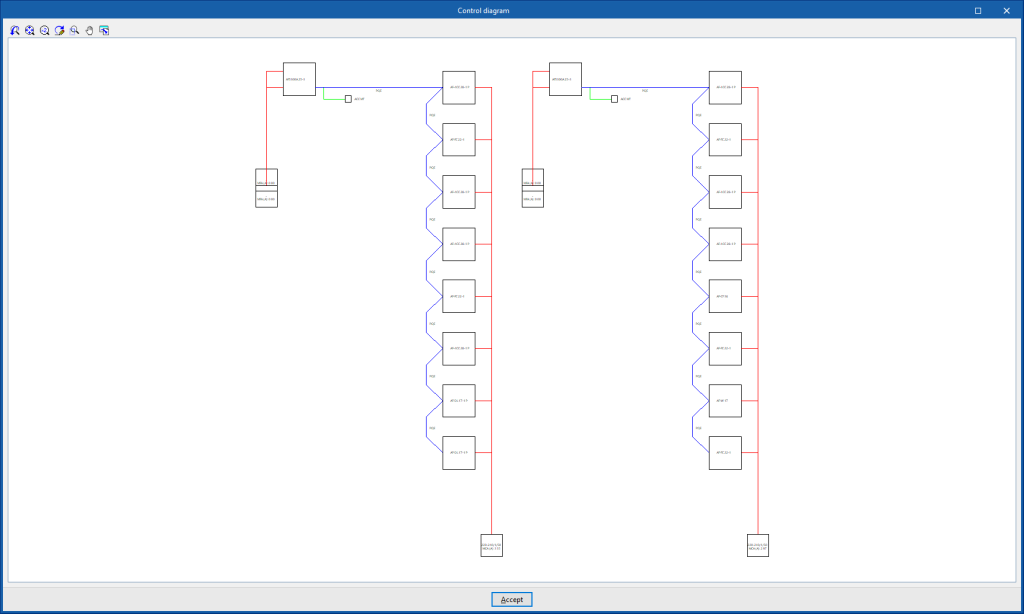
Control diagram of the system
By using the "Control diagram" option in the "Results" group of the main toolbar, the program generates and displays the control diagram of the VRF systems.
The control diagram can also be incorporated into the job drawings.
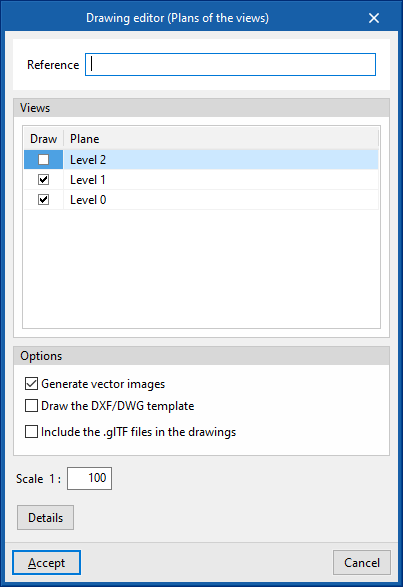
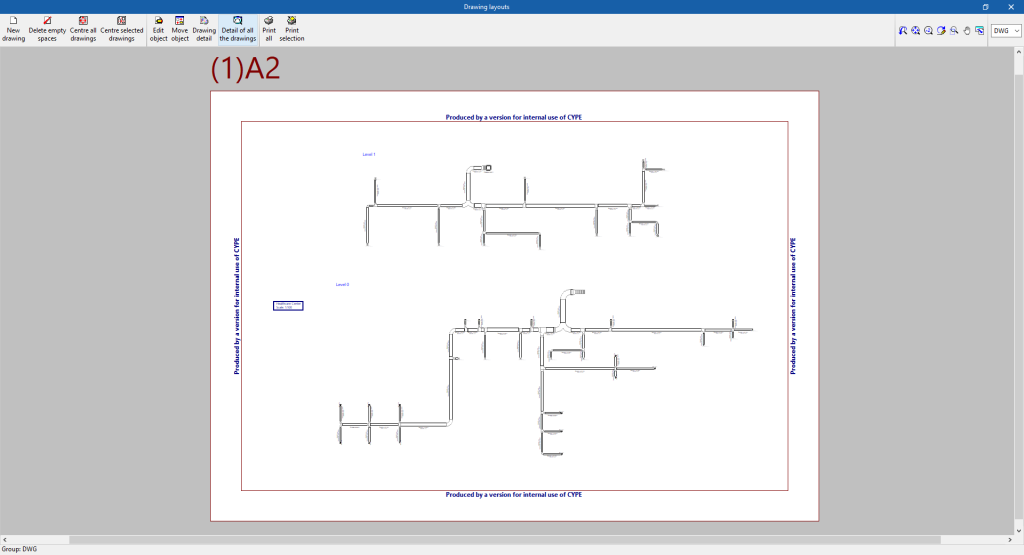
Drawings in DWG, DXF or PDF format
The program can print the drawings of the job on any graphic peripheral configured on the computer, or create DWG, DXF or PDF files.
The following options can be configured when editing drawings:
- Views to be drawn
- Options
- Generate vector images
- Draw the DXF/DWG template
- Include .glTF files in the drawings
- Scale
- Details
The drawings can be obtained via the "Drawings" option at the top of the interface or via the "Reports" option in the "Results" group of the main toolbar.
Results in the "Bill of quantities" tab
If the work is carried out in the "Bill of quantities" tab, CYPEHVAC will provide the following documents:
- Exporting the bill of quantities in FIEBDC-3 format (BC3)
- Bill of quantities reports (in HTML, PDF, TXT, RTF or DOCX format)
GLTF file compatible with BIMserver.center
When a project is exported to the BIMserver.center platform, a 3D model is automatically exported in GLTF format for the integration of the system model in the Open BIM project, so that it can be visualised:
- on the online platform;
- in the BIMserver.center app for iOS and Android;
- in virtual reality and augmented reality;
- in other CYPE programs.
Integration into the BIMserver.center platform
Many of CYPE's programs are connected to the BIMserver.center platform and allow collaborative work to be carried out via the exchange of files in formats based on open standards.
Please note that, to work on BIMserver.center, users can register on the platform free of charge and create a profile.
When accessing a program connected to the platform, the program connects to a project in BIMserver.center. This way, the files of the projects that have been developed collaboratively in BIMserver.center are kept up to date.

Options available in CYPEHVAC
In the "BIMserver.center" group of the main toolbar, under the "Installation" tab, there are the features needed to use CYPEHVAC together with other BIMserver.center tools:

Update
Update information contained in models previously imported into the project or import new models if desired.
Share
Exports the information of the system developed with CYPEHVAC to BIMserver.center to share it with other users, including the quantities and analysis reports of the system.
During the export process you can define information related to the identification of the files to be exported and the types of files that are generated:
- Name
- Description
- Additional files
- Reports (optional)
- DXF/DWG drawings (optional)
Licenses and related modules
CYPE programs are activated via electronic licenses which may contain one or more modules. The list of modules compatible with each program may vary depending on the product purchased and the type of license.
To consult the list of modules compatible with this program, go to "CYPE program modules".
Please note that the list of modules available in the license will depend on the product purchased.