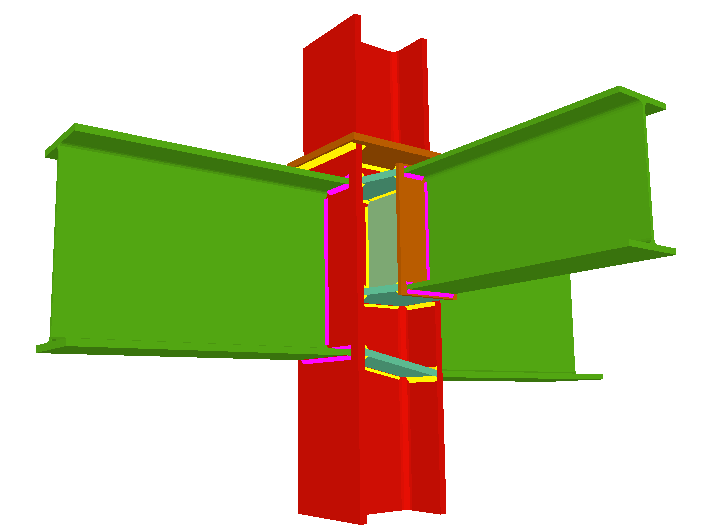
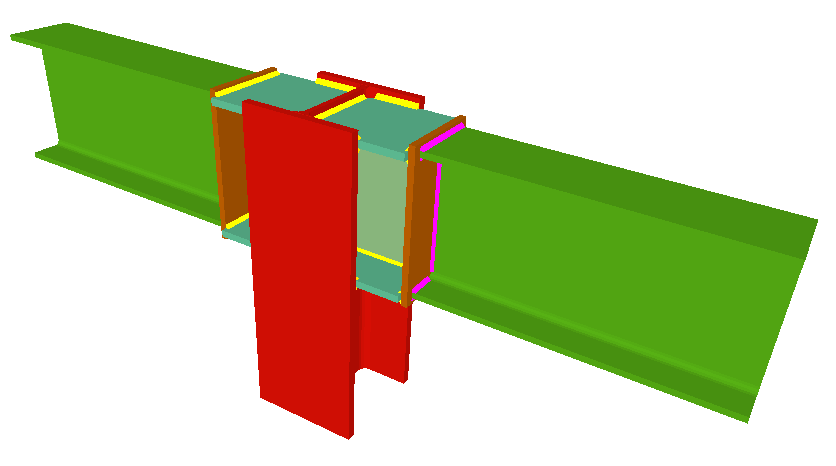
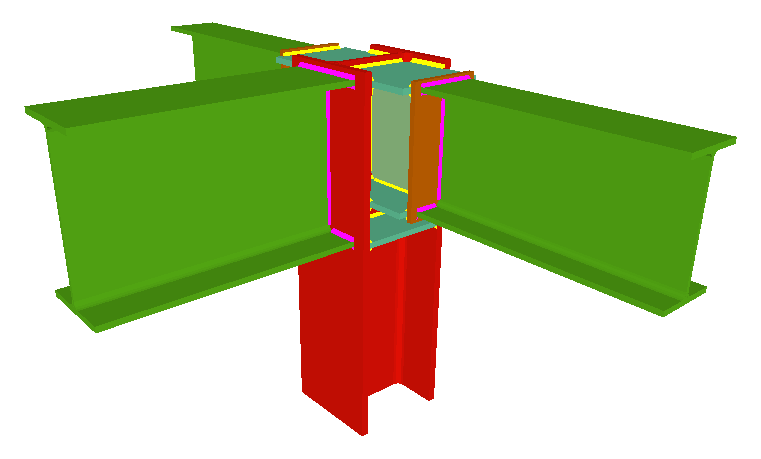
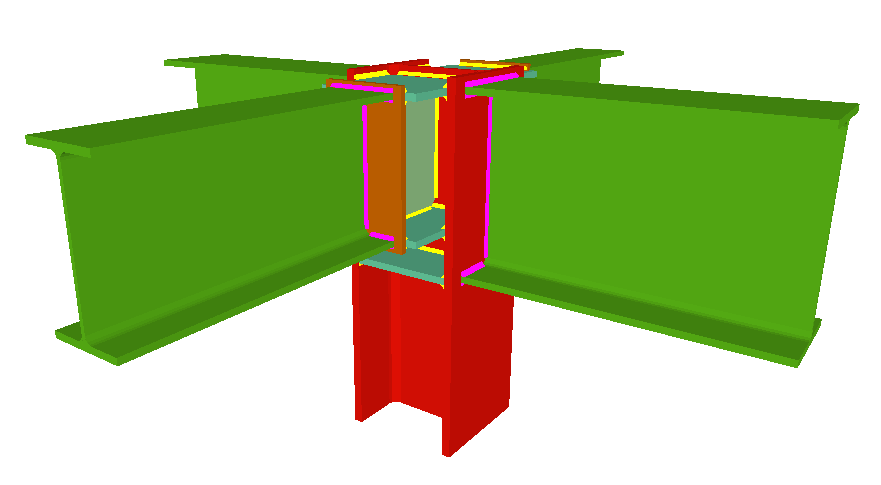
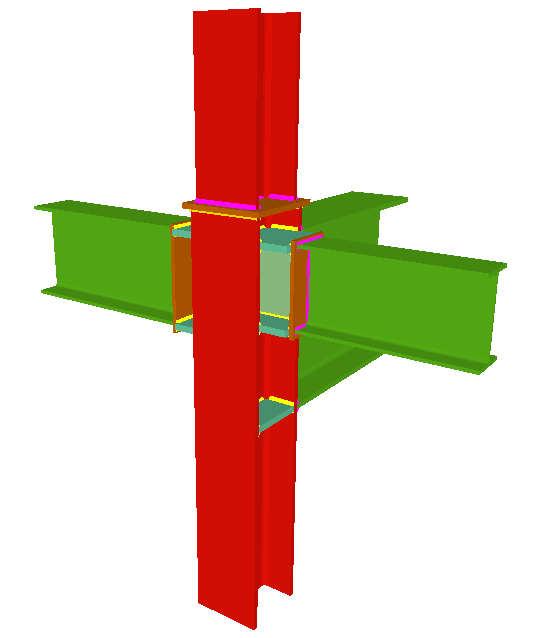
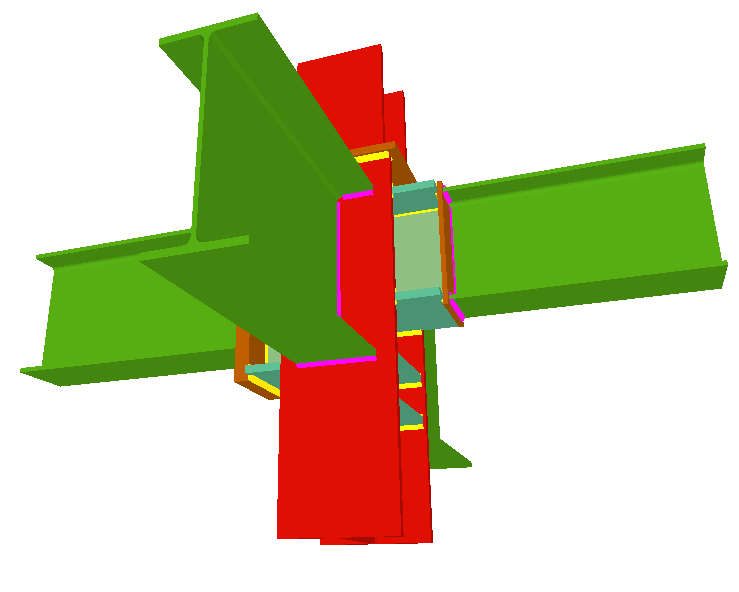
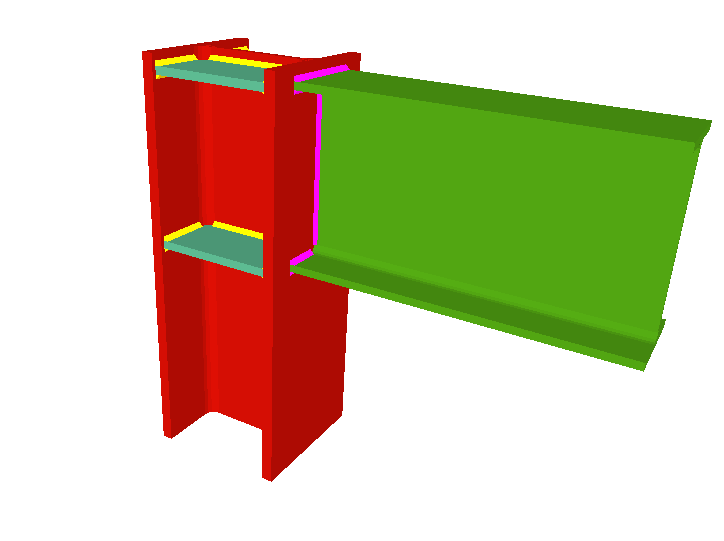
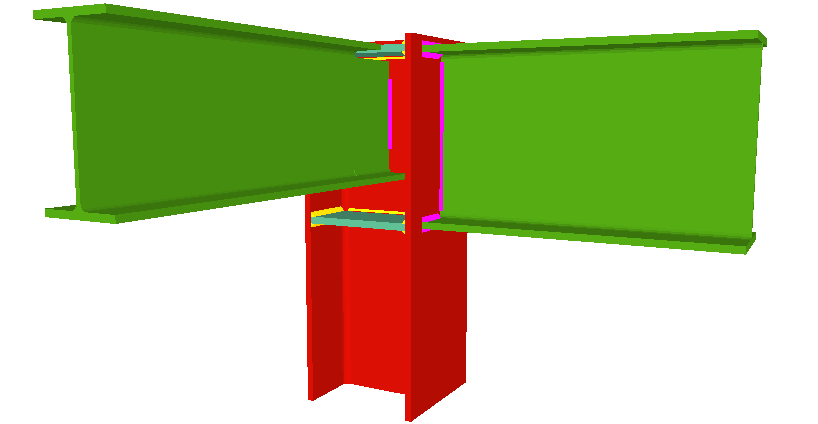
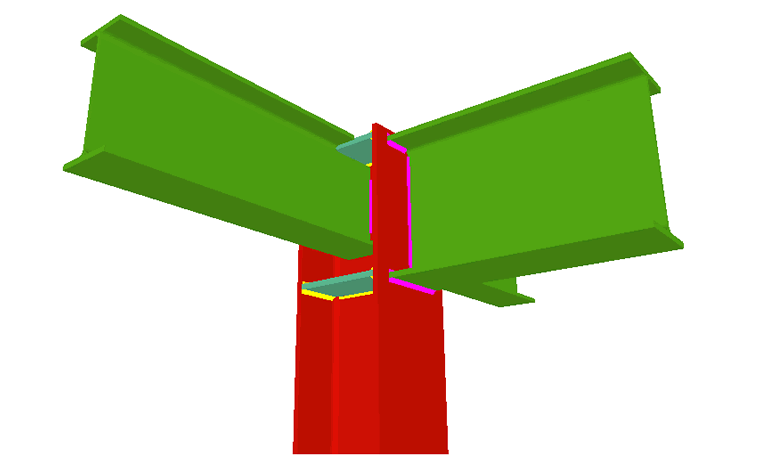
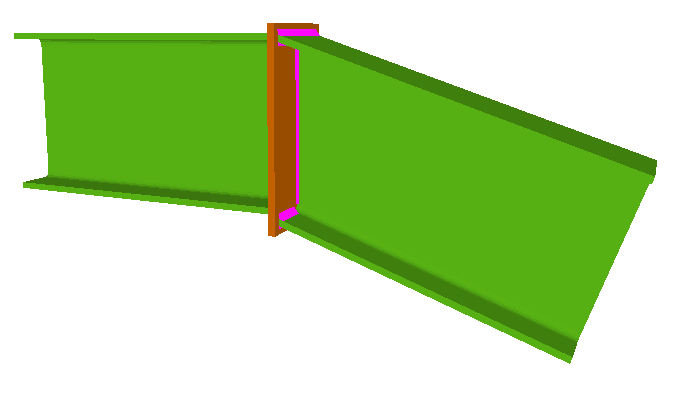
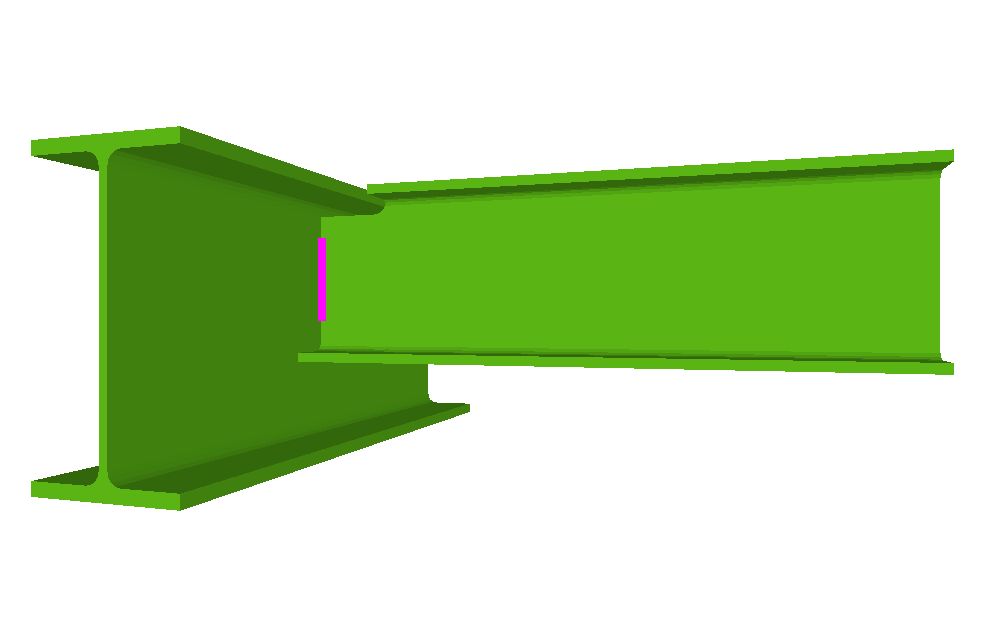
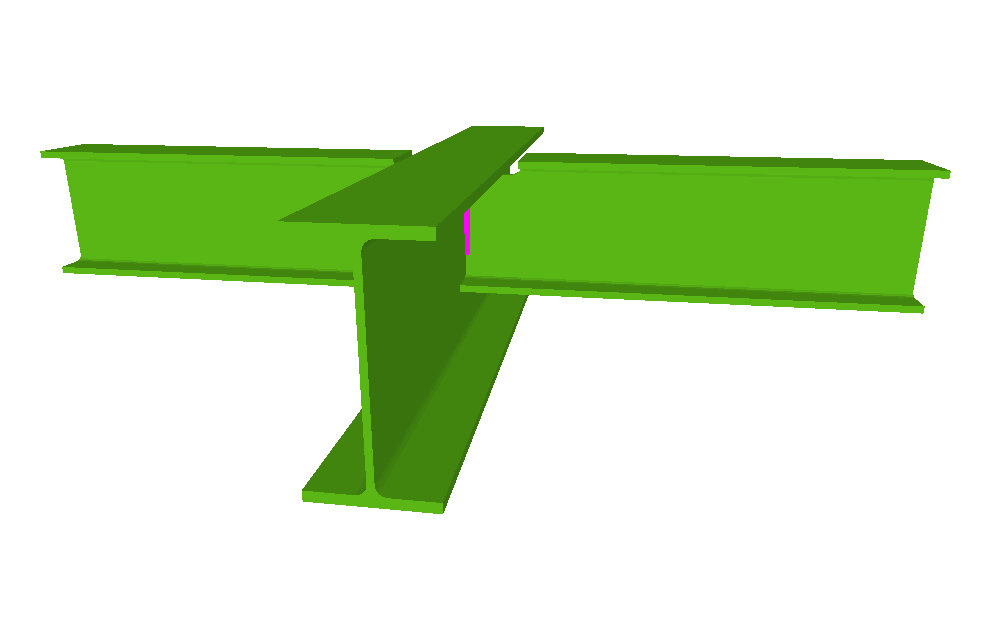
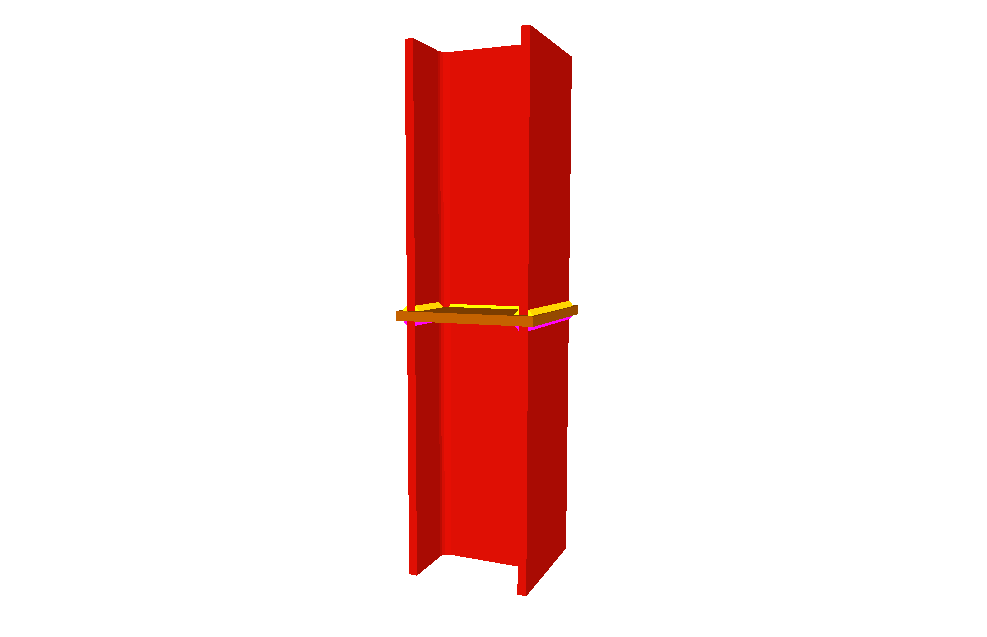
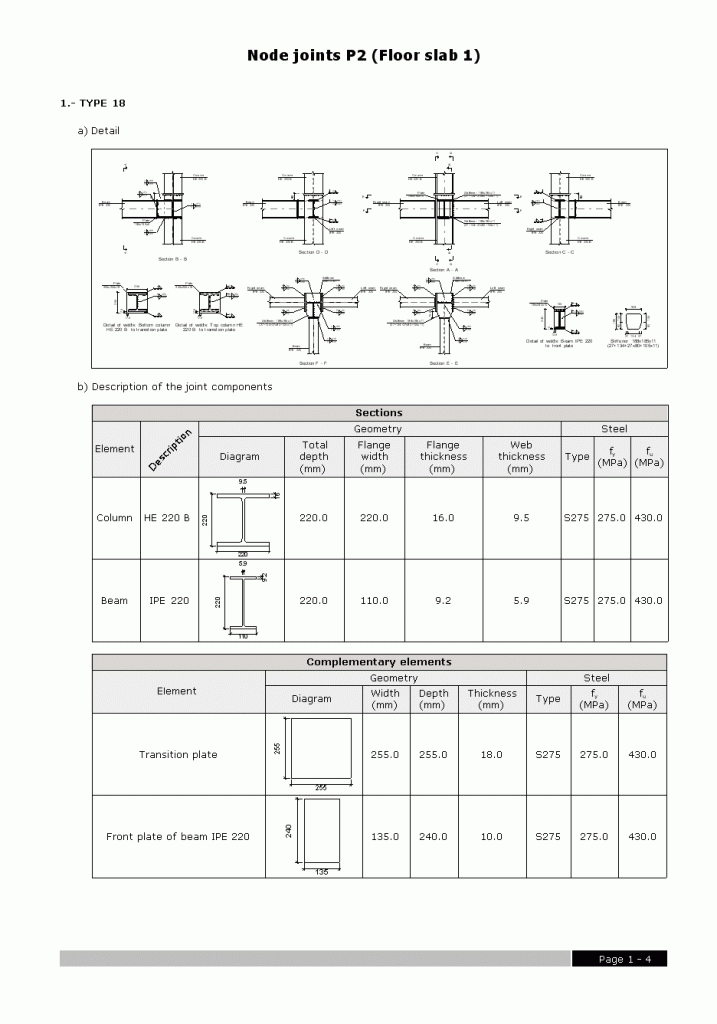
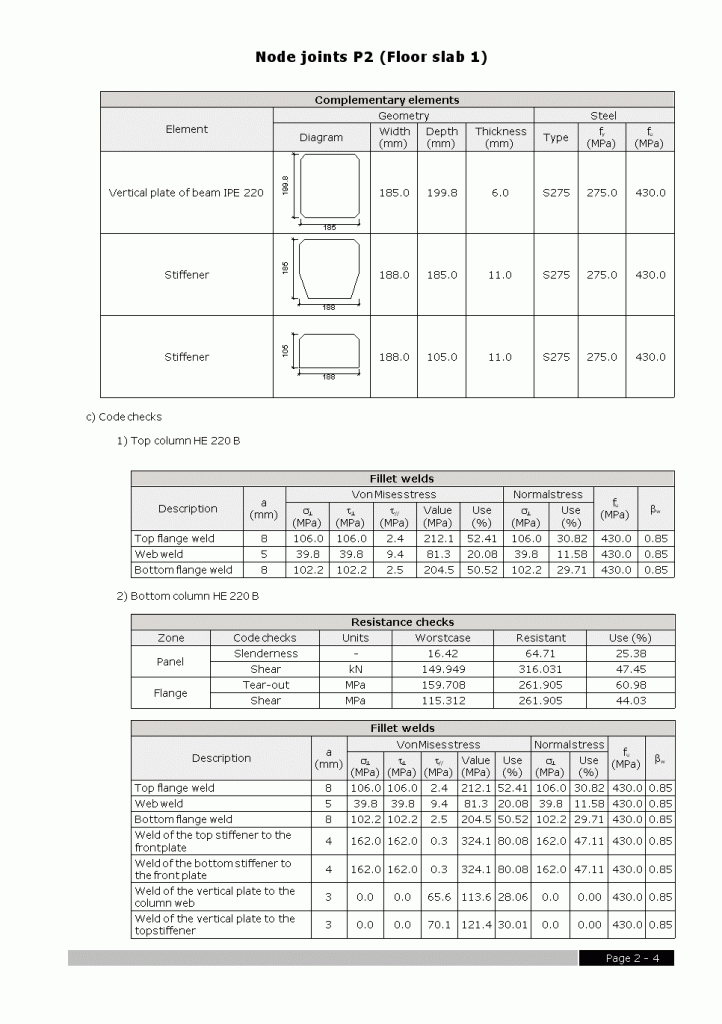
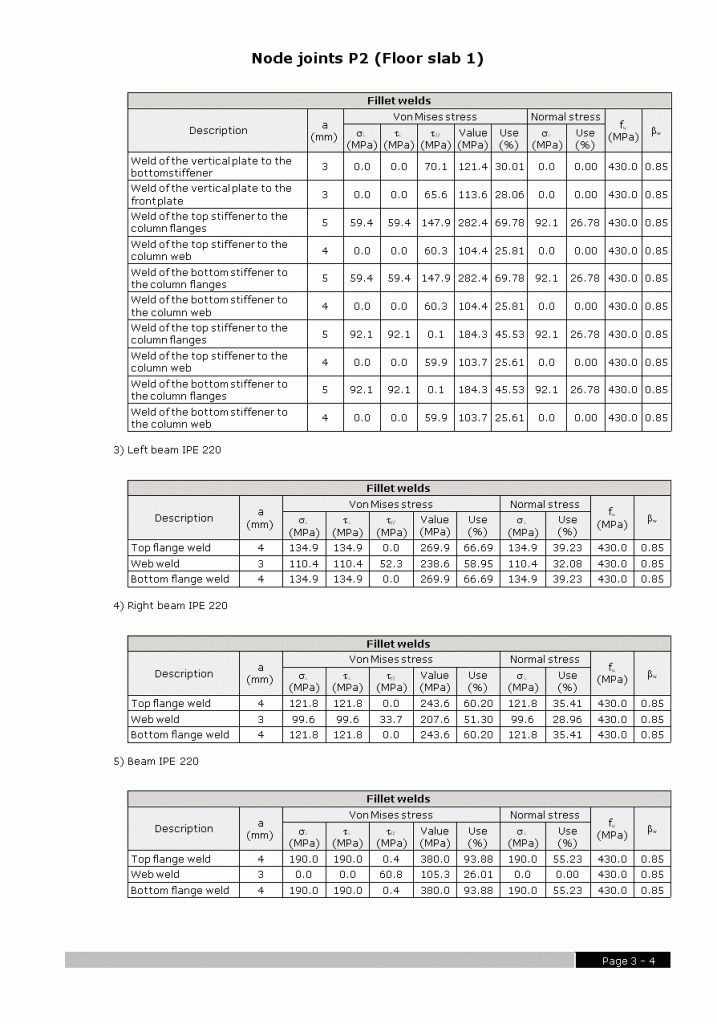
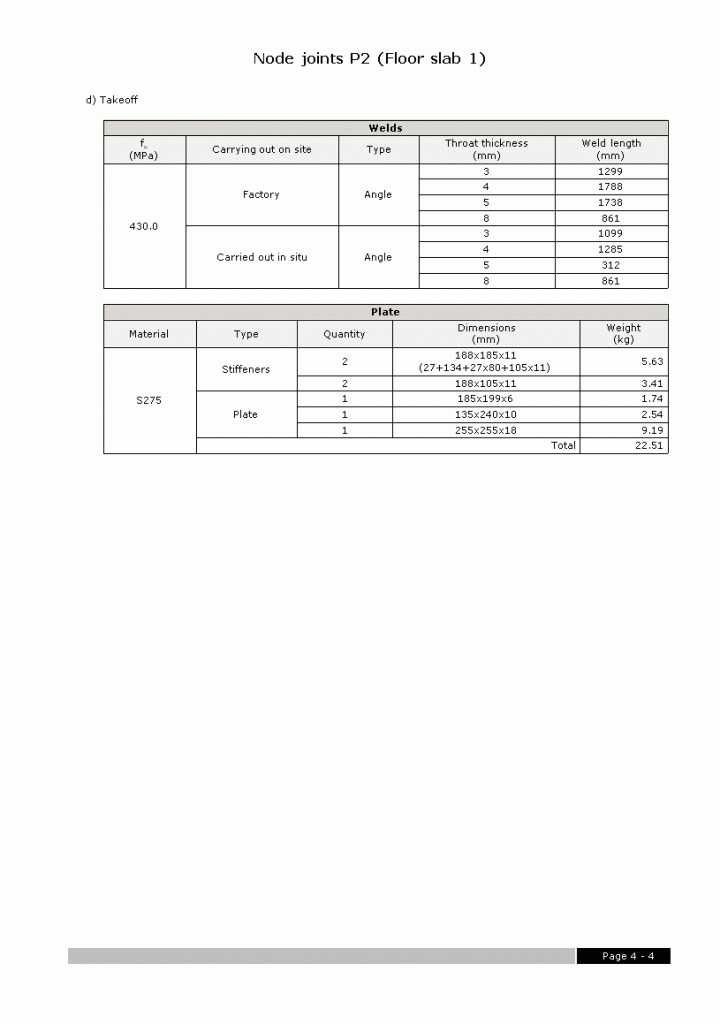
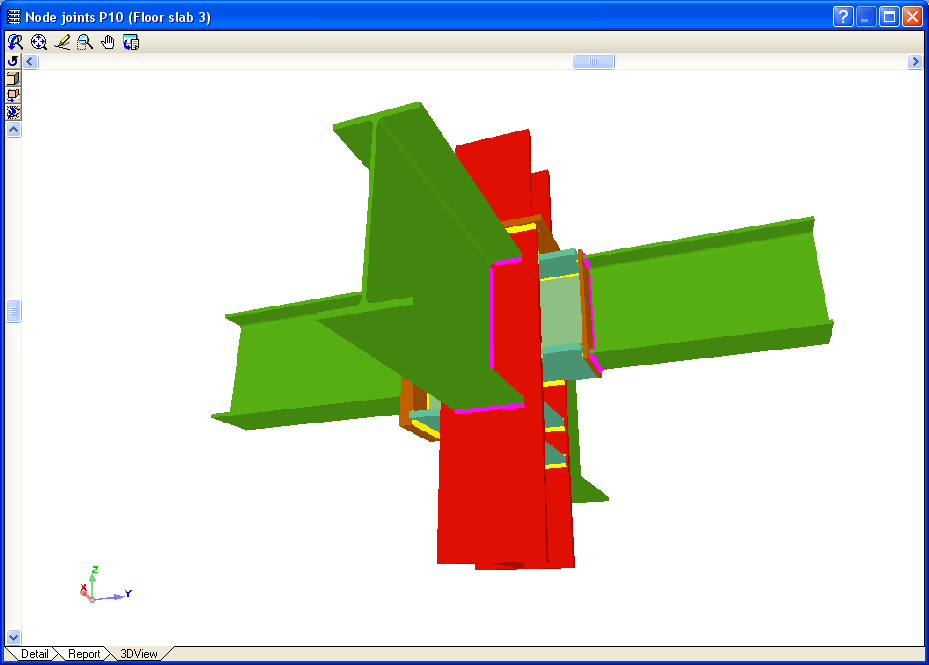
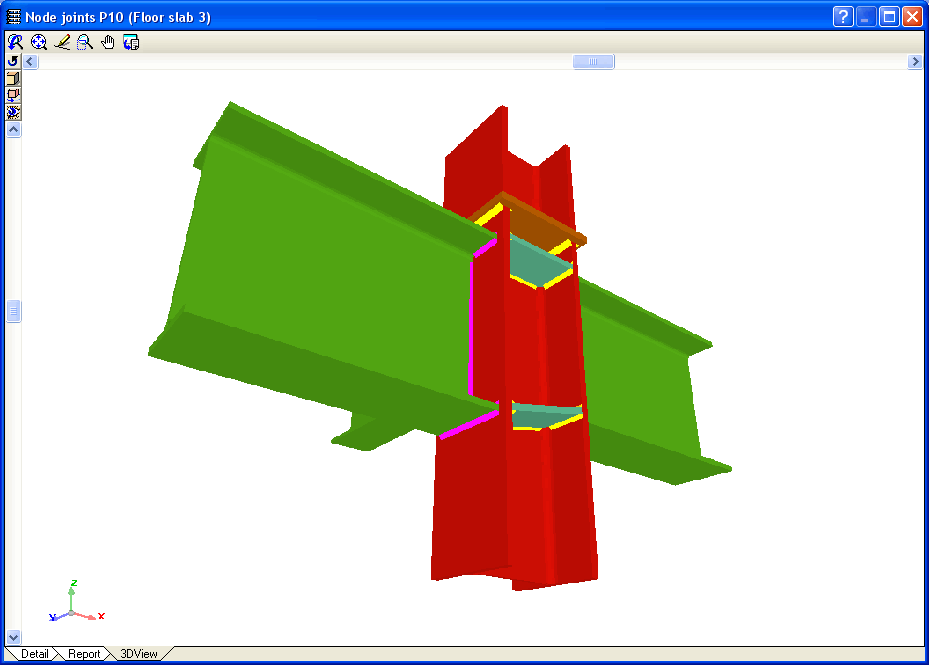
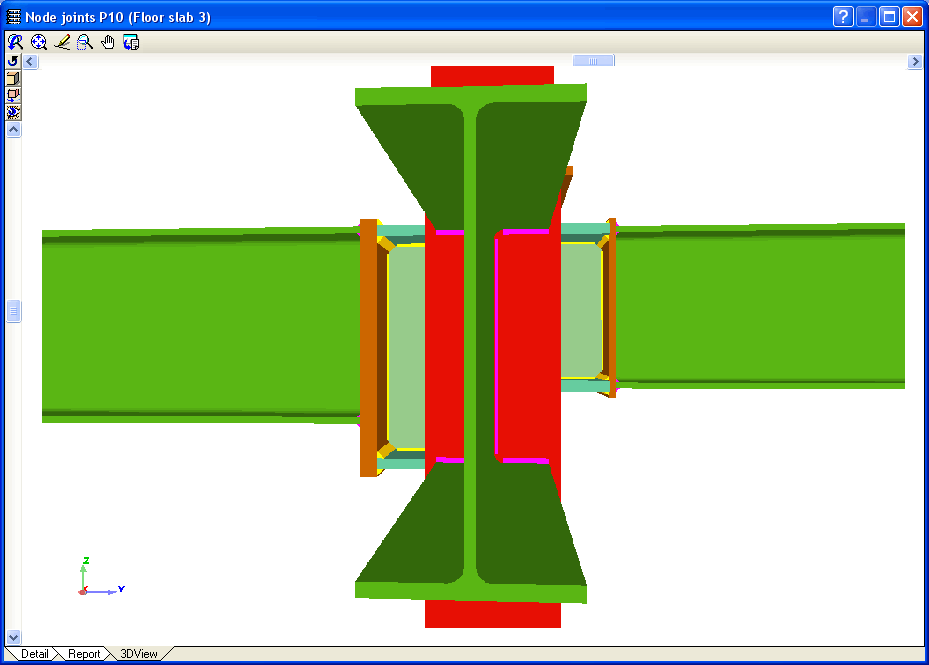
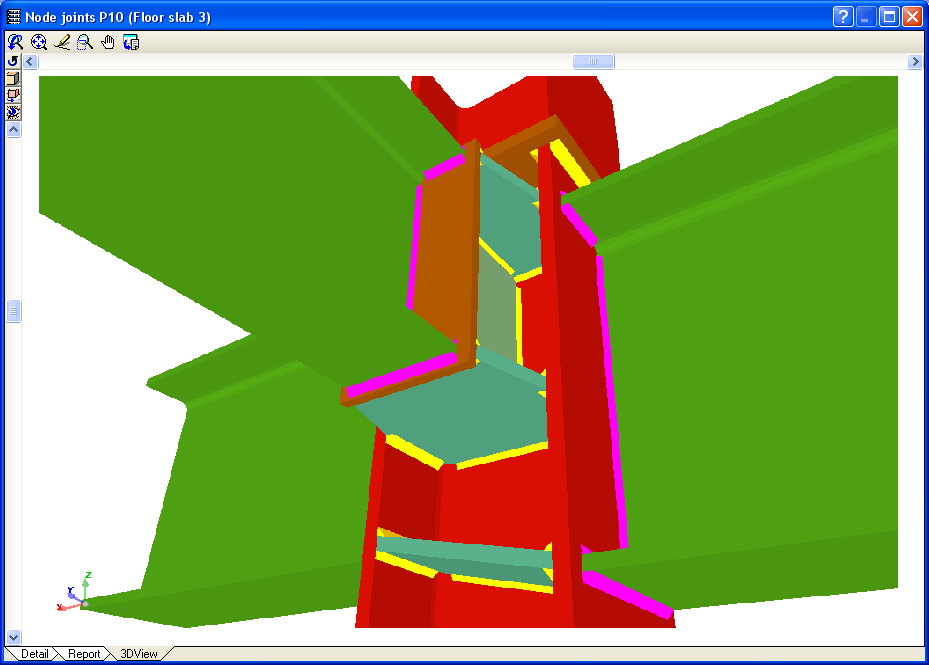
Welded connections of rolled and welded steel I sections for building frames
The "Joints III. Welded – Building frames with rolled and welded steel I sections" module allows CYPECAD, CYPE 3D and Integrated 3D structures of CYPECAD to carry out the automatic design of the most common welded connections of rolled and welded steel I sections in building frames. More information on the types of joints that can be designed and the codes available to design them can be found in the Types of implemented building welded connections section and Implemented codes for the design of building welded connections section.
Types of implemented building welded connections
Design options
The design options for welded and bolted connections may be configured in the Options menu (Joints > Options). This dialogue box can be accessed via the following menu options:
- In CYPECAD and its Integrated 3D structures:
- Beam Definition tab > Job > Joint analysis options
- Results tab > Joints > Joint analysis options
- In CYPE 3D:
- Joints > Options
- Joints > Options
This dialogue box contains three tabs:
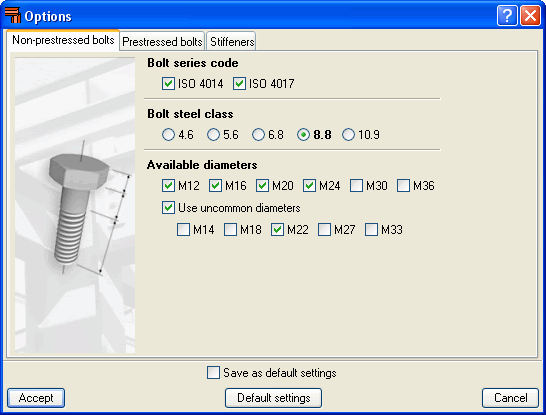
- Non-prestressed bolts
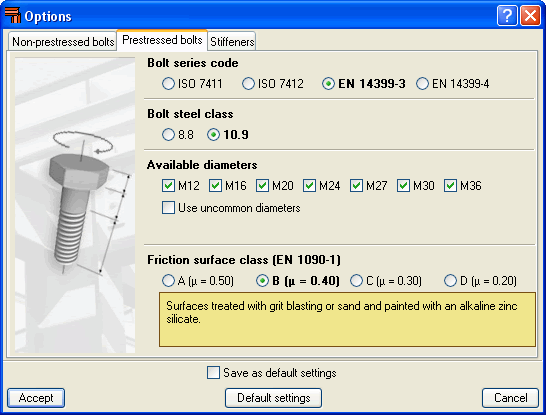
Contains the design options for non-prestressed bolts (Bolt series code, Bolt steel class and Available diameters). Options selected here will only affect bolted connection design. - Prestressed bolts
Contains the design options for prestressed bolts (Bolt series code, Bolt steel class, Available diameters and Friction surface class). Additionally, the type of friction surface must be indicated to check the bolt for slipping. Within this dialogue, the program also defines the properties of the selected surface in accordance with the article of the selected code. Options selected here will only affect bolted connection design. - Stiffeners
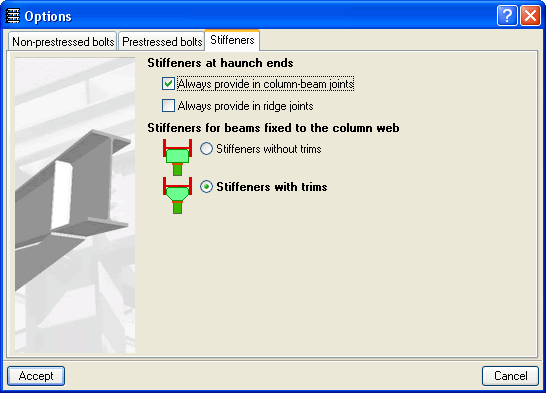
Contains two option groups which configure the layout of the stiffeners:- Stiffeners at haunch ends
Contains two options which when activated force the program to always provide stiffeners, one in column to beam connections and the other in ridge connections. Affects welded connections designed with the Joints I module and bolted connections designed with the Joints II module.
Regardless of whether this option is activated or not, the program always provides stiffeners at the ends of the haunches if the design requires their presence. - Stiffeners for beams fixed to the column web
Activates the trimming of stiffeners for beams fixed to column webs. It only affects welded connections designed with the Joints III module and bolted connections using the Joints IV module (the other modules do not contemplate connections consisting of beams fixed to column webs).
This option does not imply changes in the structural check but only takes into account aspects related to the aesthetics and the number of trimming operations undertaken in the fabrication process. Upon activating the trimming option, it will be carried out if the following conditions are met:- The smallest side of the trim has to be greater than 10mm.
- The angle formed between the inclined side of the trim and the plane perpendicular to the web has to be greater than 15 degrees.
- Stiffeners at haunch ends
Design of building welded connections
Joints III in CYPECAD, Integrated 3D structures and CYPE 3D
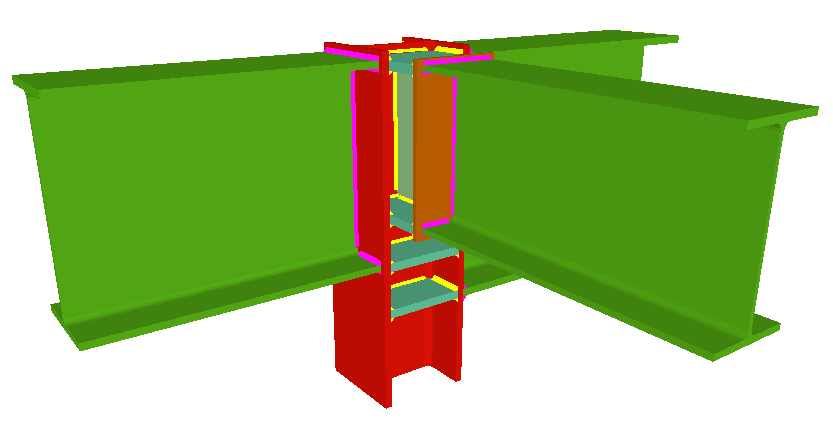
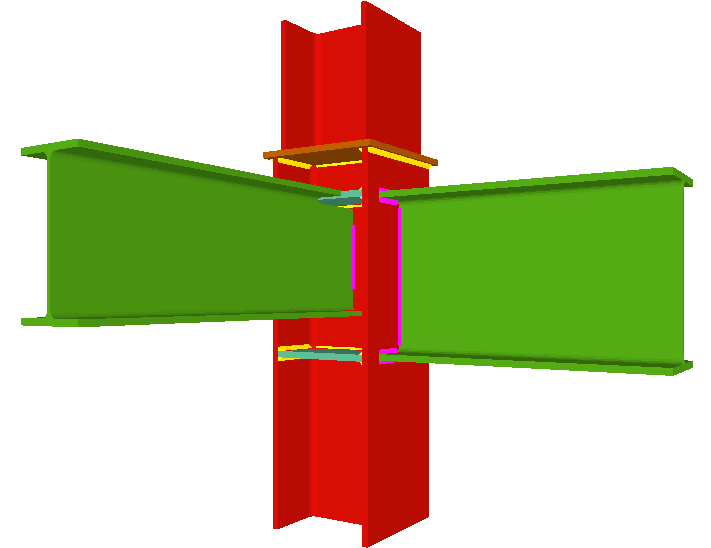
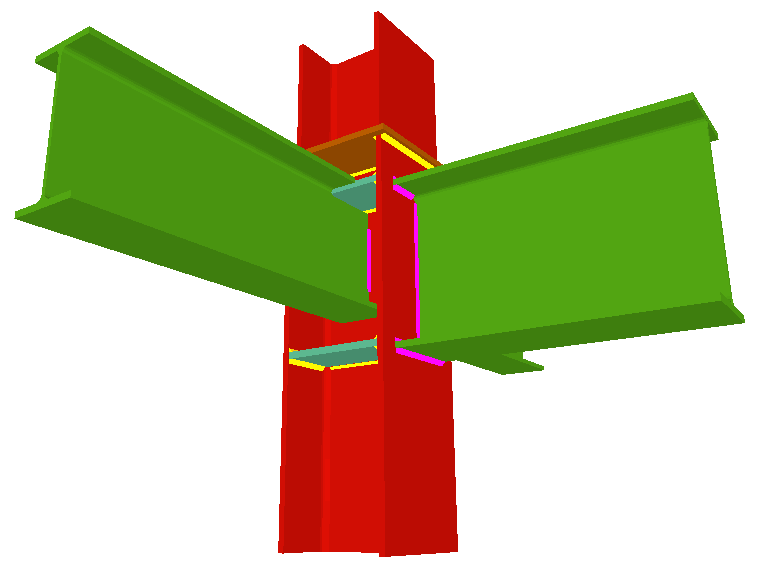
As occurs with the Joints I, Joints II and Joints IV modules, the Joints III. Welded – Building frames with rolled and welded steel I sections module designs the joints at floor level (with column transition) and at column ends. In the case of CYPE 3D and Integrated structures of CYPECAD, as the concept of floor level does not exist, the joints may be placed at an intermediate level of a column span (continuous column) and at the connecting node between two different column spans (a transition plate between the two column spans is provided).
Beam to column moment or simple connections
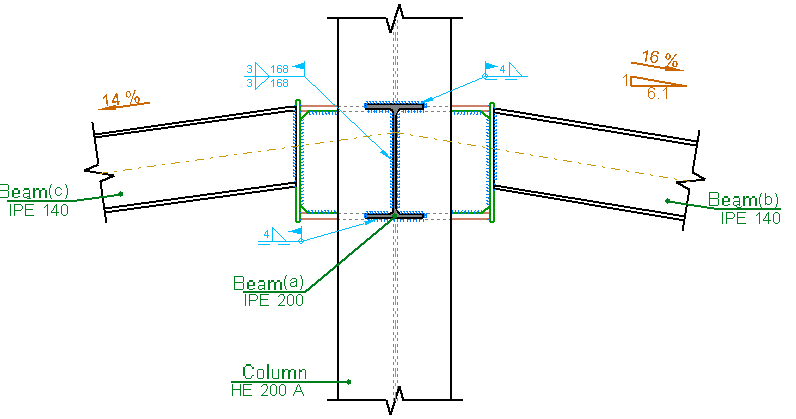
- Differing depths
Elements pinned or fixed to columns may have different depths. - Sloped beams
- Sloped beams at joints with elements fixed to the column web and flanges
In this case, the beams may be inclined with respect to the horizontal plane if the elevations of the top or bottom beam flanges coincide at the cut-off point of the joint. - Sloped beams at joints with elements fixed to the column flanges and pinned to the column web.
In this case, elements fixed to the columns may be inclined with respect to the horizontal plane if the joint occurs at the end of a column. At floor level or at intermediated column spans, these beams must be horizontal. To be able to design these joints with sloped beams at any column span, the user license must have the necessary permits to be able to use the Joints I module.
- Sloped beams at joints with elements fixed to the column web and flanges
Beam to column moment connections
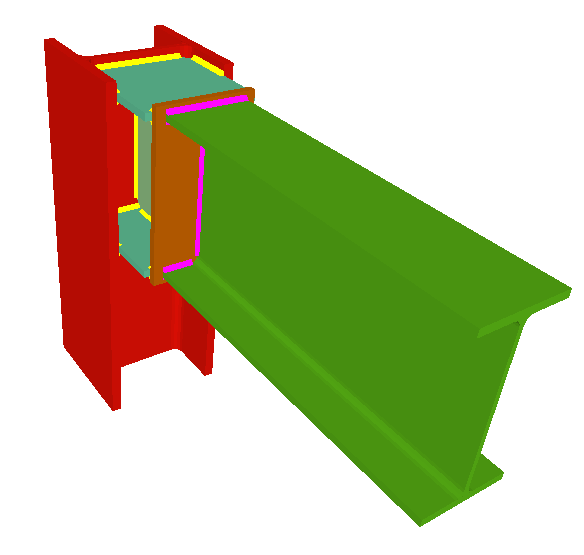
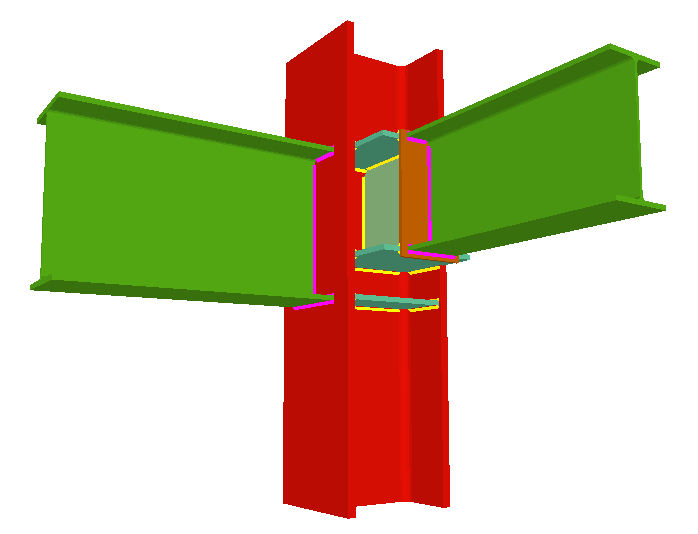
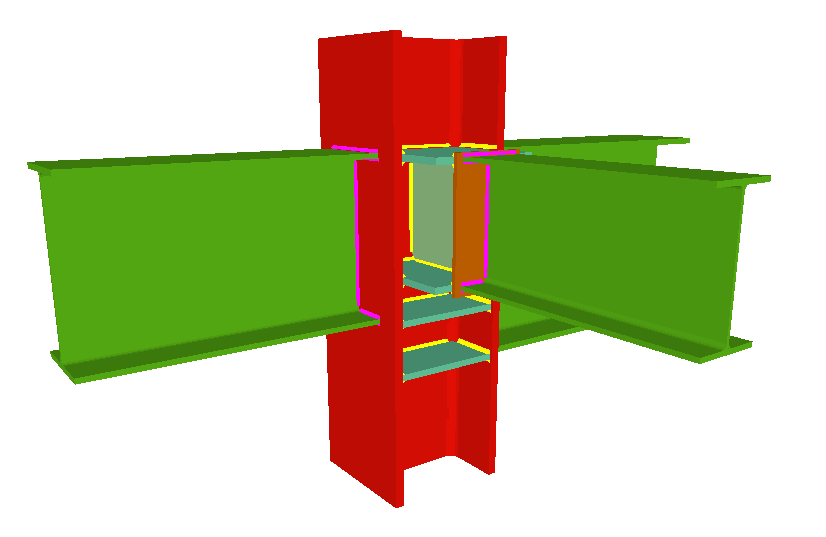
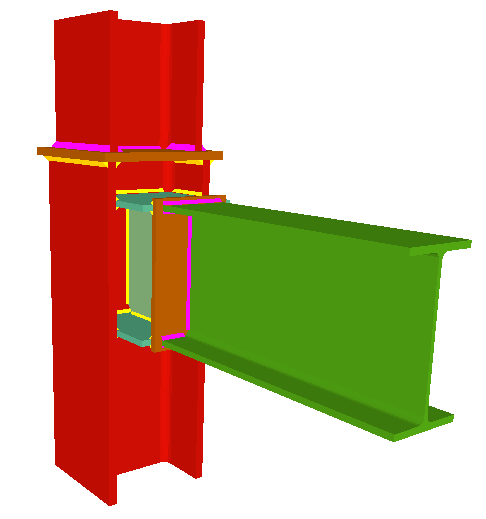
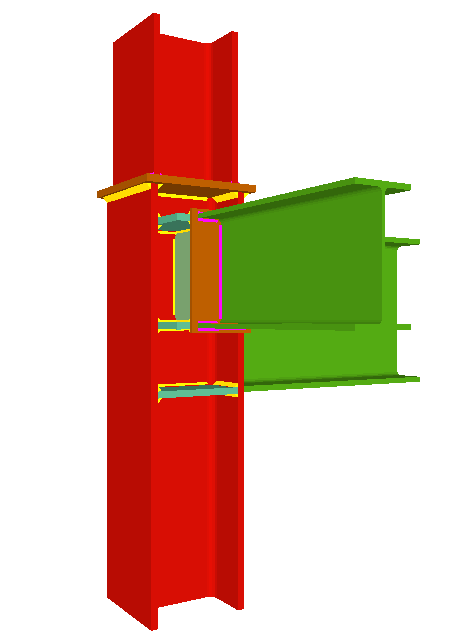
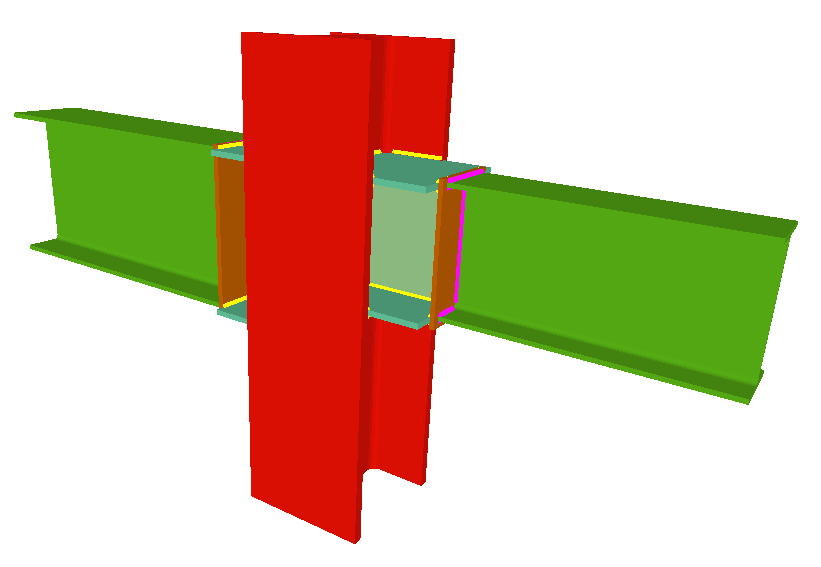
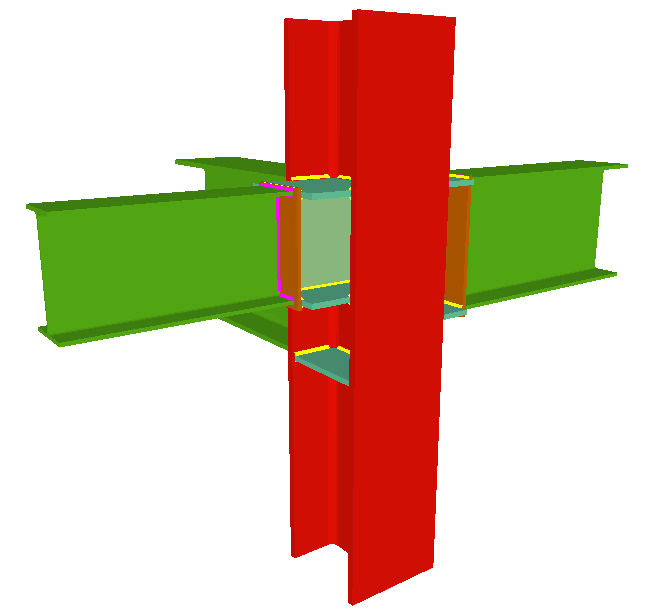
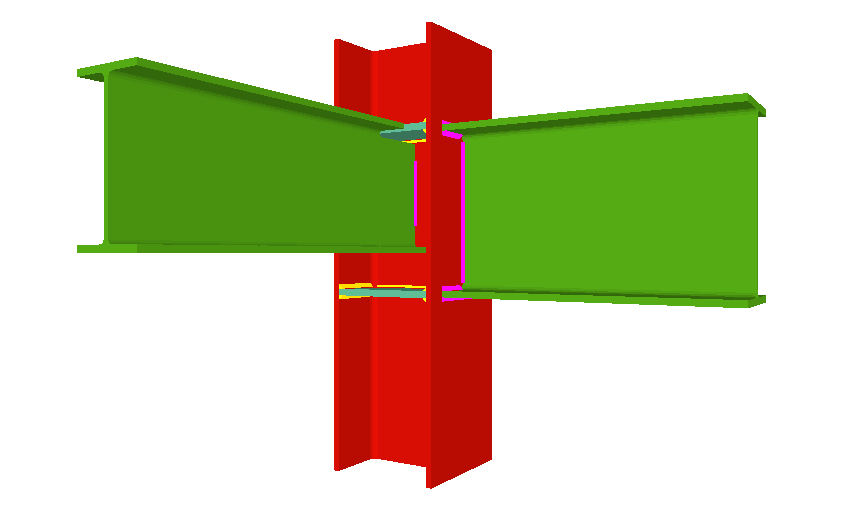
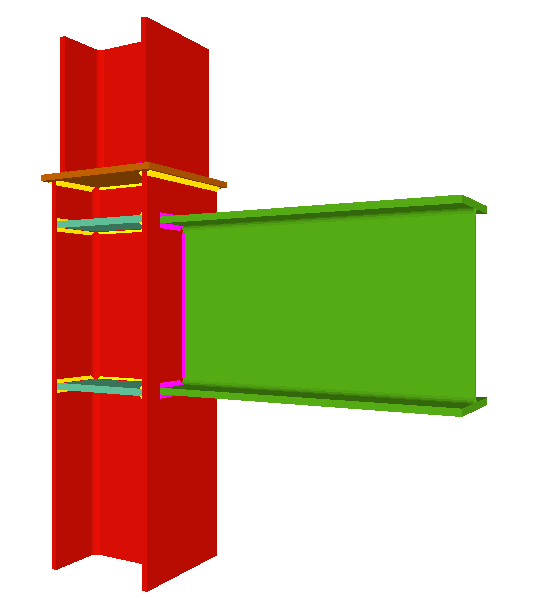
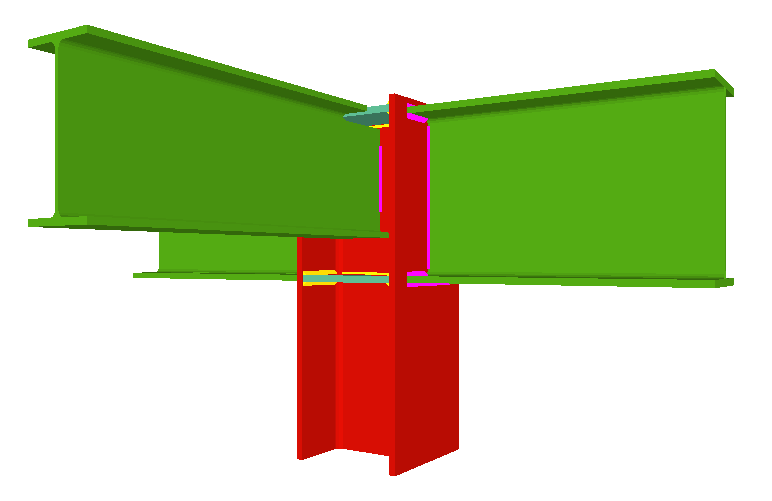
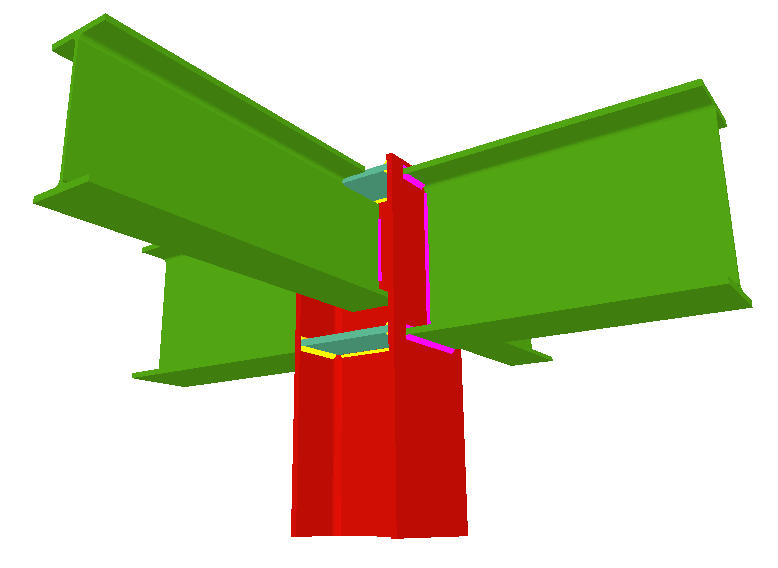
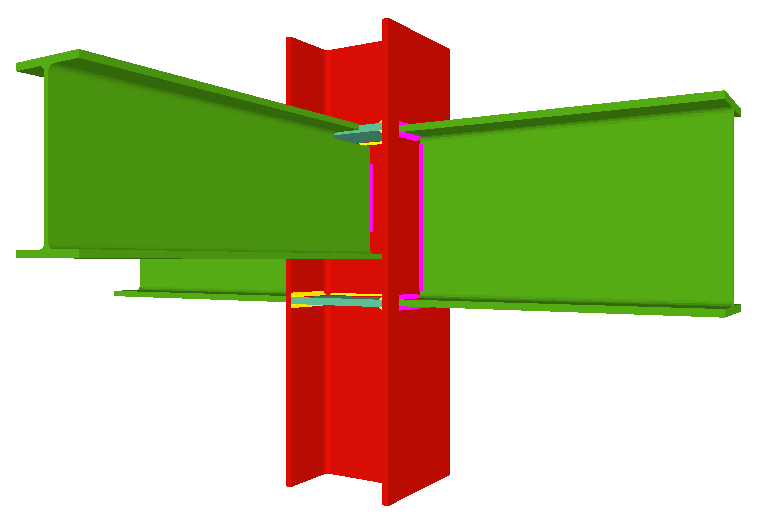
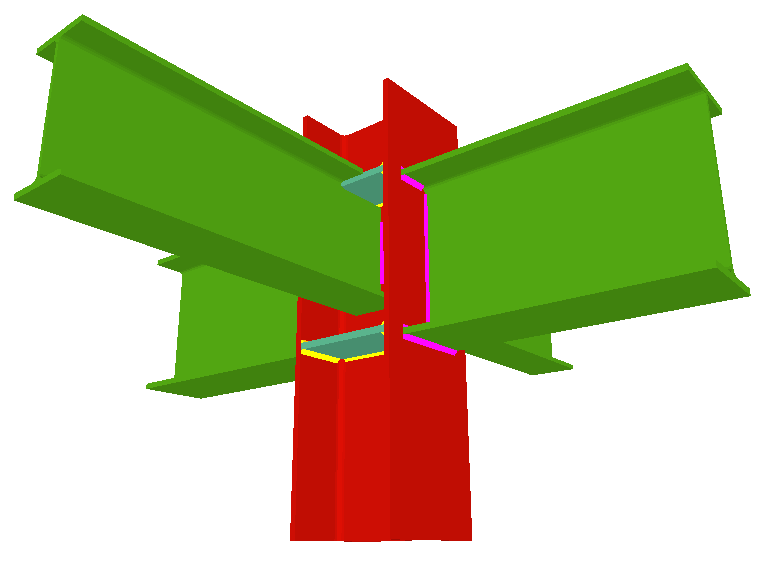
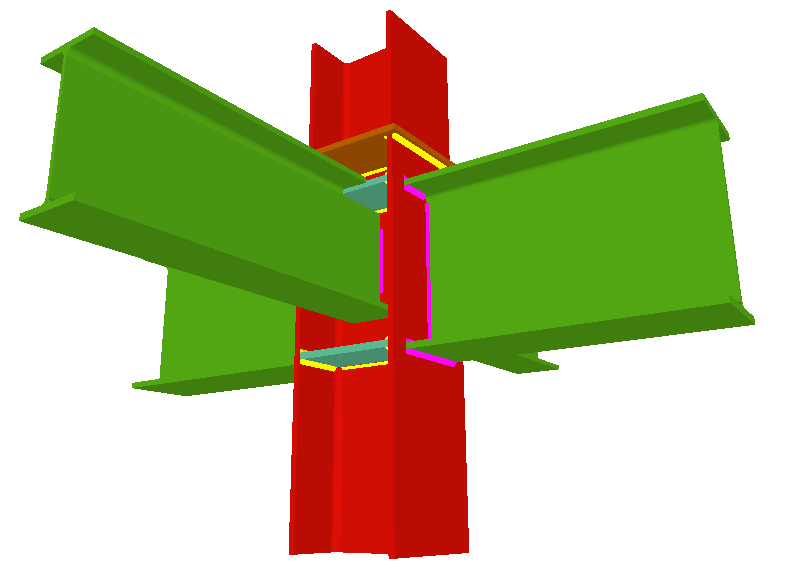
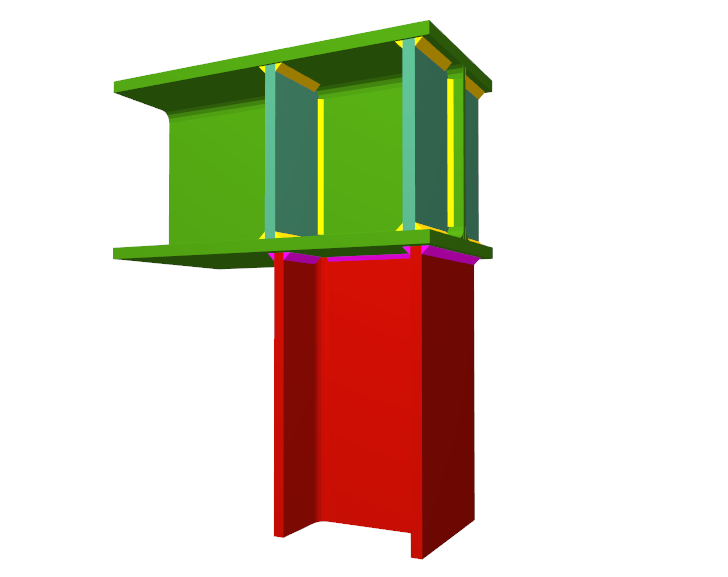
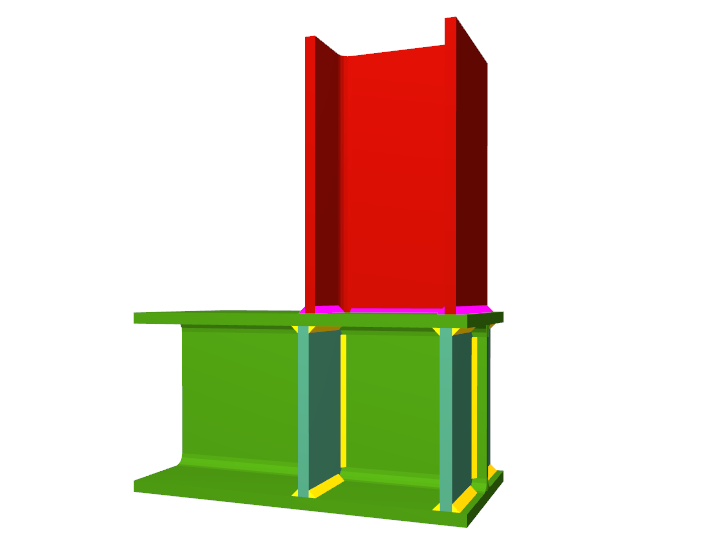
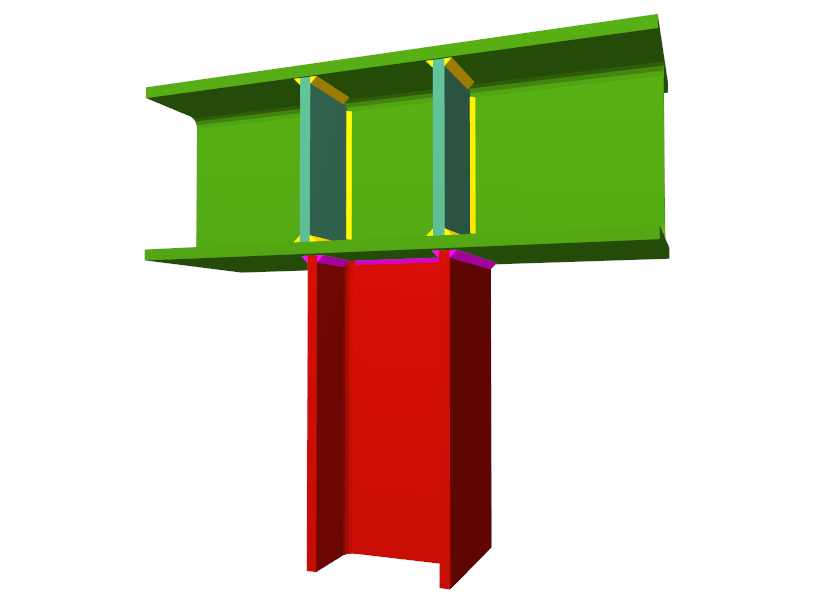
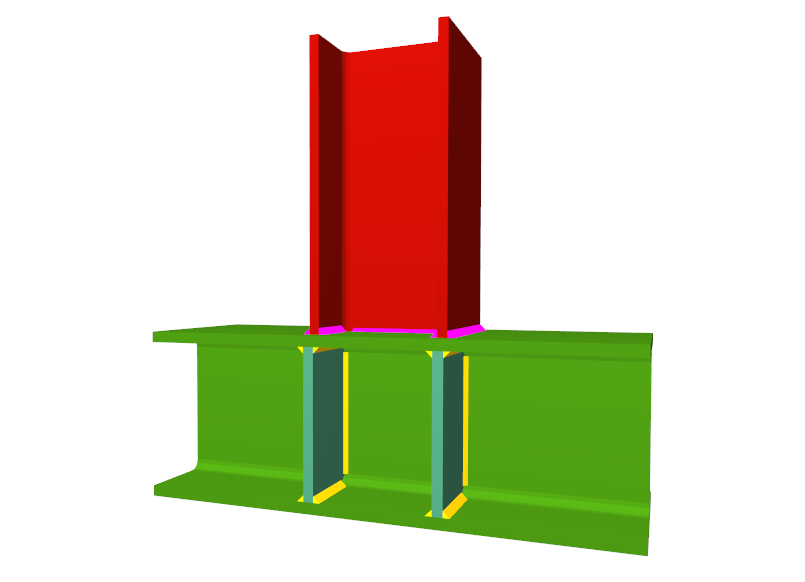
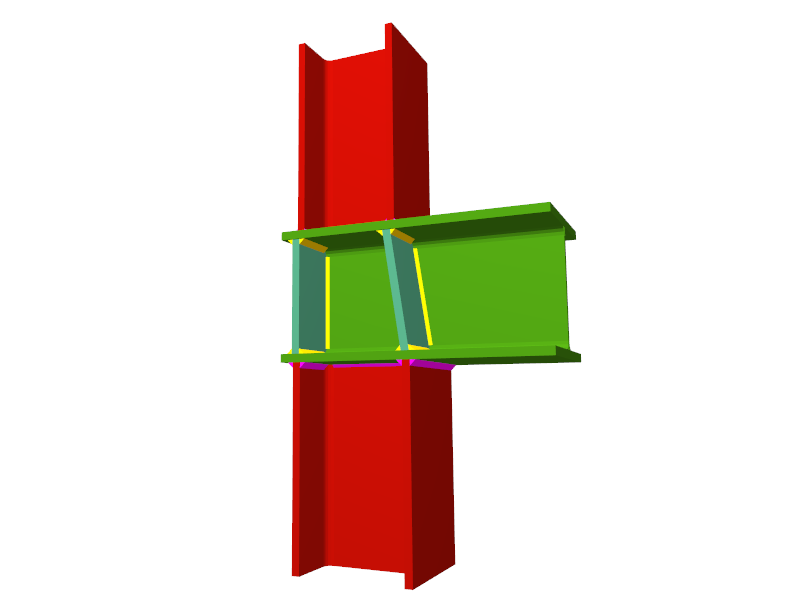
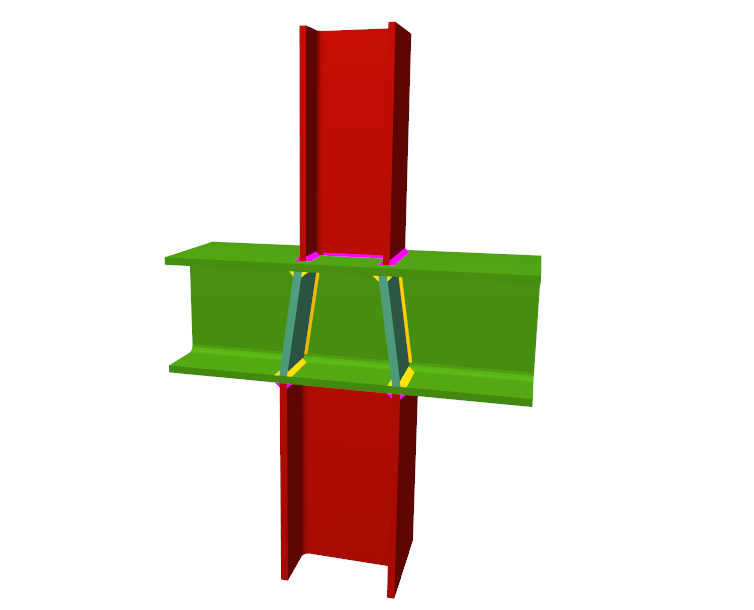
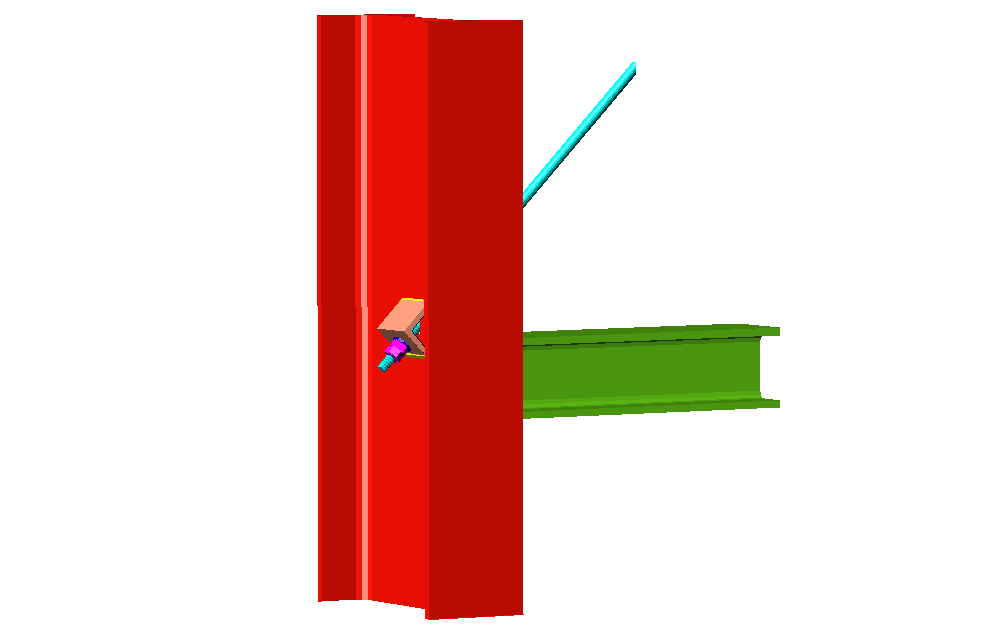
Using the Joints III module, joints consisting of beams fixed to the column web and flanges can be designed.
- Beams fixed to column flanges
- Stiffeners
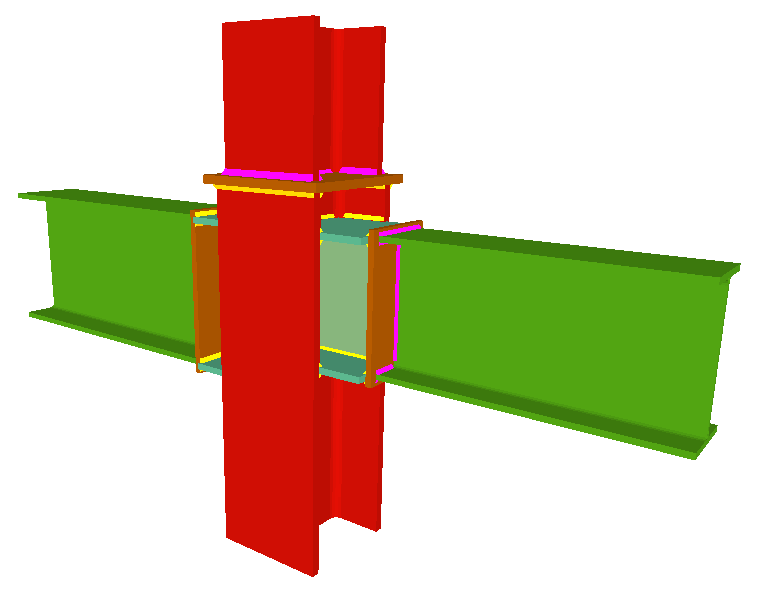
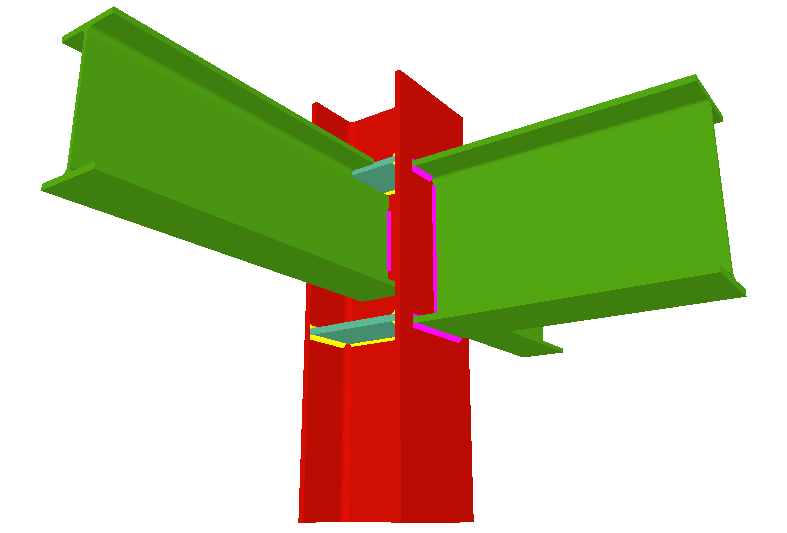
Stiffeners are always provided in correspondence with all the flanges.
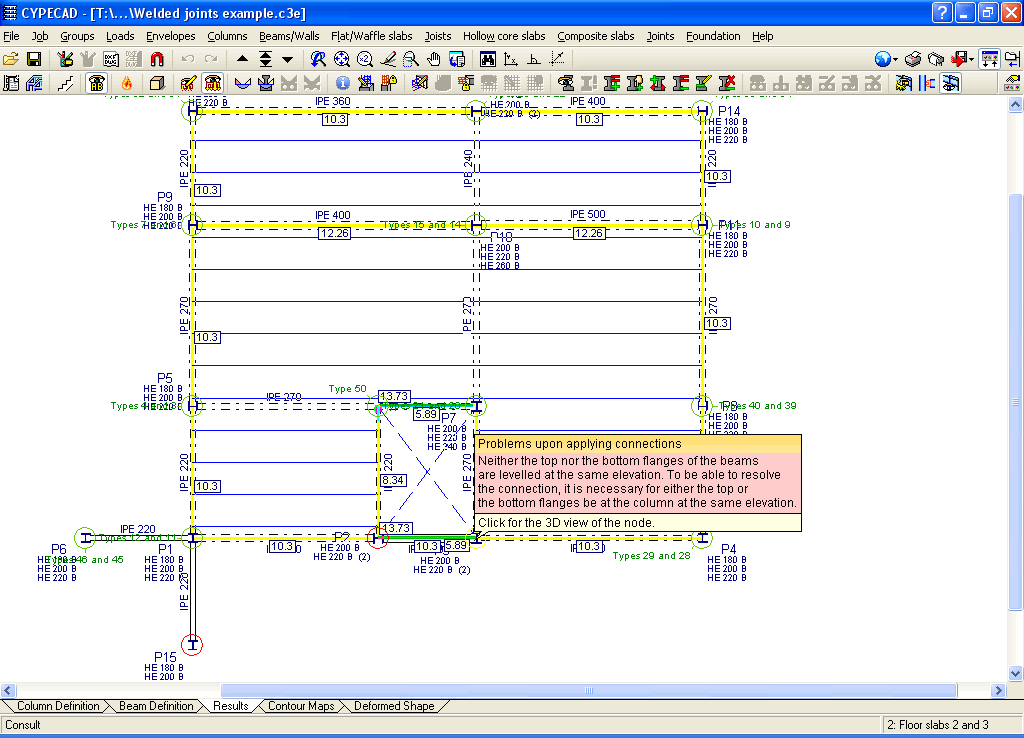
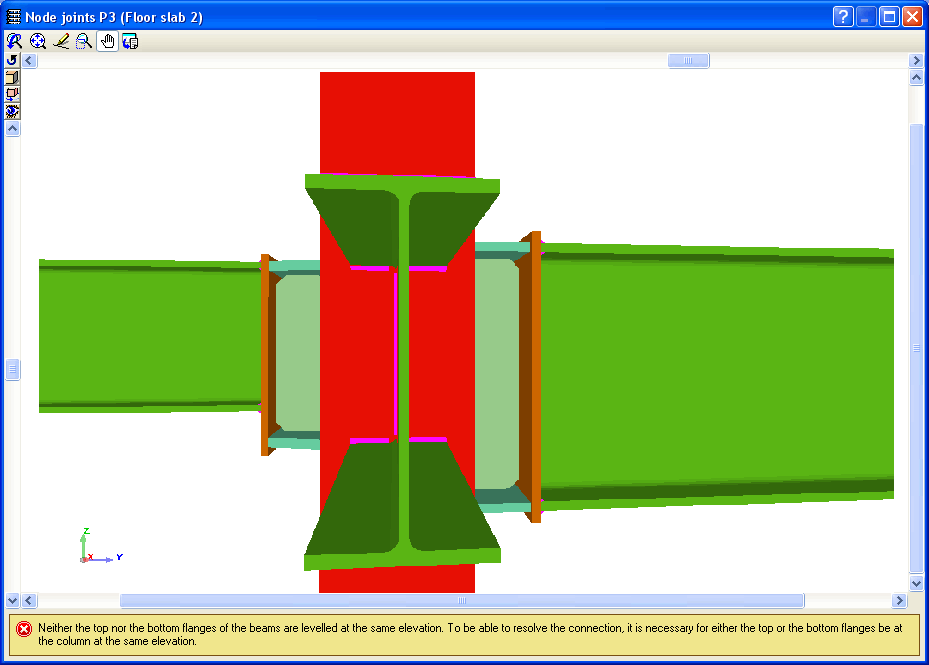
When the elevation difference between the beam flanges which are to be fixed to the column flanges is small, a stiffener cannot be welded correctly to each flange. In these cases, the Joints III module may design the joints using two construction solutions:- A single horizontal stiffener between both flanges. This is used when the free distance between the column flanges is less than or equal to the thickness of the stiffener.
- An inclined stiffener between the flanges. This is used when the free distance between the beam flanges is greater than the thickness of the stiffener and less than the distance which allows for two stiffeners (one for each flange) to be placed.
In these cases, the user must bear in mind that the program does not allow for a beam that is fixed to the web to bear on an inclined stiffener.
- Stiffeners
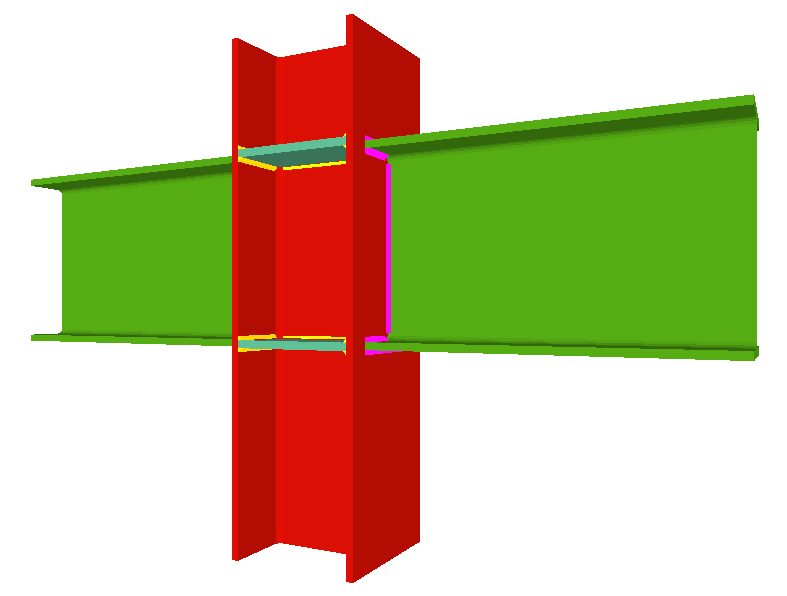
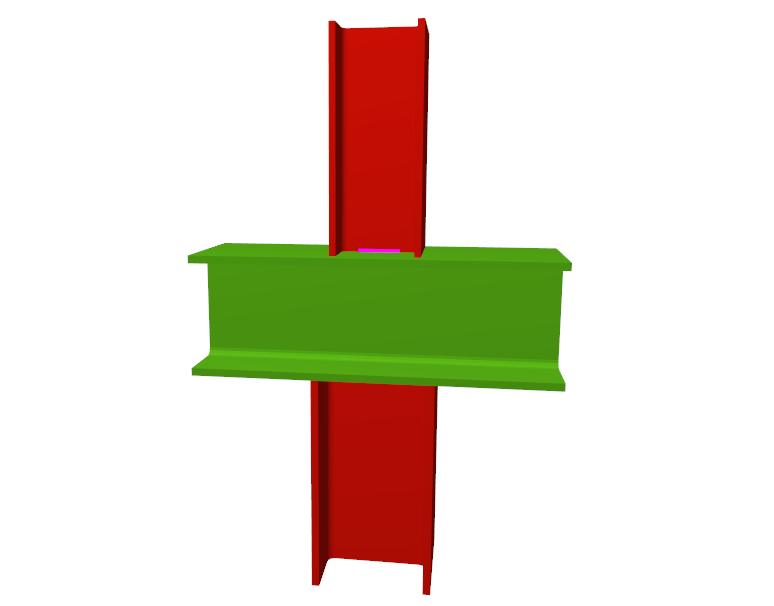
- Coplanar webs
The webs of the beams must be in the same plane as the column web - Haunches
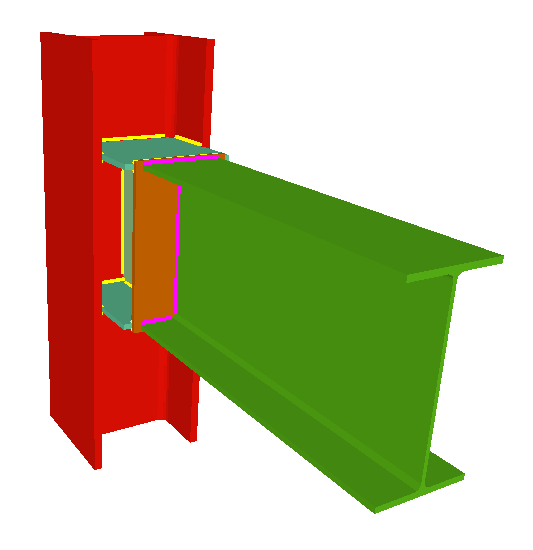
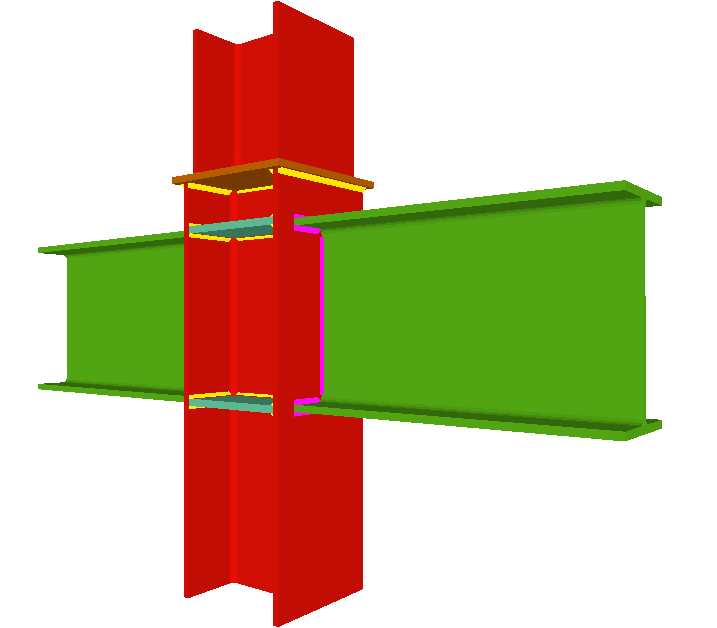
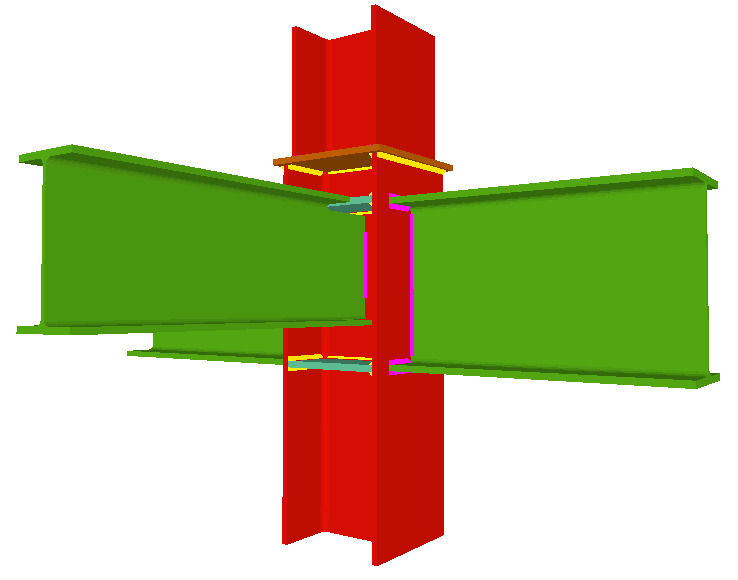
The Joints III module does not use haunches in its joint design, as they are not usually used in building frames. To be able to place haunches at elements fixed to column flanges, using CYPE 3D or the Integrated 3D structures of CYPECAD, the user license must have the necessary use permits for the Joints I (welded) and Joints II (bolted) modules. - Beams fixed to column webs
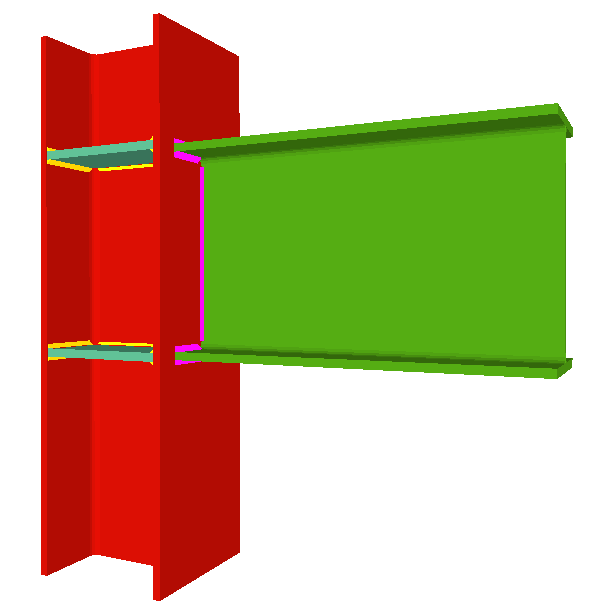
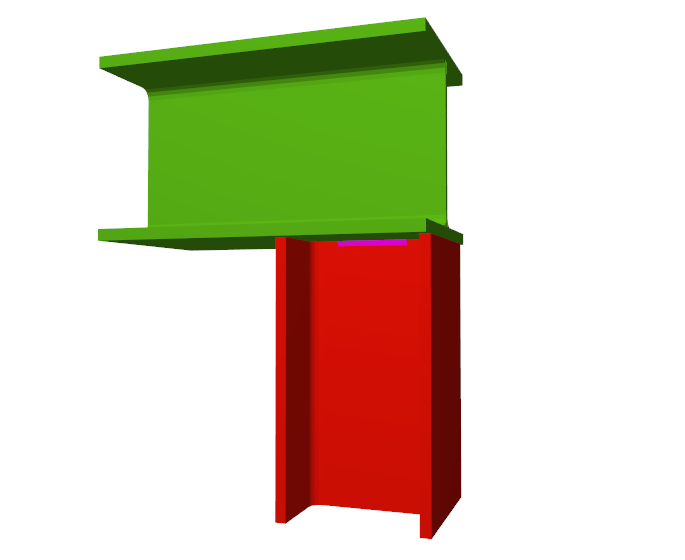
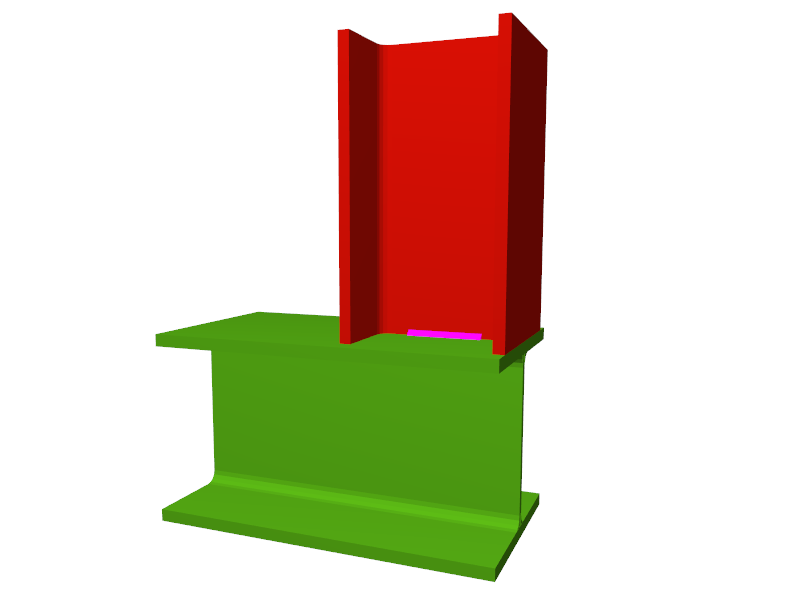
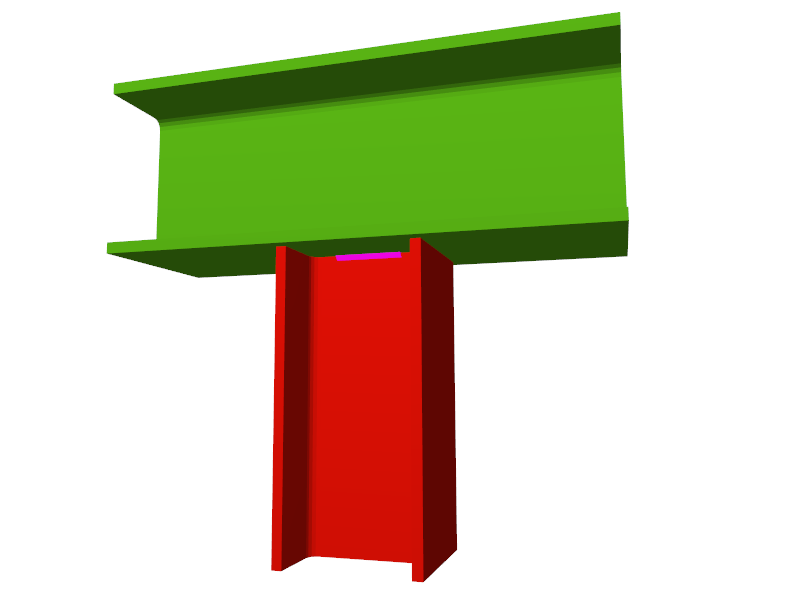
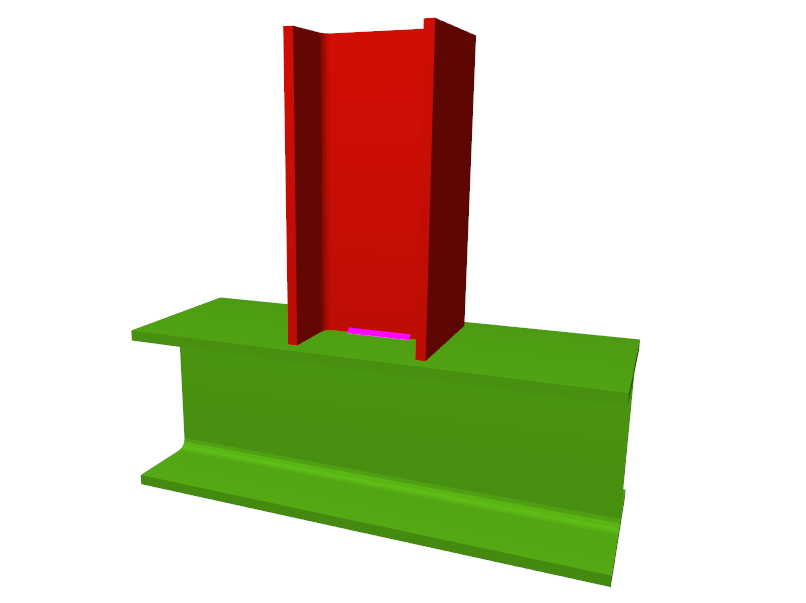
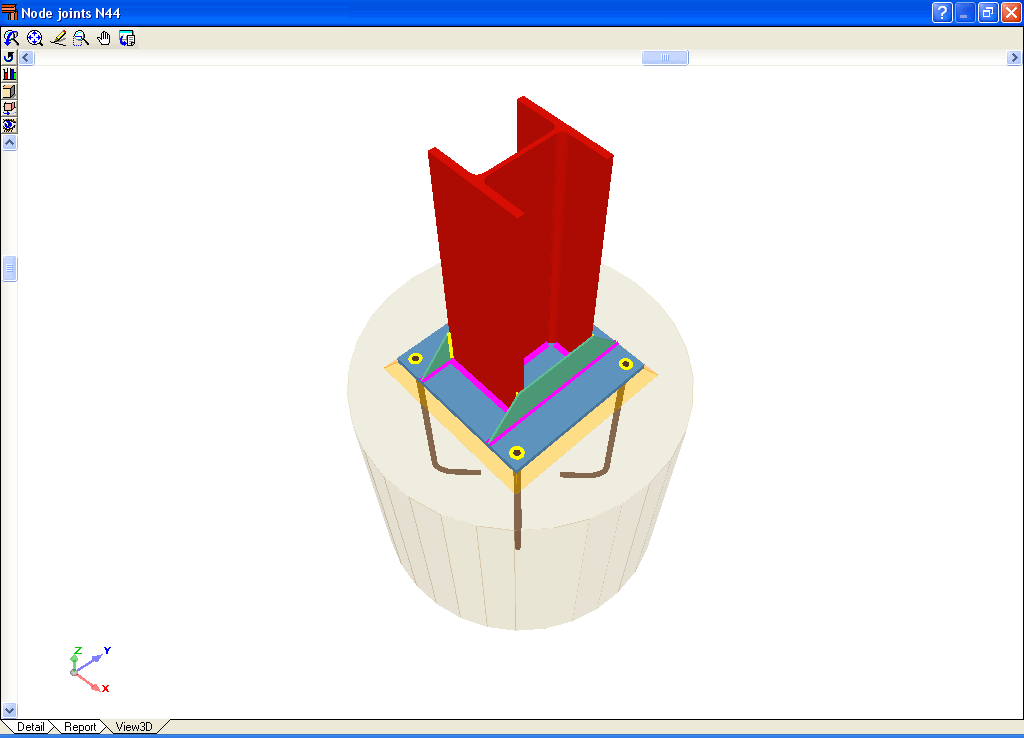
- Beams fixed to column webs bear on front plates, which are connected to the web of the column by means of the following welded elements:
- Plate perpendicular to the column web which allows the beam to behave as a continuous element between the front plate and the web of the column.
- Stiffeners in correspondence with the flanges of the beam fixed to the column web or with the stiffeners placed by the beams fixed to the column flanges.
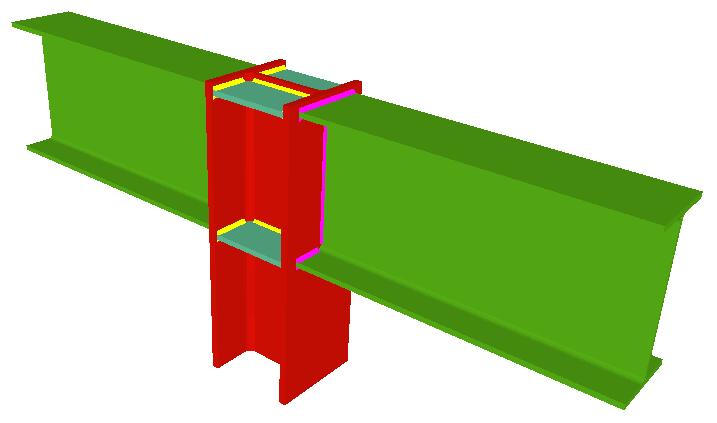
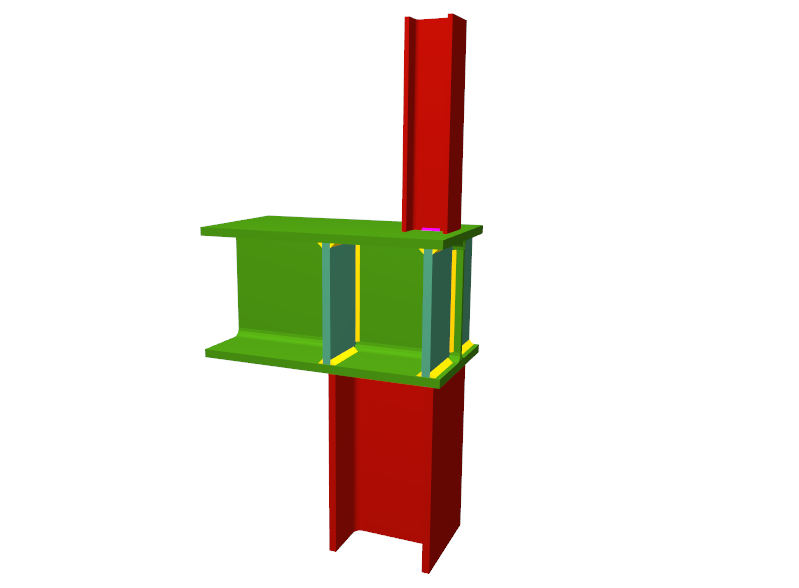
Beam to column simple connections
For the Joints III module to design a node containing beams pinned to the column, at least one of the beam to column connections must be a moment connection, except for when the joint is a 'Beam to column web welded simple connection at the last span of the column'.
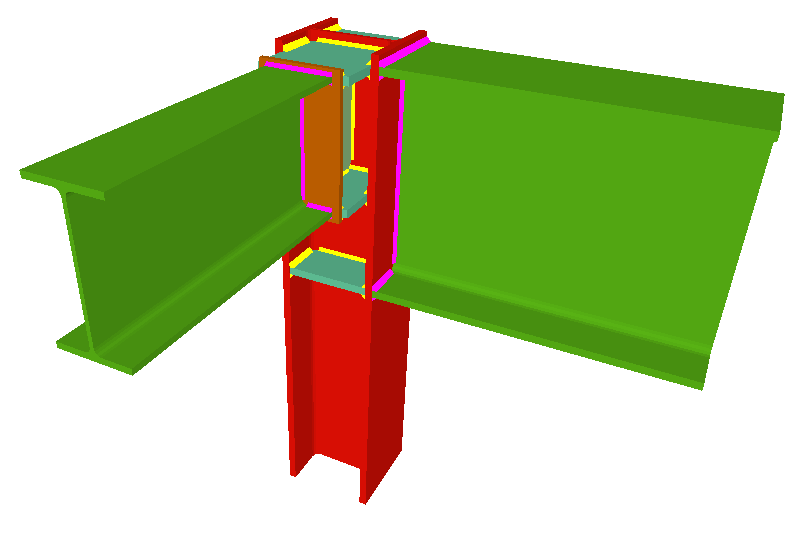
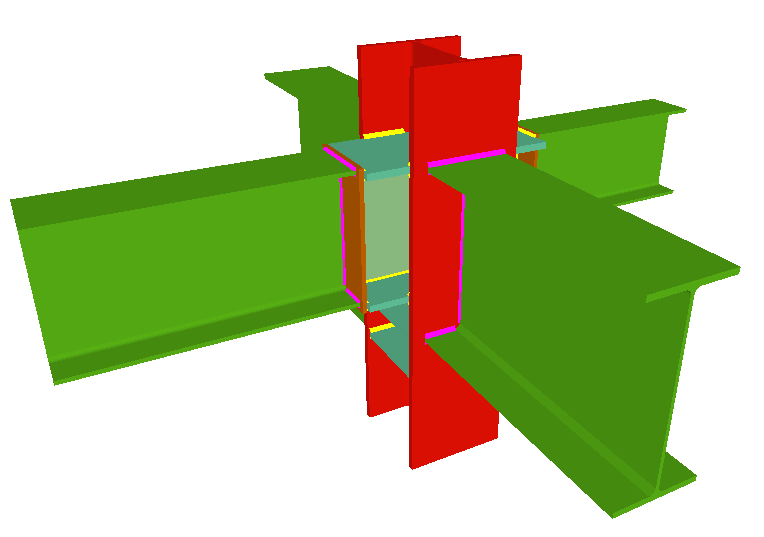
Moment connection between beams with coplanar webs
Using the Joints III module, a joint containing two beams with coplanar webs can be designed with the following conditions:
- Two extended beams (beam overlap) in any direction and with the same depth.
- One of the beams is horizontal and the other may have an ascending or descending inclination. The depths of the beams may differ and the flanges do not necessarily have to coincide, as long as the flanges of the beam with the smaller depth are contained between the flanges of the other beam.
- Haunches are not provided.
Non-deformable bar ends
When welded or bolted connections are designed or when the structure is designed with the joints, the program analyses, for each node of the job, the spatial layout of the bars and the fixity conditions. The program then determines the dimensions of the nodes and generates the rigid ends in which the portions of the bars are considered to be non-deformable due to them being contained within the node.
Consulting welded joints
Following the analysis, the joints that have been designed by the program can be consulted.
CYPE 3D and CYPECAD place different coloured circles at the nodes to indicate whether or not all the connections of the node have been designed, if there are only a few that have been designed or if the node does not contain any designed connections.
If the cursor is brought close to a node in which there are connections that have been designed, an information window will appear indicating the types of connections designed for that node. By clicking on the node a dialogue box with three tabs is displayed containing the following information:
- The construction details of the resolved connections
- A report of the checks and take-off of the resolved connections
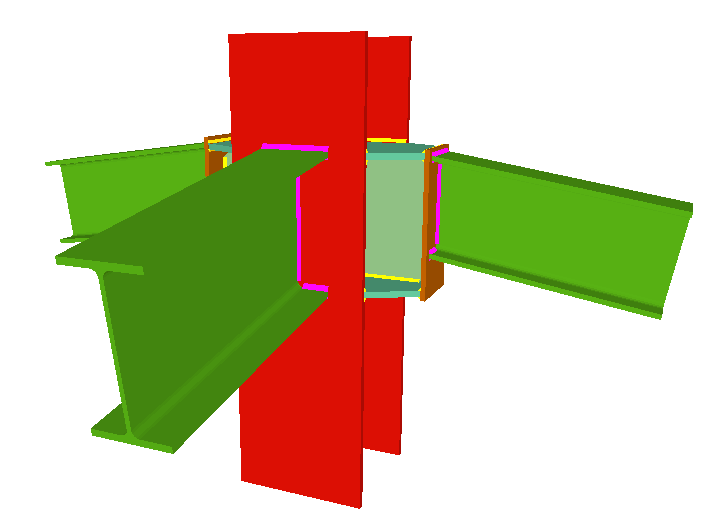
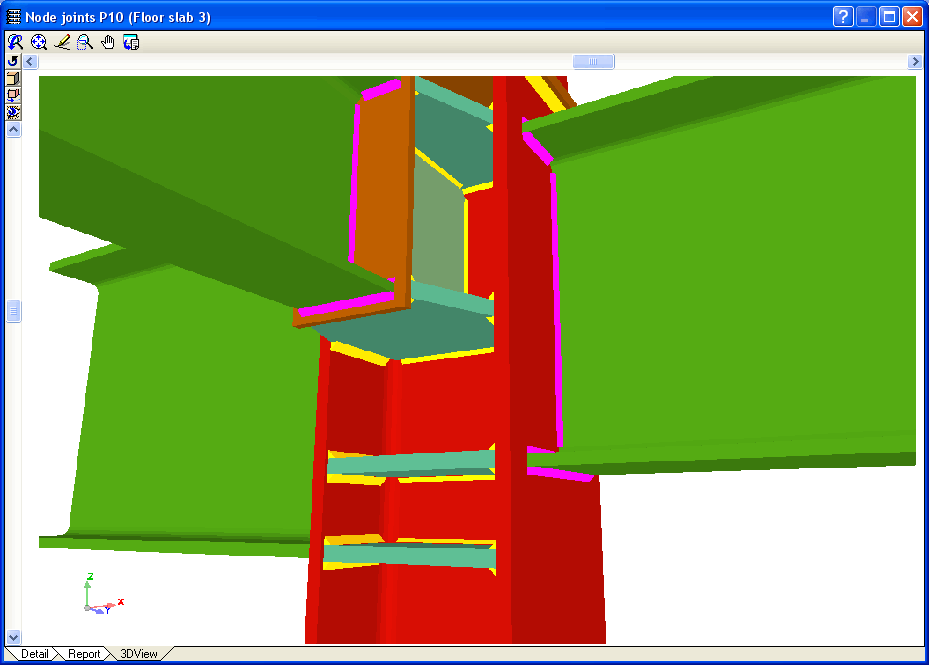
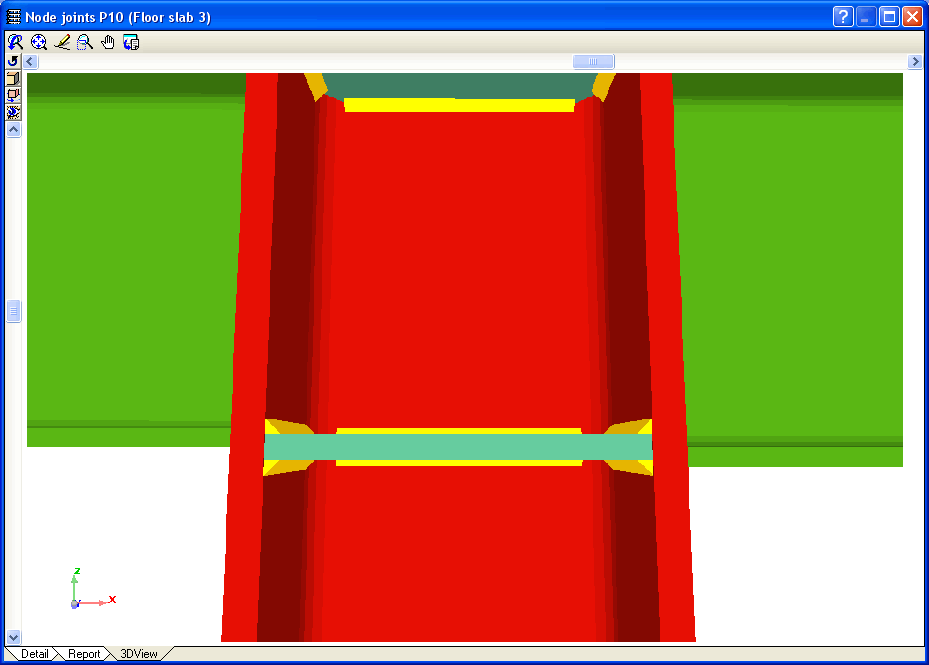
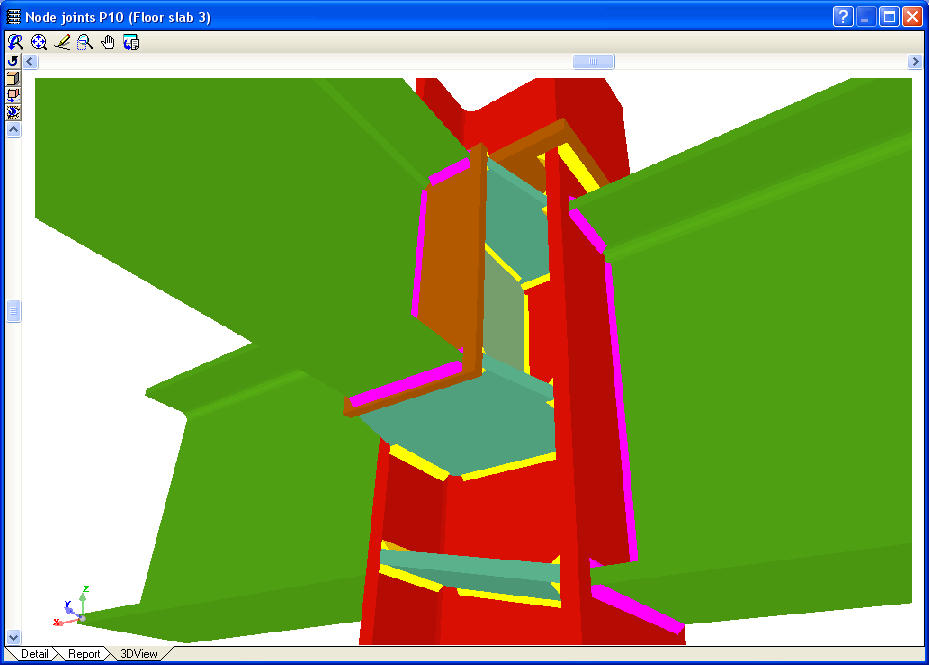
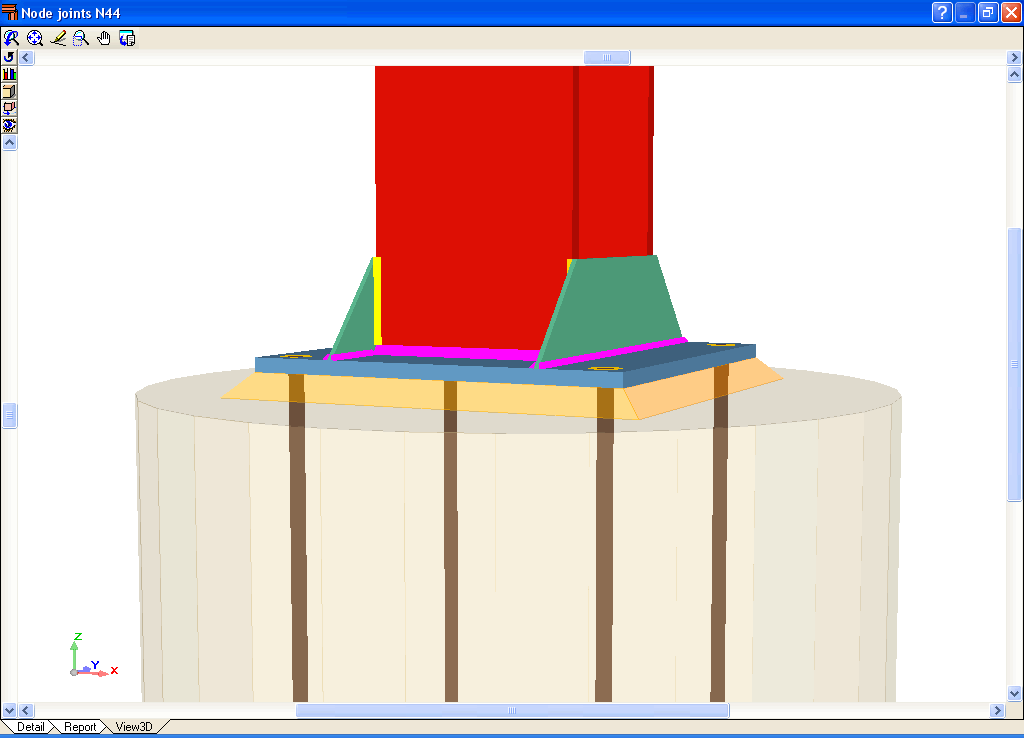
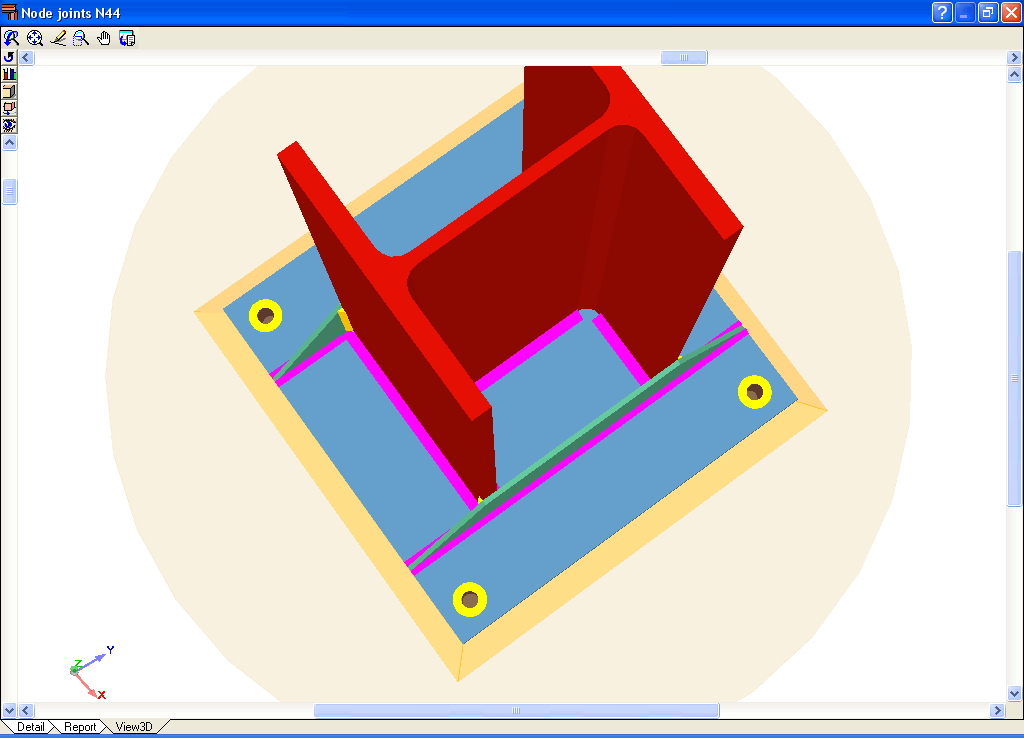
- Real 3D views of the connections. It is possible to visualise a 3D view of each connection designed by the program with an isometric or conical perspective. The elements making up the joint (columns, beams, stiffeners, welds, bolts and plates) are drawn in different colours. Prestressed bolts and non-prestressed bolts are also represented in two colours to differentiate between them. The user may also freely rotate and amplify the 3D view. These characteristics greatly help the user to understand the assembly of the joint. The 3D view of the joints can be visualised by selecting the 3D view tab that appears in the bottom part of the window that is activated upon consulting the joint.
If the cursor is brought close to a node in which there are no designed connections, but belongs to one of the connections recognised by the program, a window appears informing of the causes that have prevented that joint from being designed.
Even if the user license has not acquired the joints modules, the program allows the user to activate the joint design process. Once the process has concluded, the user can see the 3D views of the joints that could be resolved with the non-acquired modules, even though neither the joint details, check reports nor take-off reports are displayed. When the cursor is placed over one of these nodes, a warning appears indicating the non-acquired modules used to design the joint.
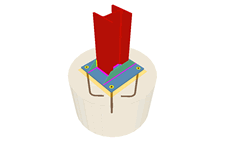
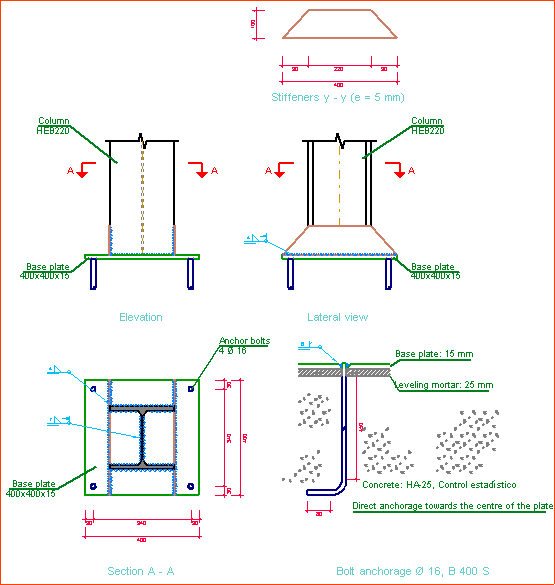
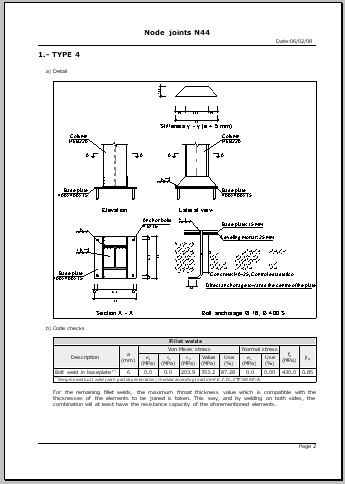
Baseplates designed using the Joints III module
The Joints III. Welded – Building frames with rolled and welded steel I sections designs baseplates on footings, piles and mat foundations.
The Joints III module also designs the baseplate connection points of integrated 3D structures, if these are located on footings, pile caps, slabs, shear walls, walls, concrete columns or beams (in the case of these last four elements, they are designed if no other steel beams or steel bars of the integrated 3D structures connect at that node).
The designed baseplate properties include:
- Type of baseplate: rolled and welded steel I section baseplates are designed
- Welds: Includes the analysis and design of plate, stiffener, column and bolt welds.
- Automatic match: Automatically matches the baseplates of the same job (bearing in mind the type of section, the forces and external fixities). This way and without the user having to intervene, the number of different types of plates is reduced, obtaining more uniform results.
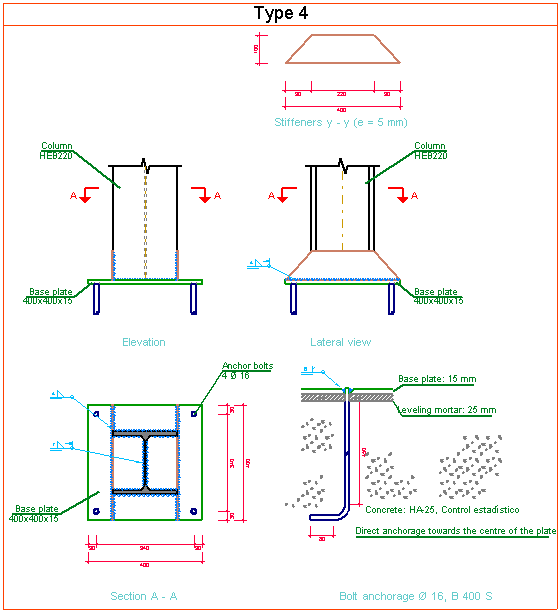
- 3D view with colour representation of the elements and welds: A 3D view can be seen on screen whereby the plate, column, stiffeners, bolts, and welds carried out on site and in the workshop are displayed in different colours, in the same way as with I section connections. This helps to obtain a better understanding of how the support is assembled.
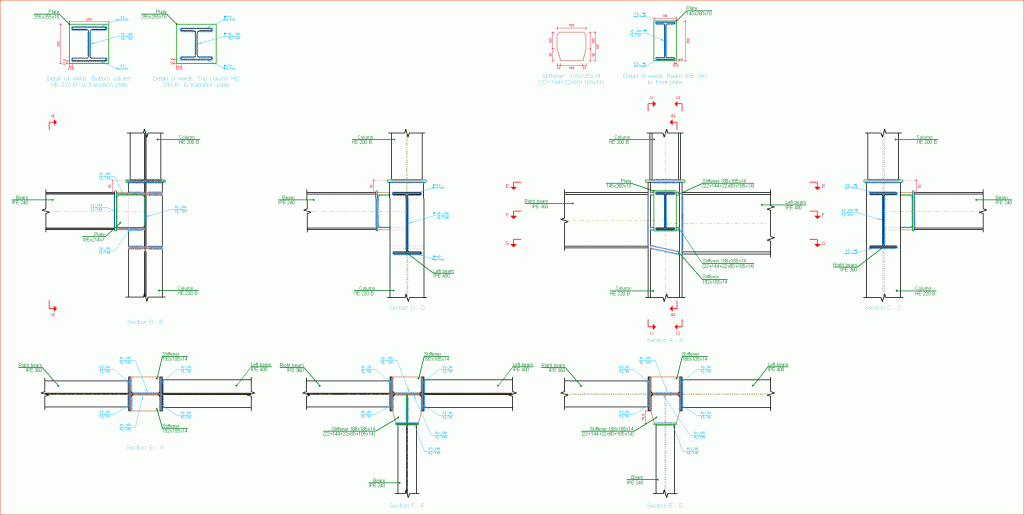
- Baseplate details: Baseplate details are generated in which the design weld details are displayed as well as those corresponding to the stiffeners. These details can be included in the job drawings.
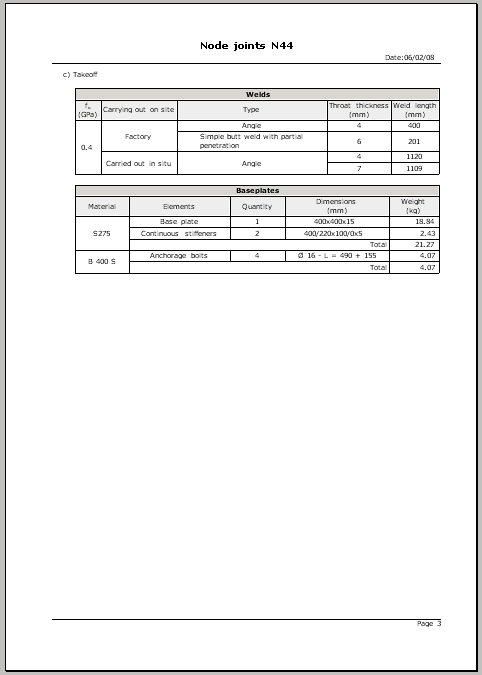
- Code check and takeoff reports: Code check and takeoff reports of the baseplates are generated, and integrated with the rest of the designed connections.
More information on baseplate design can be found in the Baseplate section of CYPE 3D.
Joints report
CYPE 3D and CYPECAD generate a joints report with the following data:
- Welded connections and specifications
- Code
- Materials
- Construction layout
- Checks
- References and symbols
- Baseplate checks
- Relationship of the designed joints
- Calculation report
- Construction detail of each type of joint
- Description of the components of each type of joint
- Check results of each type of connection
- Weld and plate take-off for each connection type
- Complete take-off of welds and plates of the designed joints
Joints drawings
The construction details of the joints designed by the program can form part of the drawings of the structure. The Joints drawings include the following elements:
- Construction detail of the joint
- Schedule with specifications of the welds in steel structures
- Code
- Materials
- Construction layout
- Checks
- Reference and symbols table
- Complete take-off of welds and plates of the designed joints
Implemented codes for the design of building welded connections
The following codes have been implemented in CYPECAD, CYPE 3D and Integrated 3D structures of CYPECAD for the design of welded joints in building frames:
- ABNT NBR 8800 (Brazil)
- ABNT NBR 8800:2008 (Brazil)
- ANSI/AISC 360-05 (LRFD) (USA - International)
- ANSI/AISC 360-10 (LRFD) (USA - International)
- CTE DB SE-A (Spain)
- EAE (Spain)
- Eurocode 3 EN 1993-1-8:2005 (General Document)
- Eurocode 3 NF EN 1993-1-8/NA:2007-07 (With National Application Document for France)
- Eurocode 3 NP EN 1993-1-8:2005/NA:2010 (With National Application Document for Portugal)
- Eurocode 3 UNI EN 1993-1-8:2005 (General Document adapted to Italy)
- IS 800:2007 (India)
- NTC: 14-01-2008 (Italy)
The corrections carried out by the European Committee for Standardization on Eurocode 3 (EN 1993-1-8:2005 / AC:2009) have also been implemented.
Depending on the country from which the licensee has acquired the license, each program will only activate the implemented design codes corresponding to that country. More information about this aspect and the possibility of acquiring additional codes is available under Programs and codes included in the user license.
Other features
In order to access further features offered by the program, there are several modules that can be found on the "CYPECAD modules" and "CYPE 3D modules" webpages.