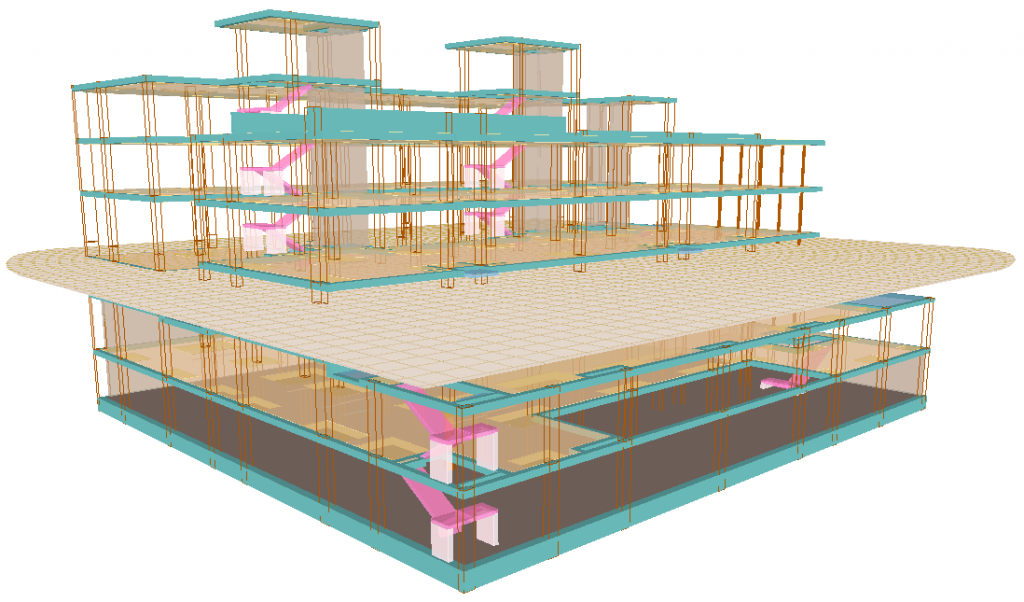
Analysed structural elements
Supports
The structural supports that CYPECAD analyses and designs are:
- Columns
- Reinforced concrete columns
Rectangular, circular, and polygonal section.
More information - Steel columns
Rolled, reinforced and cold-formed steel columns.
More information - Composite steel and concrete columns
Embedded concrete-cased sections or closed concrete-filled sections
More information - Timber columns
Rectangular or circular-section timber columns
More information
- Reinforced concrete columns
- Shear walls
More information
- Rectangular
- Any geometric shape composed of rectangles
- Rectangular
- Walls
- Reinforced concrete walls
- Plane stress walls
More information - Generic masonry walls
- Concrete block walls
These walls can be designed with or without reinforcement. Users can indicate the dimensions of the blocks or use blocks designed by manufacturers such as the Spanish company NORMABLOC which designs concrete blocks and masonry.
Some walls may contain openings. The program analyses the necessary reinforcement for the openings in the reinforced concrete walls (lintel, sills, lateral and diagonal walls) and the lintel reinforcement if there are openings in concrete block walls. Additionally, users can obtain reports of the checks that have been carried out during the reinforcement design process, which can be viewed on-screen and printed out.
The crown beam is also designed for all types of walls as is the intermediate beam at floor level in the case of generic masonry walls and concrete block walls.
- Reinforced concrete walls
Beams
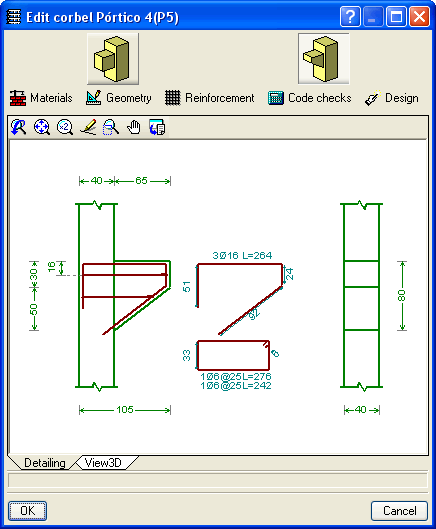
Floor slabs may be composed of reinforced concrete, steel (normal or castellated), composite and timber. Corbels can also be introduced.
- Concrete beams
More information - Steel and composite beams
More information - Timber beams
More information
Slabs
The following types of slabs can be designed in CYPECAD:
- One-way
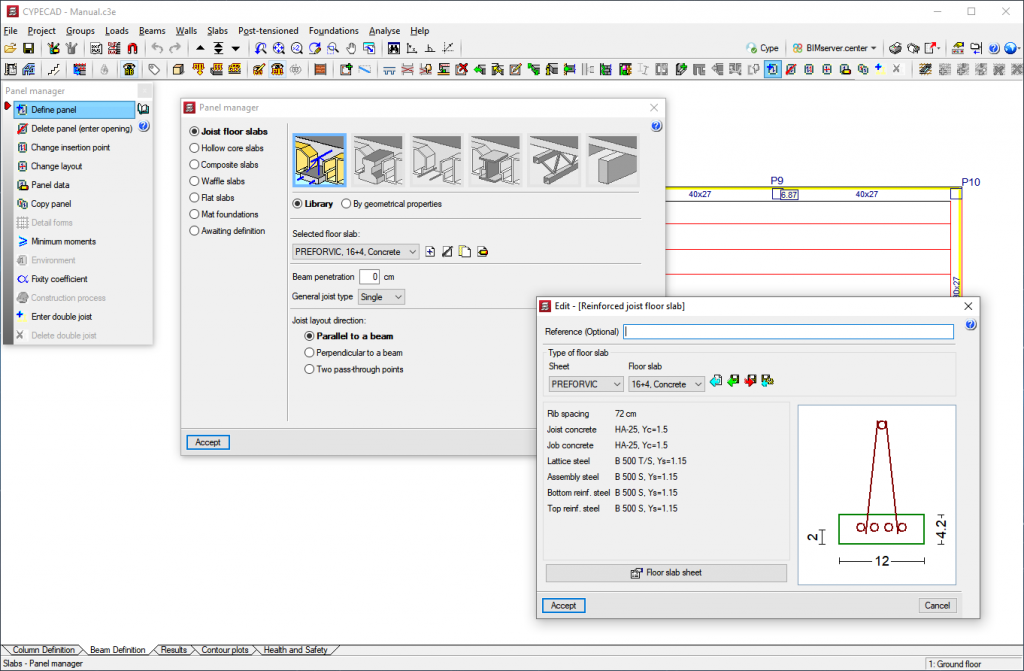
- Concrete joists
- Reinforced precast
- Precast prestressed
- Reinforced in-situ
- Post-tensioned in-situ
- Steel joists
- Timber joists
More information - Steel lattice
- Concrete joists
- Flat slabs
- Reinforced
More information - Post-tensioned
More information
- Reinforced
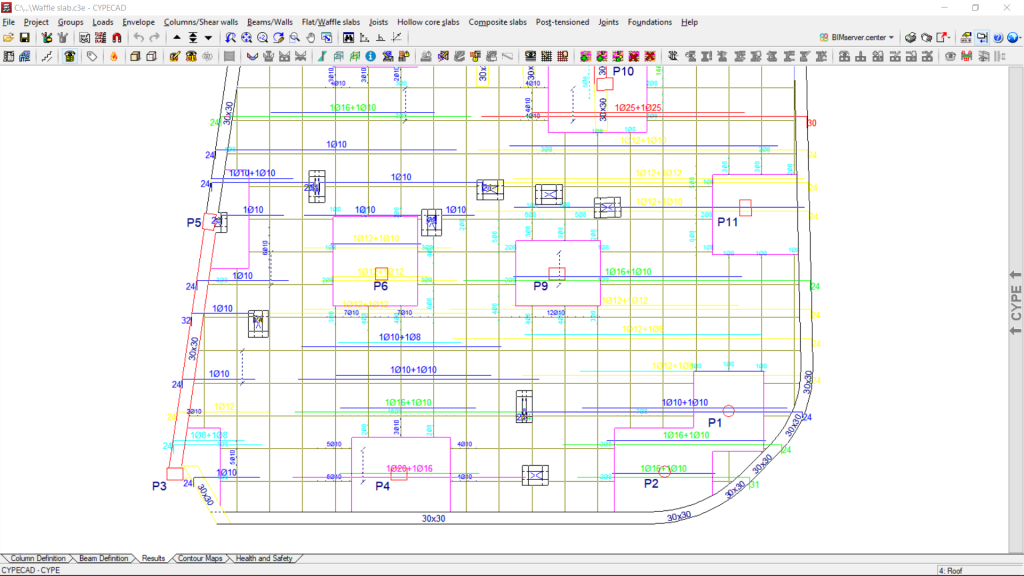
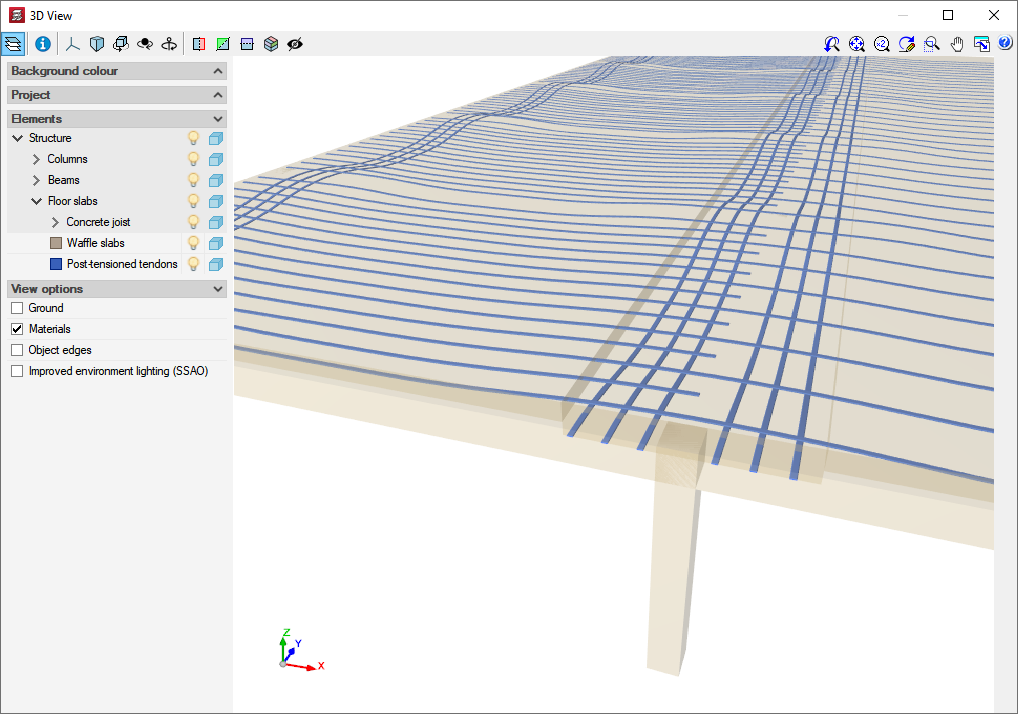
- Waffle slabs
- Reinforced
- Post-tensioned
More information
- Hollow-core slab
More information - Composite slabs (steel deck)
More information
CYPECAD allows users to check the ultimate limit state for punching shear of waffle and flat slabs, and mat foundations using two methods: point tangential stress tests and in accordance with design code criteria.
More information on Punching shear verification.
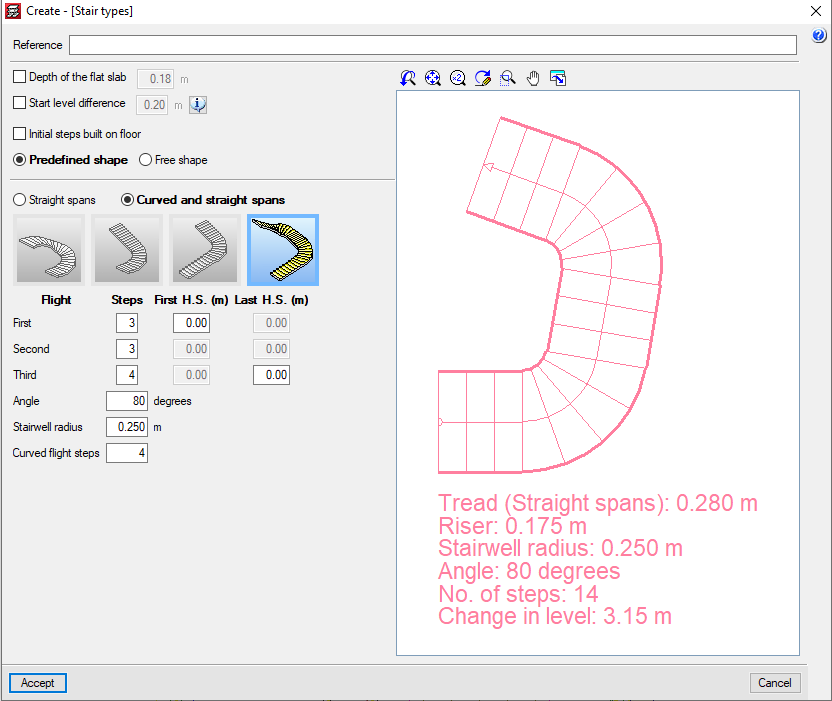
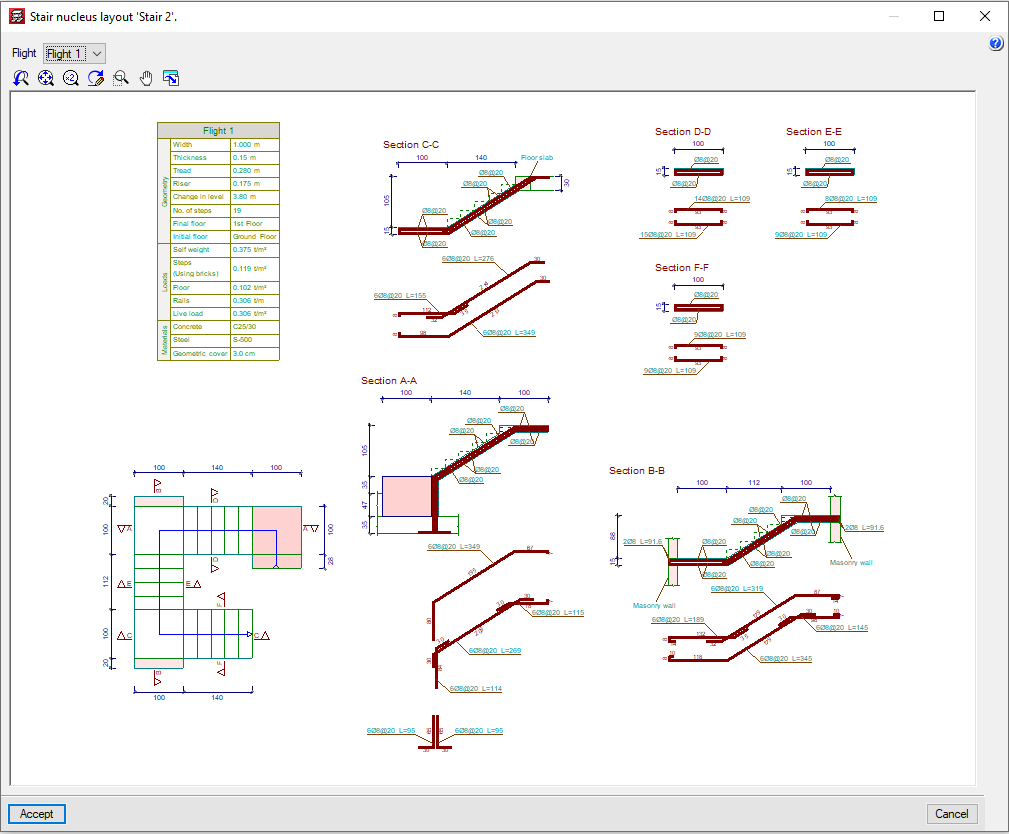
Stairs
CYPECAD analyses and designs straight and curved stair slab reinforcement as isolated elements of the structures. The program establishes the reactions on the main structure based on geometry, type, and arrangement of the supports, and applied gravitational loads, which are then applied as line and surface loads (for the steps built on the floor) in the dead and live load loadcases.
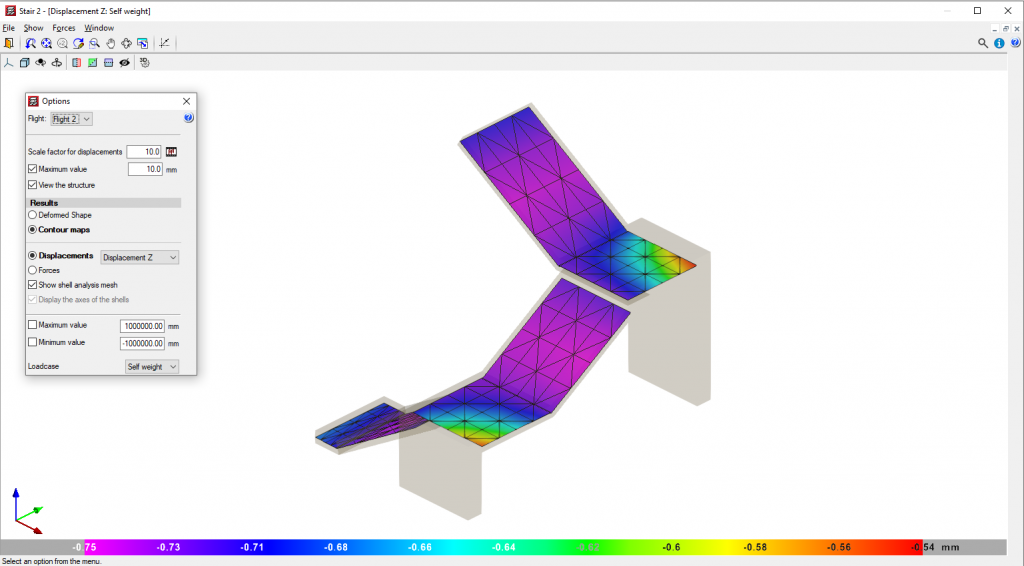
The program designs stairs using the finite element method, using the two usual loadcases when designing stairs: permanent loading and live loading.
CYPECAD displays the reinforcement of each span of the stairwell on screen. It is also possible to view the displacements, forces, and deformed shape of each span in 3D.
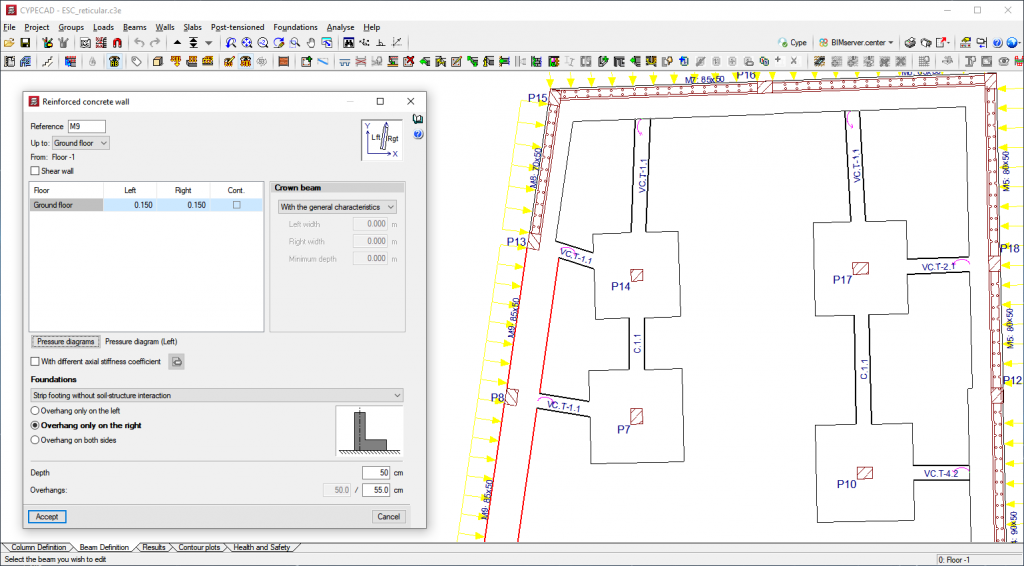
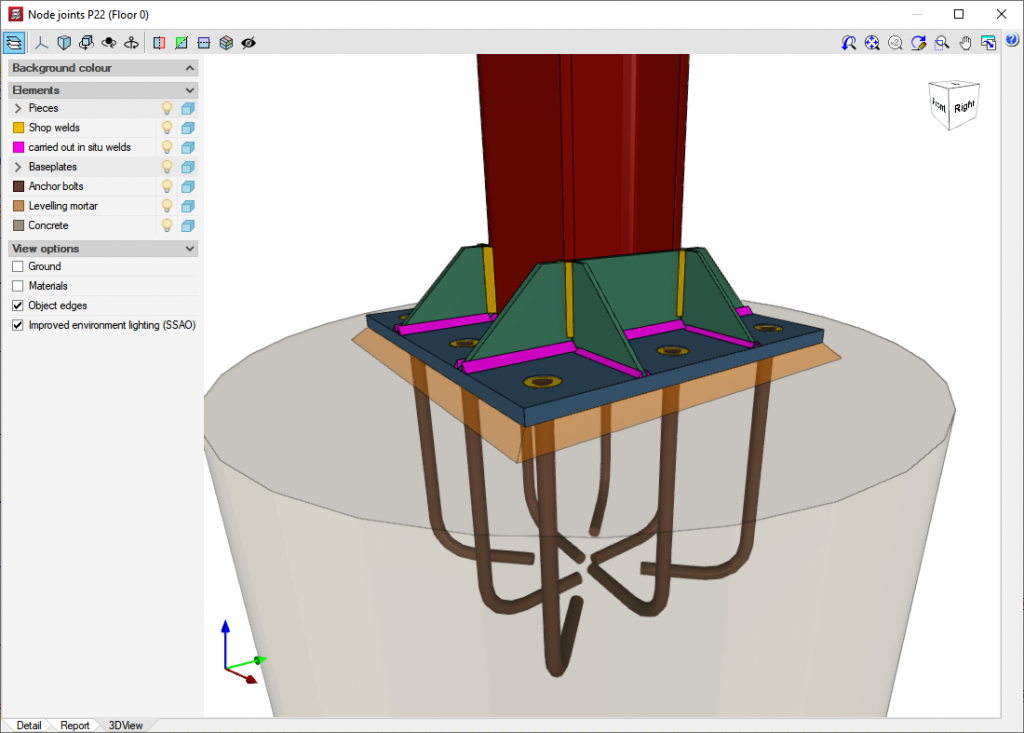
Foundation
The foundations designed by CYPECAD can be: fixed (with footings or pile caps) or floating (with mat foundations and foundation beams, where users have to define the subgrade modulus when applying the Winkler theory).
Additionally, the program allows users to analyse the foundations alone (without inserting a superstructure) by defining column starts.
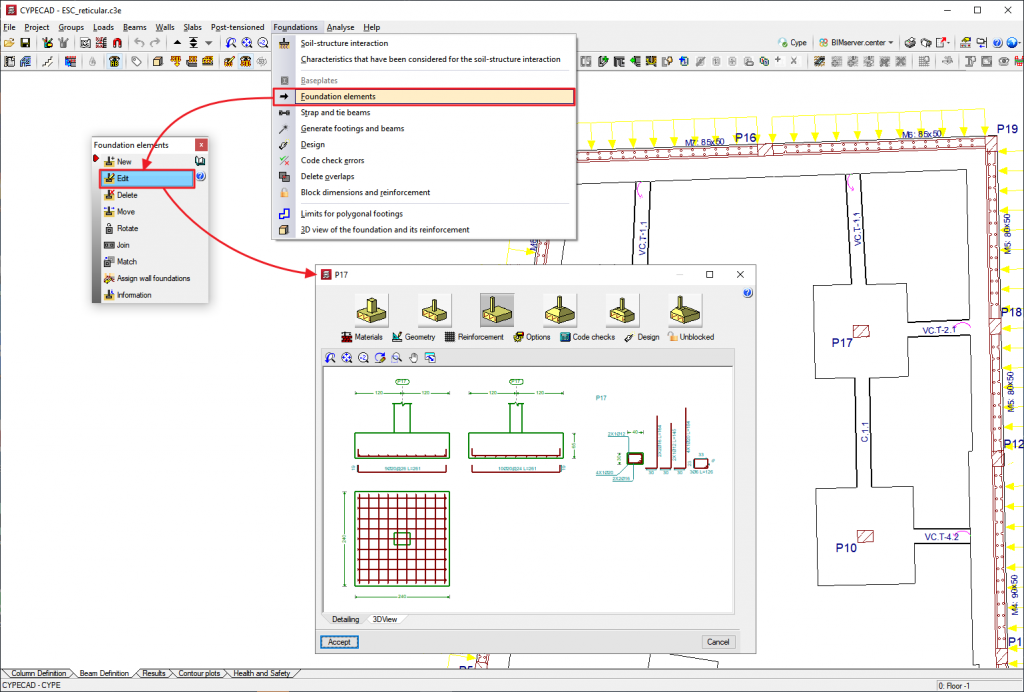
- Pad footings
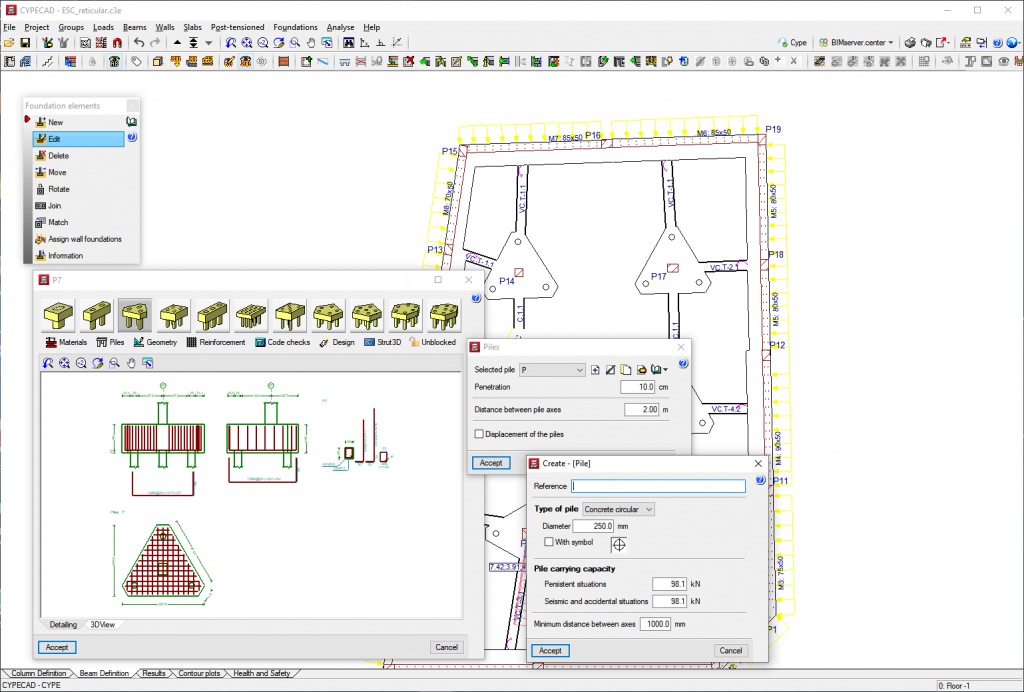
These can consist of reinforced concrete or mass concrete, be for a single or combined for multiple supports (columns, shear walls and walls), which can be placed freely on the foundation element. - Pile caps
They can hold a number of supports (columns, shear walls and walls), and can be placed freely on the foundation element.
A wide range of types are available:
- Rectangular pile caps for one, two, four and five piles
- Triangular pile caps for three piles
- Strip pile caps for three to thirty piles
- Rectangular pile caps for multiple piles (grid distribution from three to thirty piles per side)
- Pentagonal pile caps for five or six piles
- Hexagonal pile caps for six or seven piles
- Strap beams and tie beams
Act on footings and pile caps. - Mat foundations and foundation beams
The mat foundations and foundation beams are considered to be supported on an elastic foundation (ballast coefficient method), according to the Winkler model, based on a constant of proportions between forces and displacements, the value of which is the ballast coefficient.
Foundation beams and mat foundations are part of the overall structure and therefore interact with the rest of the structure (they are part of the overall stiffness matrix of the structure). Therefore, loads can be applied to these elements, as well as to any beam or slab of the structure they are part of.
The limit states to be checked are those applicable to the design of reinforced concrete elements (ultimate limit states), and force, equilibrium, and uplift checks (serviceability limit states).
CYPECAD carries out checks for shear and punching shear in mat foundations and foundation beams. - Base plate
For any steel column arrangement (simple and composite sections).
More information at:
- Foundation analysis and design
General description. - Footing analysis and design
Includes references to strap and tie beams. - Pile cap analysis and design
Includes references to strap and tie beams. - Advanced design of surface foundations
This module complements the analysis and design of footings and pile caps. - Punching shear verification in CYPECAD
In waffle slabs, flat slabs, and mat foundations. - Baseplates
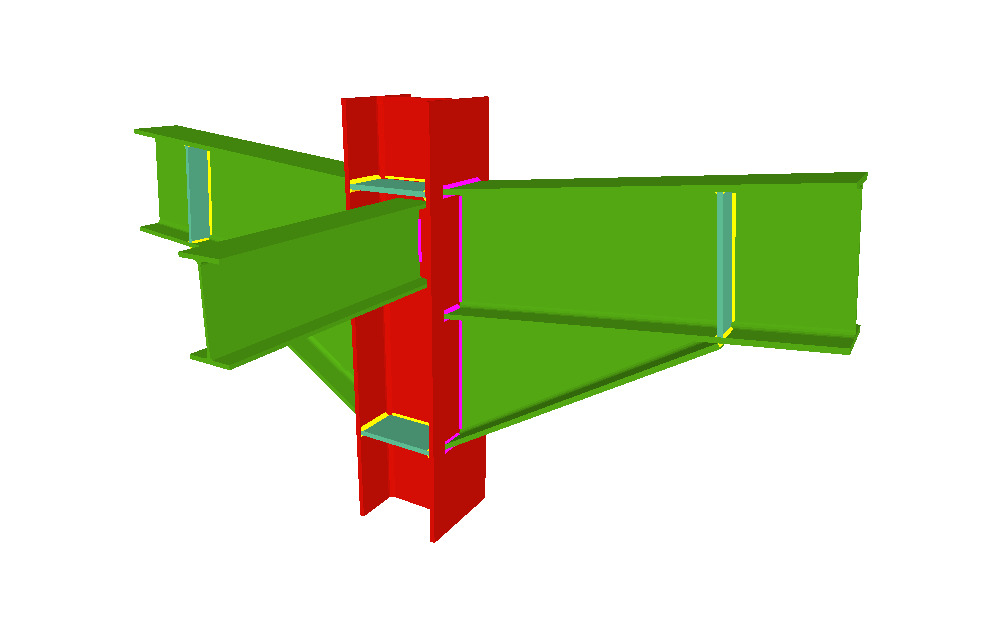
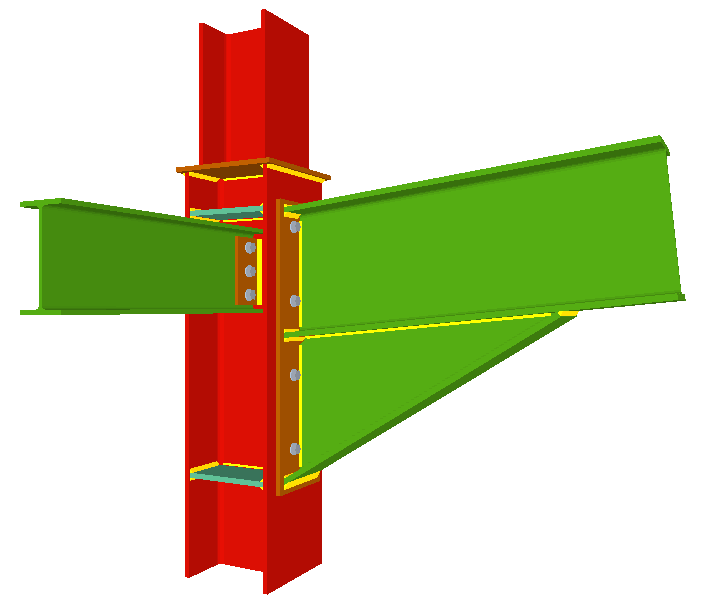
Welded and bolted joints
CYPECAD and CYPE 3D have five modules for analysing and designing steel-section joints.
- Joints I. Welded. Warehouses with rolled and welded steel I-sections
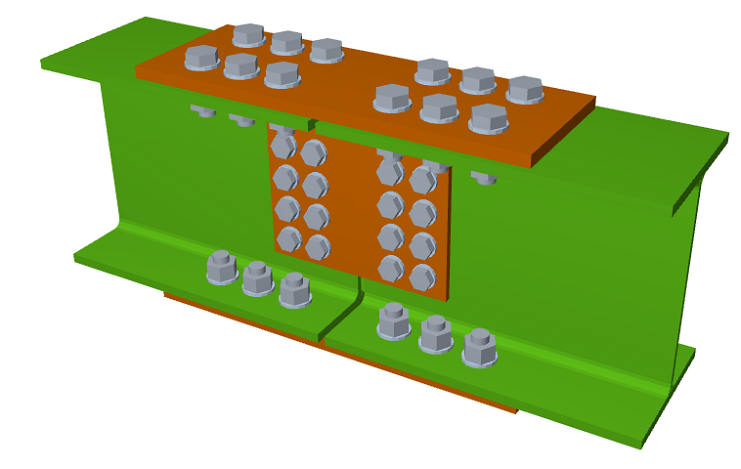
More information - Joints II. Bolted. Warehouses with rolled and welded steel I-sections
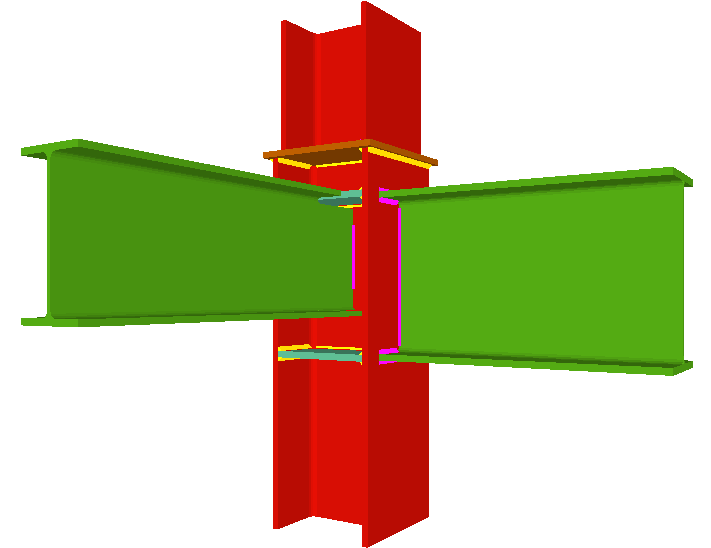
More information - Joints III. Welded – Building frames with rolled and welded steel I-sections
More information - Joints IV. Bolted. Building frames with rolled and welded steel I-sections
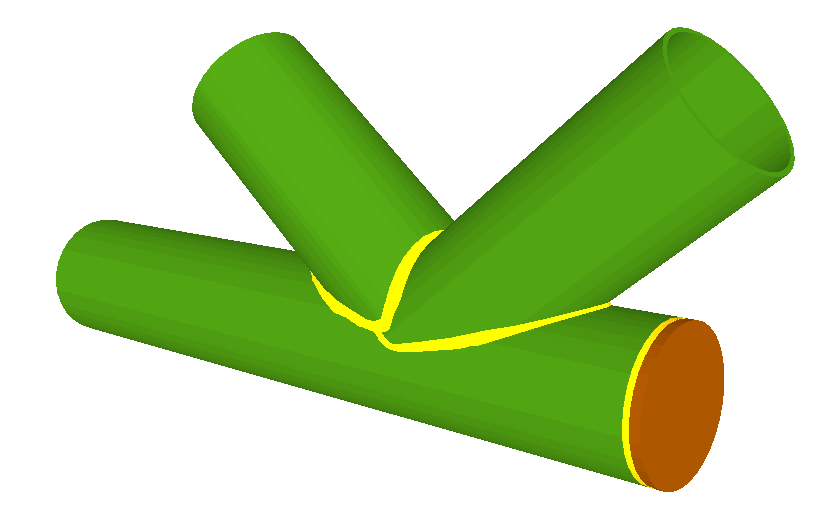
More information - Joints V. Flat trusses with hollow structural sections
More information
The Joints I, Joints II and Joints V modules have a wider field of application in warehouses designed using CYPE 3D and with Integrated 3D Structures of CYPECAD, while the type of joints designed by the Joints III and Joints IV modules have a wider field of application in building structures made up of frames that are designed in CYPECAD.
In any case, the Joints I, Joints II, Joints III and Joints IV modules have common types of joints that are developed and completed in the same way in each module.