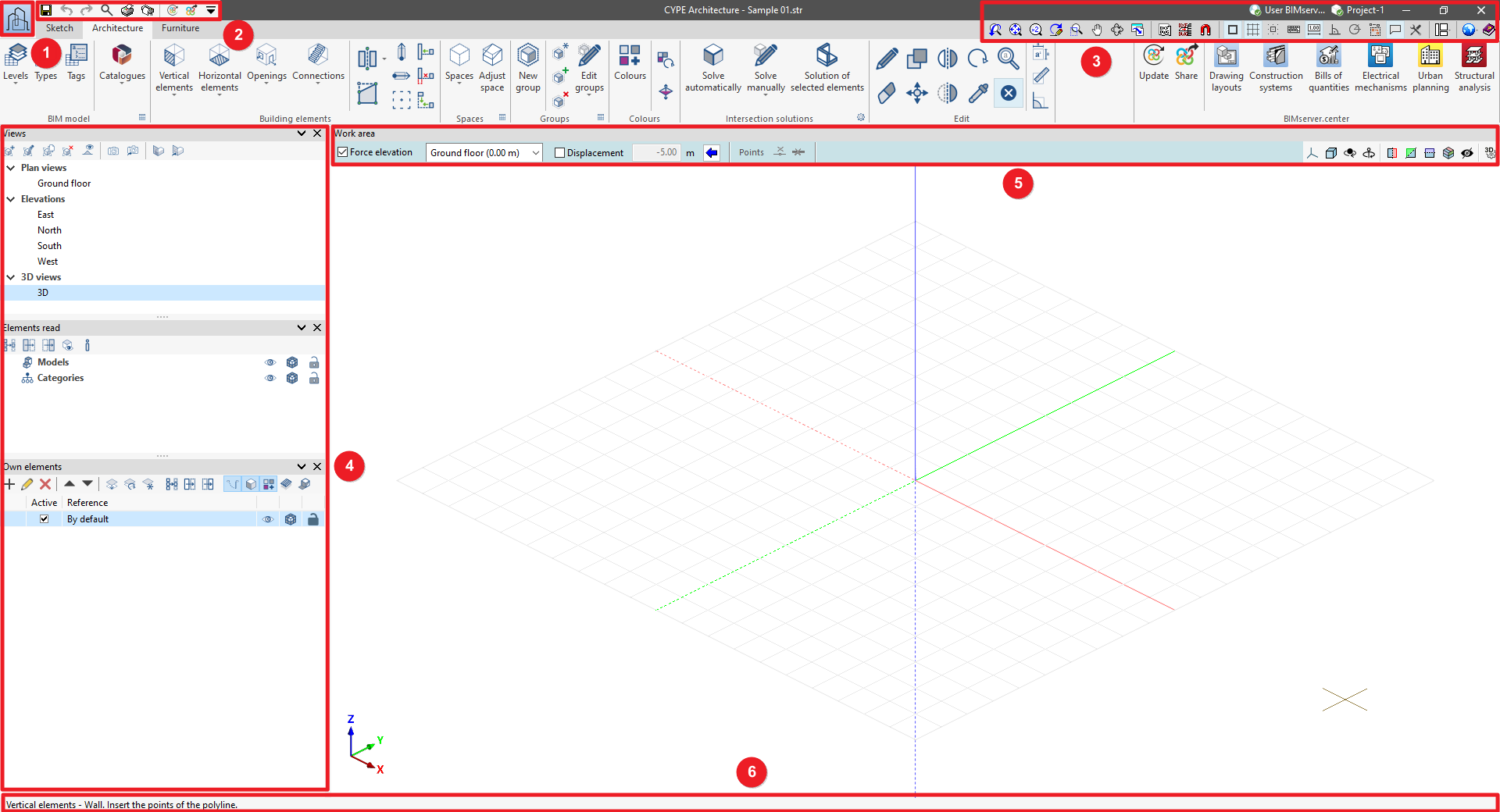
General tools in the CYPE program interface
General tools in the CYPE program interface
CYPE programs have common tools that are available in the following areas of the general interface:
- "File" menu (1)
Creates, opens or saves jobs, accesses the file manager and uses or manages the electronic license.
- Tools in the top left area (2)
Saves the file, can undo and redo changes and obtain reports and drawings, and can be used for searching and quickly accessing other program tools.
- Tools in the top right area (3)
Checks the connection with BIMserver.center, modifies the drawing views, manages the templates and their snaps, activates different aids when entering elements, controls the system of dockable windows, accesses the general configuration options and opens the "Help" menu.
- Left side panel (4)
By default, this area contains the panels for managing views, levels, elements read and own elements.
- Tools in the "Work area" (5)
The "Work area" window has options for entering elements on the work area on the left-hand side and tools for controlling the visibility of the 3D model on the right-hand side.
- Status bar (6)
Located at the bottom of the general interface, it displays contextual information about what is being carried out in the application.
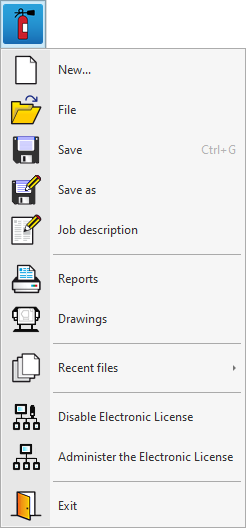
“File” menu
The "File" menu can be accessed by clicking on the icon with the program logo in the top left-hand corner of the program's general interface.
The following options are available:
- New
Creates a new job, closing the job that is already open. The program will also ask if the data of the current job is to be saved.
- File
Provides access to the file manager, closing the job that is open. The program will ask if the data of the current job is to be saved. It will then open the “File manager” window, where the files the program can read can be located and operations such as opening, searching, compressing and sharing jobs that have already been created or loading examples can be carried out.
- Save (Ctrl + G)
Saves the current job.
- Save as
Saves the current job by specifying a different file name, save path, and description.
- Job description
Checks and modifies the current job’s description.
- Listados / Planos
Provides the reports or drawings of the current job.
- Latest files
Allows users to check and open the latest files opened with the program.
- Use Electronic License / Disable Electronic License
Allows users to enter their email address and password for the e-licence so they can run the program. If an e-licence is being used, the “Disable Electronic License” option disconnects it and leaves it open for use on other workstations.
- Administer the Electronic License
Allows users to enter their email address and password for the e-licence administrator. From here, e-licence users' email addresses and passwords can be managed.
- Exit
Exits the application and closes it. The program will ask if the data of the current job is to be saved.
Save, undo and redo options. Search and quick access tools
The group containing the options for saving the file, undoing and redoing any modifications and the quick access toolbar can be found in the top left-hand corner of the interface.

The following options are available:
- Save (Ctrl + G)
Saves the file.
- Undo (Ctrl + Z)
Undoes the last modification.
- Redo (Ctrl + Y)
Redoes the last modification.
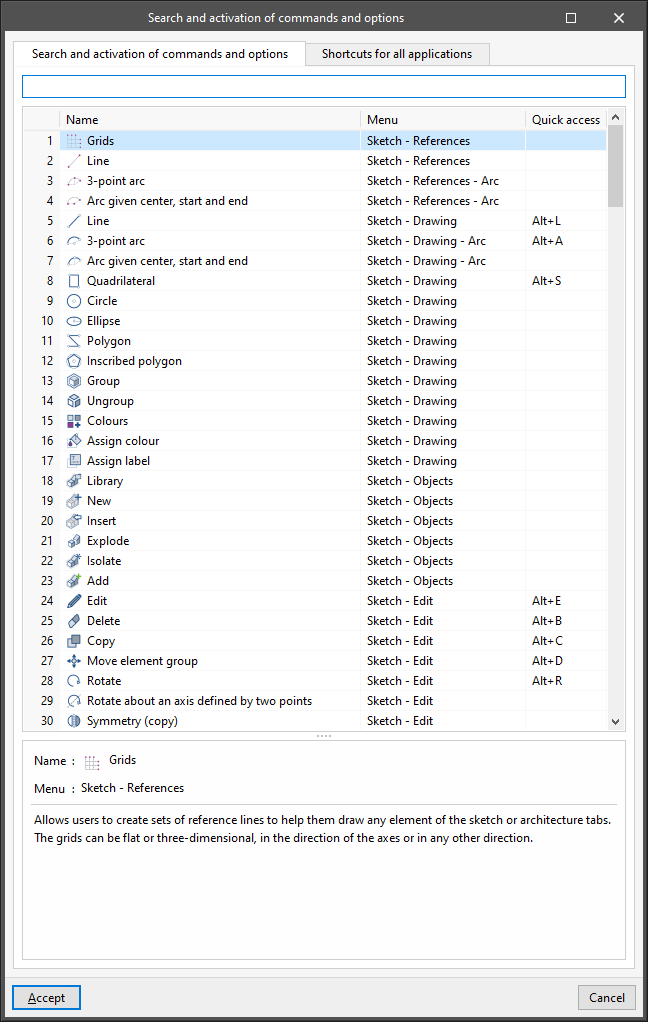
- Search and activation of commands and options (Ctrl + F)
Clicking on this option opens a window with the following tabs:- Búsqueda y activación de comandos y opciones
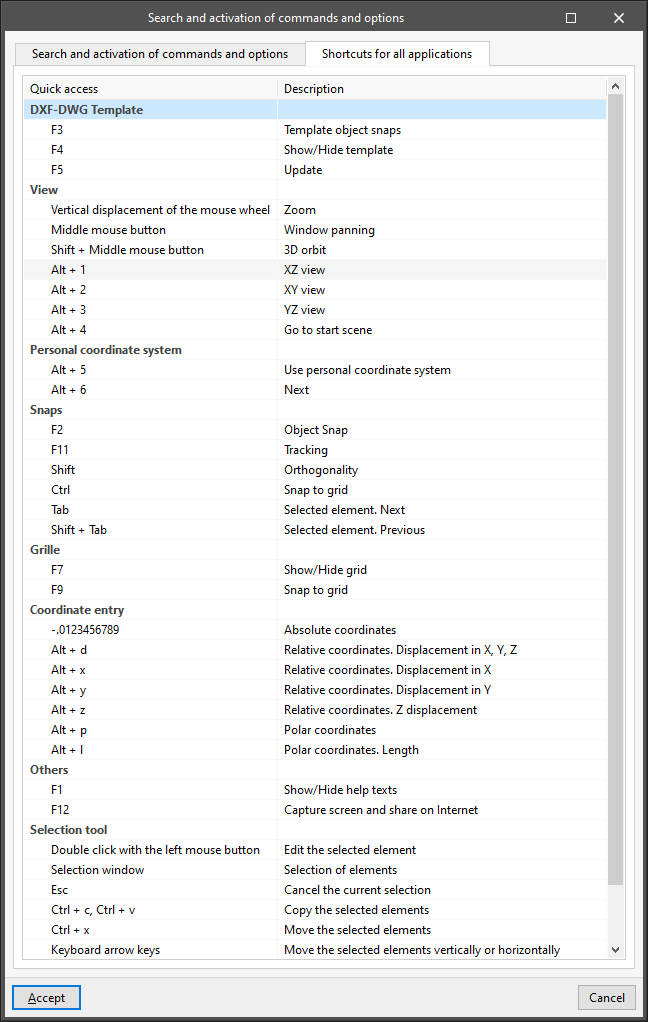
Allows users to quickly access the program's options, indicating the “Name”, the “Menu” where they are located and the corresponding “Quick access” command. - Shortcuts for all applications
Allows users to check the “Quick access” options for all the applications as well as their “Description”.
- Búsqueda y activación de comandos y opciones
- Reports
Provides job reports.
- Drawings
Provides job drawings.
The next section of this group consists of a configurable toolbar for quick access:
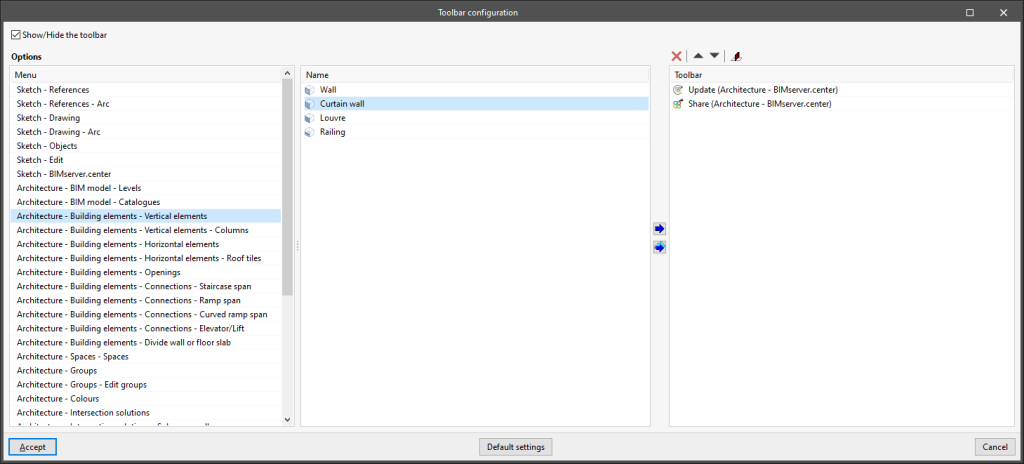
- Toolbar configuration
Allows users to configure the options visible in this section. Clicking on this option opens a window with the following options:- Show/Hide the toolbar
Shows or hides the options in this section. - Options
On the left are two lists with the ‘Name’ of all the options available in the program, sorted by the ‘Menu’ in which they are located.
On the right is the list of options visible in the quick access “Toolbar”. The tools at the top allow users to delete, reorder or place a separator between the options incorporated in the toolbar.
Using the buttons in the lists, users can incorporate the selected option or incorporate all the options from the selected menu into the toolbar. - Default settings
Loads the default configuration of this toolbar.
- Show/Hide the toolbar
Tools for drawing views
The group of tools for drawing views is located in the top right-hand corner of the interface and allows users to control the drawing views on the screen.

The following options are available:
- Previous window (Ctrl + P)
Restores the previous drawing view to the current view.
- Full window (Ctrl + W)
Displays the entire drawing. The same action can be performed by double-clicking on the middle mouse button.
- Zoom out 2X
Enlarges the view of the drawing to twice the size of the drawing compared to the "Full window" option.
- Redraw (Ctrl + R)
Redraws the current view of the drawing without changing its size.
- Highlight zoom (Ctrl + M)
Allows users to zoom in and out by clicking on the drawing. To do this, a window is drawn to adjust the view to the set size. The mouse wheel can also be used, where the zoom level can be increased or decreased to zoom in or out.
- Window panning (central mouse button)
Allows the position of the drawing to be changed. To do this, after activating the option, left-click on the screen and, holding down the button, move the cursor. The central mouse button can also be pressed and, while holding it down, it can be dragged. Once this is done, press this option again to deactivate it and continue with the previously used option.
- 3D orbit (Shift + central mouse button)
Allows the scene to be rotated around the rotation pivot. To do this, after activating the option, left-click on the screen and hold down the mouse button to move the cursor. Alternatively, the "Shift" key and the central mouse button can be pressed and, while holding them down, dragged. Once a rotation has been carried out, press this option again to deactivate it and continue with the previously used option.
The 3D orbit behaviour depends on the options marked in the top toolbar of the work area:- If the "Rotation about a point" option is activated, the point under the cursor will be used as the rotation pivot.
- If the "Rotation about the camera" option is activated, the scene rotates around the vertical axis of the camera.
- Otherwise, the pivot shall be analysed considering the visible elements in the scene.
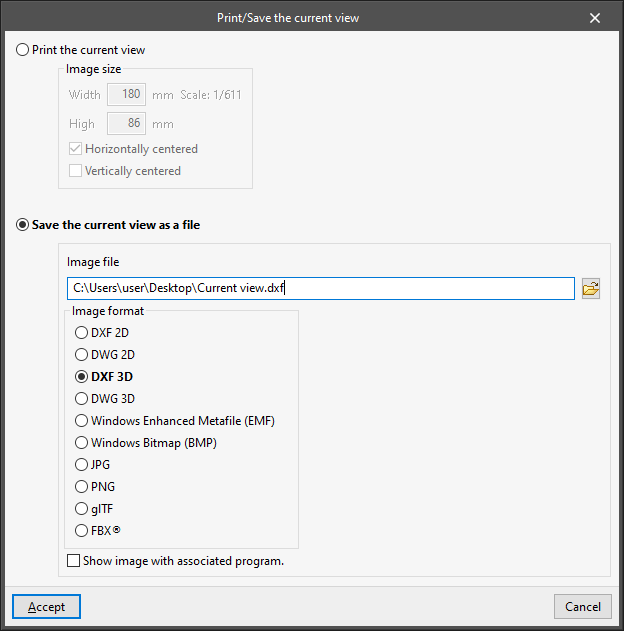
- Print the current view
Allows users to print the current view displayed in the workspace or to generate a file with the drawing in a graphical format. If the current view contains a template, this template will also be included in the drawing.
When using this tool, the "Print/Save current view" window opens with the following options:- Print the current view
Allows users to print the current view displayed in the work area after configuring the following settings:- Image size
- Width
- High
- Horizontally centered (optional)
- Vertically centered (optional)
- Image size
- Save the current view as a file
Allows users to generate a file with the drawing in the selected graphic format.- Image file
Allows users to configure the path where the file will be saved. - Image format
Allows the file format to be selected.- DXF 2D
- DWG 2D
- DXF 3D
- DWG 3D
- Windows Enhanced Metafile (EMF)
- Windows Bitmap (BMP)
- JPG
- PNG
- glTF
- FBX©
- Show image with associated program (optional)
Allows users to open the file generated with the program associated with the selected format.
- Image file
- Print the current view
Importing DXF, DWG, PDF and JPG drawings
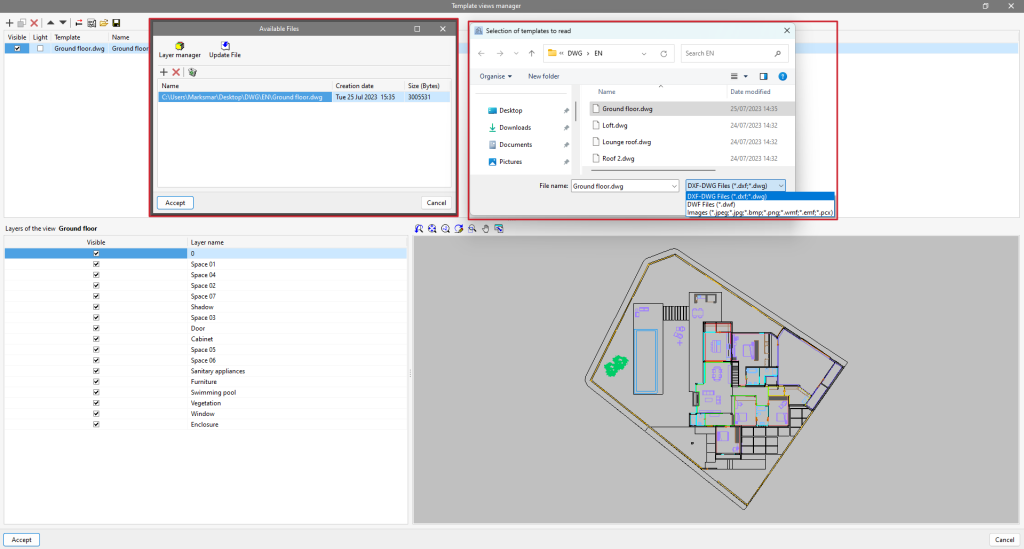
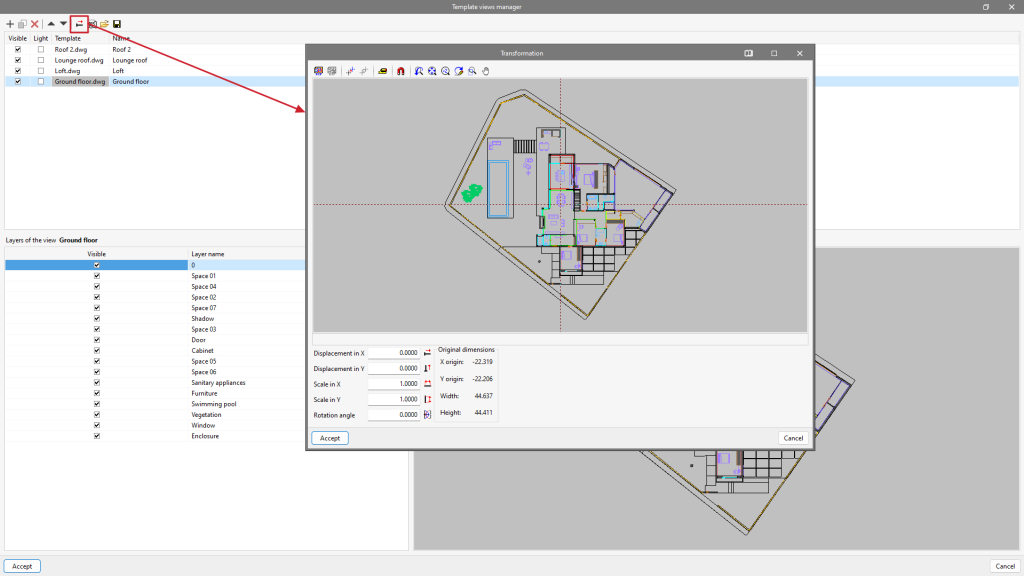
Clicking on the first tool, "DXF-DWG templates", will open a pop-up window called "Template views manager" in which templates can be managed and imported to the job in DXF, DWG, PDF or JPG formats, among others.
When clicking on the "Add" option, another window called "Available files" will appear. Here, a new file is added from "Add" and the type of format to be displayed is changed ("DXF-DWG files" appears by default). Select the file and accept the window. If the document consists of several pages, the "Page number" to be imported must be specified.
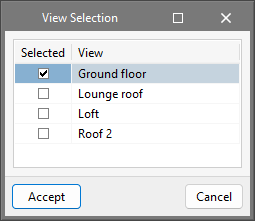
Once the templates have been imported to the job, select the tool located on the right, "DXF-DWG Templates (F4)", to proceed with the selection of views. Once the desired view has been selected, the window is accepted and it will appear in the graphic window of the current view.
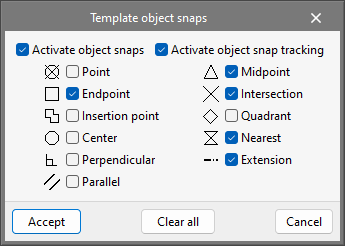
In order to snap entities or elements from the previously imported DXF or DWG file, the third tool, "Template object snaps (F3)", must be activated. From the pop-up window, the "Activate object snaps" checkbox and/or the "Activate object snap tracking" checkbox can be marked, along with the references that will be active.
Template transformation
In "Template views manager", clicking on the tool with the red arrow will open a pop-up window called "Transformation", from which users can select the visible area of the template, apply a shift, rotate and/or change the scale, among others.
At the top of the window, we find a series of tools divided into groups:
- The first group allows users to "Select the visible area of the template" or restore the original area.
- The second group allows users to "Change the origin of the coordinates of a template" or reset it to the initial position.
- The third group, "Adjust the scale of a template", allows users to select two points on the template to create a segment with a known distance to adjust the scale of the template.
- The last group allows users to manage the visibility of the drawing view.
At the bottom of the window, we can enter numeric "Displacement" and "Scale" parameters on the "X" and "Y" axes or apply a "Rotation angle".
From the "Template views manager" window, the file containing the construction drawings must be added to the list and incorporated as many times as there are floors in the building.
Once the floors have been correctly renamed, each template can be transformed by selecting the visible area for each floor and changing the coordinate origin to a common (or easily identifiable) element in all of them. Lift shafts, staircases, columns, etc. are recommended as a reference.
Tools to assist with entering elements
This tool group is located on the top right-hand side of the interface and offers features to assist with entering elements into the model.

The following options are available:
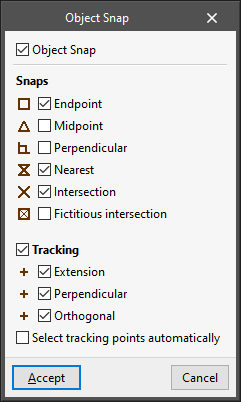
- Object snap (F2)
Allows users to activate object snaps previously entered in the program to snap or track them when entering new elements in the model.- Object snap (optional)
The object snap system can be configured to suit the needs of each situation:- Snaps (optional)
Allows users to directly snap the following points of the elements already entered in the program:- End point (optional);
- Midpoint (optional);
- Perpendicular (optional);
- Nearest (optional);
- Intersection (optional);
- Fictitious intersection (optional).
- Tracking (optional)
Allows users to generate and use the following tracking from the elements already entered in the program:- Extension (optional);
- Perpendicular (optional);
- Orthogonal (optional).
- Select tracking points automatically (optional)
If this option is activated, the program selects nearby track points automatically. If it is deactivated, the cursor must be moved for a few seconds over the points to be tracked.
- Snaps (optional)
- Object snap (optional)
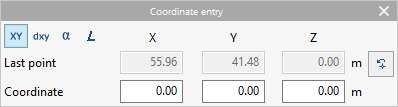
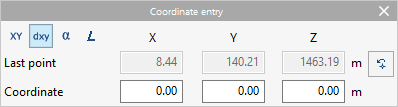
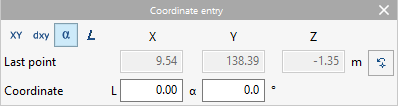
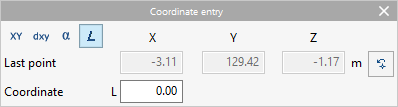
- Coordinate entry
Allows users to enter elements into the model by defining the position of their points by numerical coordinates.- Coordinate selection
The first row of options allows users to select the coordinates to be used:- Absolute coordinates
- Relative coordinates
- Polar coordinates
- Polar coordinates (Length)
- Last point
This section shows the absolute coordinates of the last point entered:- "X", "Y", "Z"
- Coordinate
This section shows different numerical fields in which the coordinates of the new point to be entered are entered. After typing in the numerical values, pressing the "Enter" key will enter the point of the element in the model. The available fields depend on the selected coordinates:- "X", "Y", "Z" (in "Absolute coordinates")
Allows users to directly type in the absolute coordinates "X", "Y" and "Z" of the new point. - "X", "Y", "Z" (in "Relative coordinates")
Allows users to enter the "X", "Y" and "Z" coordinates of the new point relative to the coordinates of the last point entered. - "L", "α" (in "Polar coordinates")
Allows the "L" length to be written in the direction given by the "α" angle between the new point and the last point entered. - "L" (in "Polar coordinates (Length)")
Allows users to enter the "L" length between the new point and the last point entered in the direction defined by the cursor on the screen.
- "X", "Y", "Z" (in "Absolute coordinates")
- Coordinate selection
- Allows for dimensions to be defined upon entering each element
If this option is activated, when a new point is inserted in the model, a panel opens next to it, allowing for dimensions to be defined for its position. The following values can be selected and dimensioned:- Distance
- Length
- Absolute XY displacemen
- Relative XY displacement
- Absolute length and exit angle
- Relative length and exit angle
- Absolute exit angle
- Relative exit angle
- Allows for dimensions to be defined upon entering each element
If this option is activated, when inserting a new point in the model, a panel opens next to it, allowing users to dimension it in order to define its position. Values can be selected and dimensioned in the following options, which are activated depending on whether a previous element is snapped or not when inserting the points in the model:- Distance
Distance from the new point to the nearby reference point indicated. - Length
Length of the element between the new point and the original point snapped. - Absolute XY displacement
X and Y displacements of the new point relative to the original point, in absolute coordinates. - Relative XY displacement
X and Y displacements of the new point with respect to the original point, in coordinates relative to the previous element where the first point is snapped. - Absolute length and exit angle
Length of the element between the new point and the original point, and exit angle with respect to the global axes. - Relative length and exit angle
Length of the element between the new point and the original point, and exit angle with respect to the direction of the previous element where the first point is snapped. - Absolute exit angle
Exit angle with respect to the global axes. - Relative exit angle
Exit angle with respect to the direction of the previous element where the first point is snapped.
- Distance
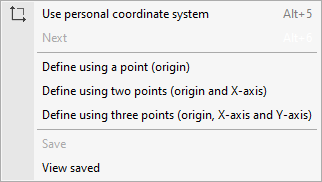
- Personal coordinate system
- Use personal coordinate system (Alt + 5)
Allows users to switch between using personal coordinate systems or the default coordinate system. - Next
Allows users to select the next defined personal coordinate system, if it has been previously saved. - Define using a point (origin)
Allows users to define a personal coordinate system by entering their origin. The direction of the "x" and "y" axes is calculated automatically. - Define using two points (origin and x-axis)
Allows users to define a personal coordinate system by entering two points: the coordinate origin and a second point indicating the direction of the x-axis. The direction of the y-axis is calculated automatically. - Define using three points (origin, x-axis and y-axis)
Allows users to define a personal coordinate system by entering three points: the coordinate origin, a second point indicating the direction of the x-axis and a third point defining the direction of the y-axis. - Save
Allows users to save the personal coordinate system by entering a "Reference" for it. - View saved
Allows users to consult the stored personal coordinate systems, edit their references and delete them.
- Use personal coordinate system (Alt + 5)
- Orthogonality (Ctrl + O)
If this option is activated, the position of the elements is forced when they are entered into the orthogonal directions of the active coordinate system.
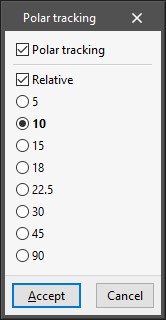
- Polar tracking
Allows users to force the lines of the tracking activated by the "Object snap" option to the directions given by the angles selected in this panel.- Polar tracking (optional)
Allows polar tracking to be activated. - Relative (optional)
If this option is activated, the selected angles shall be measured with respect to the direction given by the last points entered in the model. If deactivated, the selected angles shall be measured with respect to the coordinate system in use. - Angle selection
Allows users to select the angular increments between the different tracking lines:- 5
- 10
- 15
- 18
- 22.5
- 30
- 45
- 90
- Polar tracking (optional)
- Repeat the last selection
By pressing this option, the program selects the elements that were selected when using the last option, highlighting them in orange.
- Show information texts
If this option is activated, the program allows users to consult the information of each element in a specific panel that appears when hovering the mouse cursor over them.
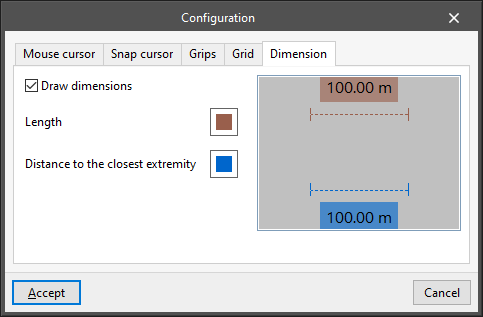
- Configuration
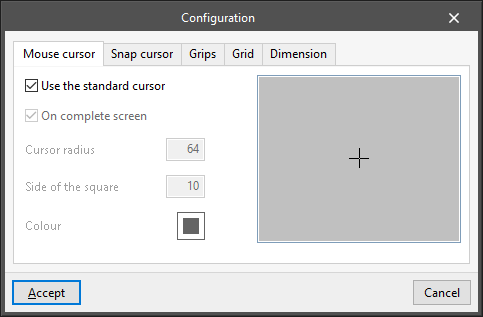
With this option, the appearance of different graphic elements that appear on the screen can be configured: - “Mouse cursor” tab
Allows users to modify the appearance of the mouse cursor:- Use the standard cursor (optional)
- On complete screen (optional)
- Cursor radius
- Side of the square
- Colour
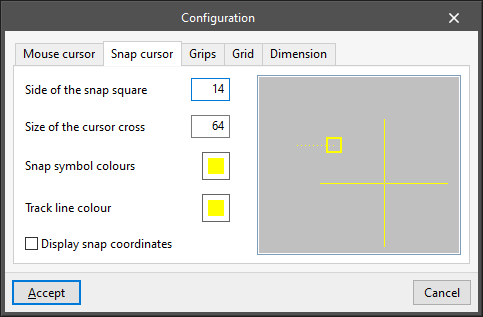
- “Snap cursor” tab
Allows users to modify the appearance of the snap cursor, which is displayed when nearby object snaps are detected:- Side of the snap square
- Size of the cursor cross
- Snap colour symbols
- Track line colour
- Display snap coordinates (optional)
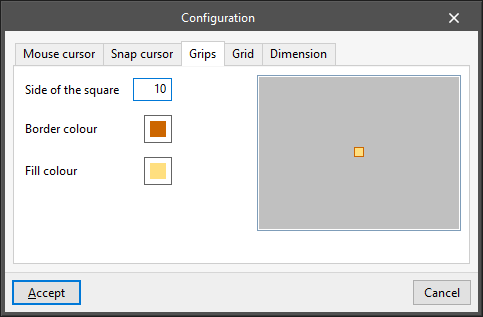
- “Grips” tab
Allows users to modify the appearance of grips or insertion points of elements in the model:- Side of the square
- Border colour
- Fill colour
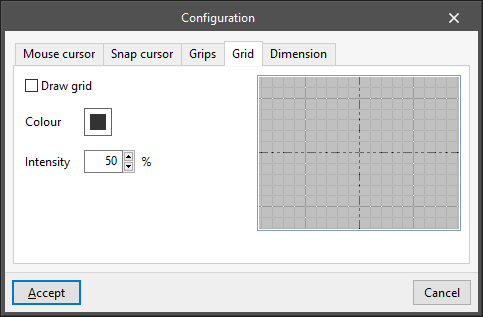
- “Grid” tab
Allows users to modify the appearance of the grid:- Draw grid (optional)
- Colour
- Intensity (%)
Dockable window system
Dockable windows can be moved and resized. They can be either floating windows, pinned to a location within the application's main dialogue box, dragged outside of it, or even moved to another monitor.
- Move windows
A docked window can be moved by clicking on the title bar at the top of the window and dragging it.
When dragging a dockable window, several visual aids are displayed to make its relocation easier. Next to the cursor, a text box appears containing the title of the dockable window being moved. Whenever the cursor approaches the edge of another window, a box appears showing a preview of the space it would occupy.
It is possible to leave a window as a floating window without docking it to another window, and it is also possible to dock windows within a floating window. Holding down the CTRL key can prevent a floating window from being docked while it is being moved.
- Group windows
It is possible to group several windows in the same space by dragging one window to the top left-hand corner or to the bottom left-hand corner of another window. When this is carried out, tabs will appear at the bottom or top of the group, allowing users to alternate between the grouped windows. If the tabs are at the bottom, the title of the group of windows corresponds to the active window. On the other hand, if the tabs are at the top, they will be used as the title.
- Show/Hide windows
The icon to close the window can be found in the top right-hand corner of each dockable window.
To manage the display of the dockable windows in the user interface, a "Window" button () has been added to the application environment, next to the "General Settings" button (icons on the top right-hand side of the program). By clicking on it, a drop-down menu appears with the available dockable windows and users are able to change their status. In addition, there is the "Reset Window Layout" option which allows users to restore the default workspace.
In some cases, such as the "Work area" of applications with a 3D environment, the window cannot be hidden. In these cases, the icon for closing the window is not displayed and, in the "Window" menu, the "Work area" will be locked.
- Collapse windows
When several dockable windows are arranged vertically, an icon is displayed, next to the close icon, which allows each window to be expanded or collapsed. When the window is collapsed, it will return to its previous size.
The window layout and display settings are saved when closing the application.
It is important to note that not all floating windows in an application are dockable windows. In order to tell them apart, the icon has been added to the title bar of windows that are dockable.
The floating window environment also includes the "Bill of Quantities" tab in all applications that have this tab.
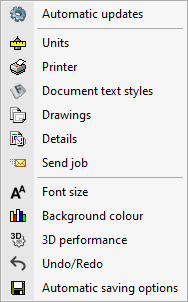
General configuration options
The general configuration options are accessible via the "Configuration" button in the top right-hand corner of the interface.

Clicking on this button displays a menu with different general configuration tools. The options displayed depend on the program being used.
The following options are available:
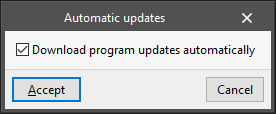
Automatic updates*
*Only in versions 2025.a and earlier. As of version 2025.b, the update notification is available in the program start window.
This activates the automatic update system for the programs:
- Download program updates automatically (optional)
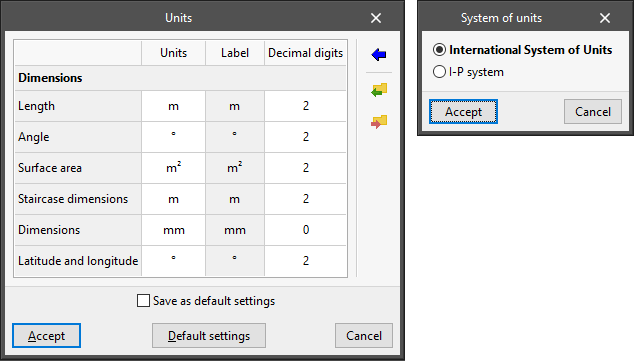
Units
This is used to configure the project's system of units. The quantities available in the table depend on the program being used.
- "Units" column
Selects the unit of measurement for each of the magnitudes. - "Label" column
Displays the label identifying the selected unit. - "Decimal digits" column
Modifies the number of decimal places used to measure each magnitude in the selected unit. - Import one of the predefined systems of units
Using this option available on the right-hand side, the units from one of the following predefined systems can be imported automatically:- International System of Units
Imports the units from the International System of units. - I-P System
Imports the units from the I-P (Inch-Pound) or imperial system.
- International System of Units
- Import/Export
Using these options, the defined system of units can be imported and exported to files on disk.
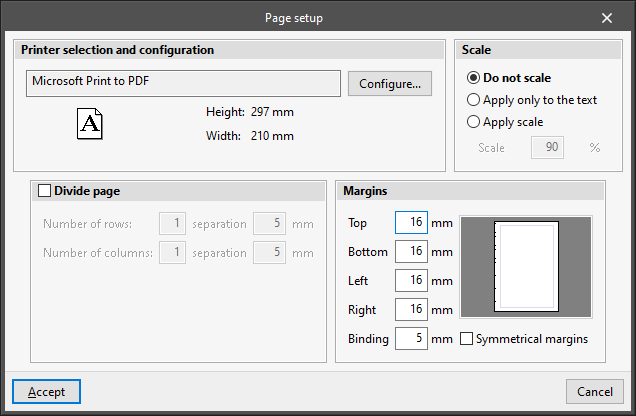
Printer
Opens the "Page setup" window with the following options:
- Printer selection and configuration
Selects and configures the printer used for printing documents. - Scale
Adjusts the scale when printing documents:- Do not scale
- Apply only to the text
- Scale (%)
- Apply scale
- Scale (%)
- Divide page (optional)
Prints the page divided into rows and columns:- Number of rows and separation between rows
- Number of columns and separation between columns
- Margins
Modifies the margins on the printed page:- Top
- Bottom
- Left
- Right
- Binding
- Symmetrical margins (optional)
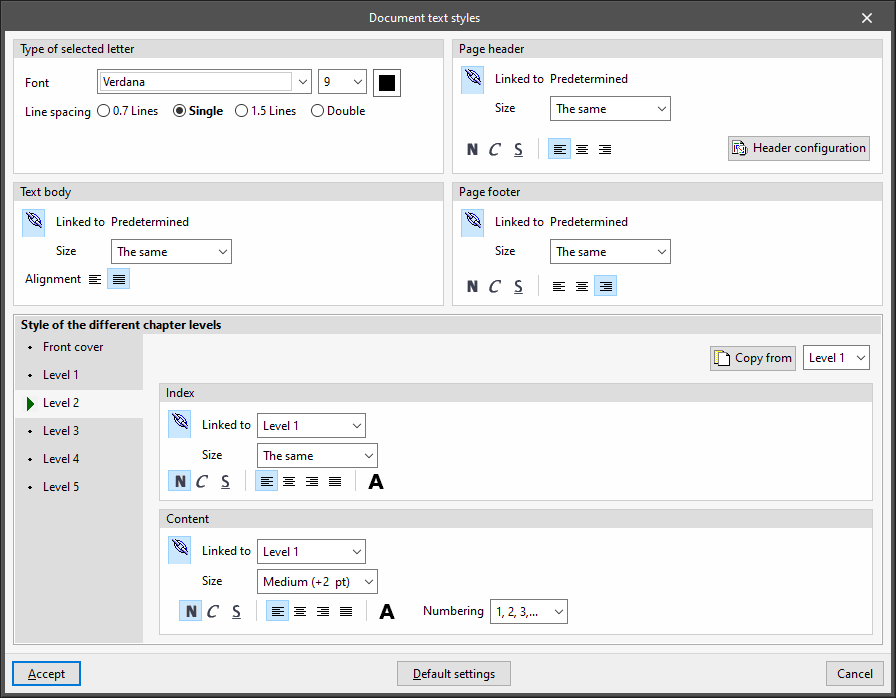
Document text styles
Configures the styles of the documents. The characteristics of each style can be linked to those of the default font style, indicating whether it has the same or different font "Size", or unlinked, to define them independently.
- Type of selected letter
Sets the default font:- Font style
- Font size
- Colour
- Line spacing (0.7 lines / Single / 1.5 lines / Double)
- Page header
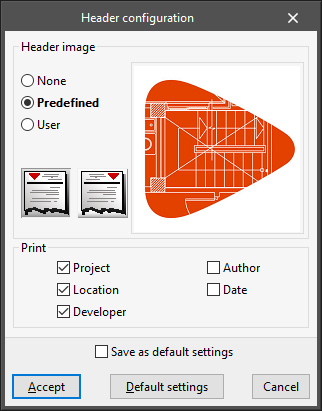
Sets the style used in the documents' page header. The format can be set to bold, italic or underlined and the alignment can be changed. The following editing panel can also be accessed:- Header configuration
Sets the image and the data to be printed in the page header:- Header image
- None / Predefined / User defined
- Image on the left / Image on the righta
- Print
- Project (optional)
- Location (optional)
- Developer (optional)
- Author (optional)
- Date (optional)
- Header image
- Header configuration
- Text body
Configures the style used in the text body of documents. The alignment can be changed. - Page footer
Sets the style used in the footer of documents. The formatting can be set to bold, italic or underlined and the alignment can be changed. - Style of the different chapter levels
Configures the style used in the different levels of chapters, both in their "Table of contents" and in their "Contents". Using the "Copy from" option, the style defined in each level is copied to any other level. The style of one level can also be linked to the style defined in another level. Also, using the "Numbering" option, users can select the heading numbering system. The available levels are as follows:- Front cover
- Level 1
- Level 2
- Level 3
- Level 4
- Level 5
Drawings
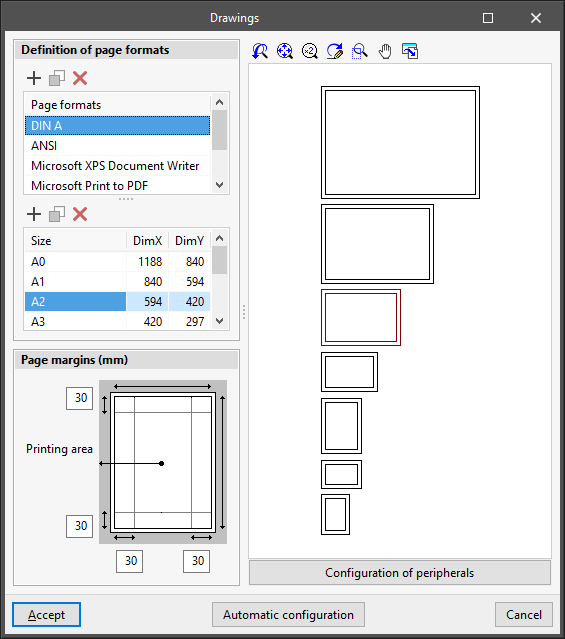
Configures the formats and peripherals for printing drawings.
- Definition of page formats
Configures the page formats and sizes available when printing drawings. Users can edit, add, copy or delete entries in two tables:- Format table
The first table defines the series of available formats.- Format
- Table of page sizes
When selecting a format in the first table, the second table defines the page sizes available in the format and their dimensions:- Sizes, Dimension X, Dimension Y
- Format table
- Page margins
Configures the print margins of drawings (top, bottom, left and right) around the "Print area". - Format viewer
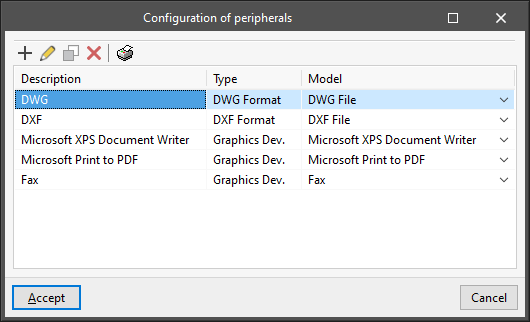
In this display area, the selected format series and the selected page size are shown schematically. - Configuration of peripherals
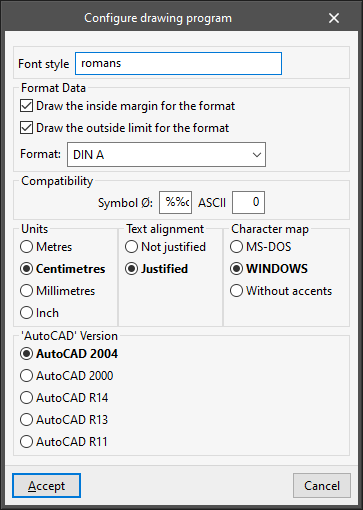
Accesses to the printing peripherals configuration table. By default, the program includes the "DWG" and "DXF" peripherals, which allow printing on these files, together with the graphic devices registered in the operating system control panel. The configuration options available when editing each peripheral vary according to its type:- Configure drawing program
This panel appears when editing the "DXF" and "DWG" peripherals and allows users to configure the printing on these files:- Font style
- Format Data
- Draw the inside margin for the format (optional)
- Draw the outside limit for the format (optional)
- Format
- Compatibility
- Symbol Ø
- ASCII
- Unit display (Metres / Centimetres / Millimetres / Inch)
- Text alignment (Not justified / Justified)
- Character map (MS-DOS / Windows / Without accents)
- 'AutoCAD' version (AutoCAD 2004 / AutoCAD 2000 / AutoCAD R14 / AutoCAD R13 / AutoCAD R11)
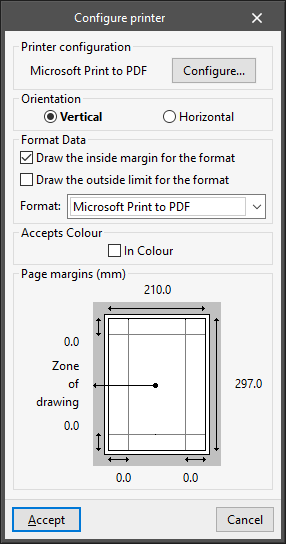
- Configure printer
This panel appears when configuring a printer type peripheral:- Printer configuration
- Orientation (Vertical / Horizontal)
- Format Data
- Draw the inside margin for the format (optional)
- Draw the outside limit for the format (optional)
- Format
- Accepts Colour
- In Colour (optional)
- Page margins
- Configure drawing program
Details
This tool is used to store user detail libraries to be included in the drawings later on.
Creating libraries
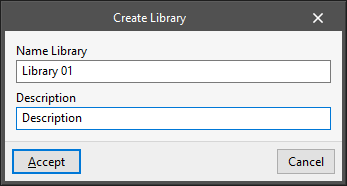
First, new libraries are created to hold the new details. These libraries can be organised in directories and subdirectories. When creating a new detail library, the program requires the following data:
- "Create Library" window
- Name of the library
- Library description
Creating details
Details are created by importing DXF, DWG or image files. After selecting the library where the detail is to be imported, the program will allow users to import a file with the detail.
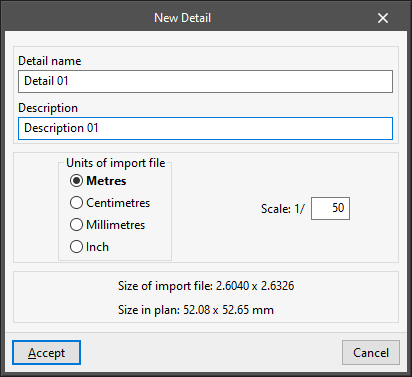
When importing a DXF or DWG, a dialogue box opens in which users must indicate the name to be assigned to the detail, a description, the drawing units with which the file is being created and the scale it is to be transferred to:
- "New Detail" window (DXF and DWG files)
- Detail name
- Detail description
- Units of import file (Metres / Centimetres / Millimetres / Inches)
- Scale (1/n)
With this data, the program calculates the final dimensions that the detail will have in the plan. Thus, the "Size of import file" and the "Size in plan" are displayed.
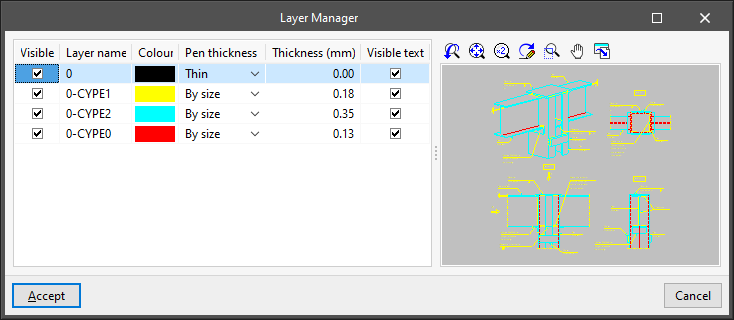
In the next window of the import process, users can choose which layers should be visible, whether texts should be activated, the pen thickness and the layer name:
- "Layer management" window
- Visible, Layer name, Colour, Pen thickness, Thickness (mm), Visible text
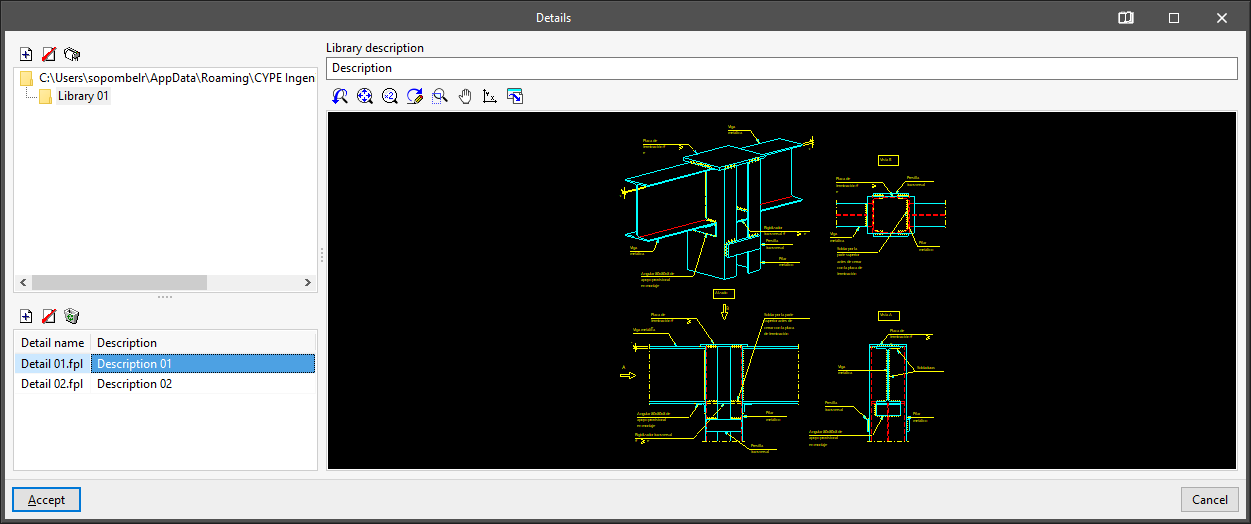
When importing an image file, a dialogue box opens where the name to be assigned to the detail, a description and the data required to define its size in plan must be indicated:
- "New detail" (image files) window
- Detail name
- Detail description
- Size in plan
- Width (mm)
- Height (mm)
- Keep aspect ratio (optional)
Also, default details from the CYPE library can be included if they are available in the program by selecting the "Add" option. This is the case of the CYPECAD construction details library.
Sending jobs
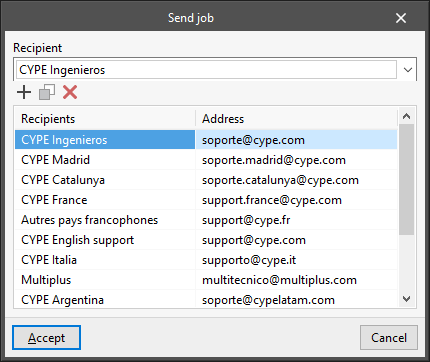
Allows users to configure the data related to sending jobs.
- Recipient
Selects the recipient of the jobs sent by clicking on "File" and then on "Send". - Recipients and addresses
Consults and edits the name and address of the recipients of the jobs to be sent.
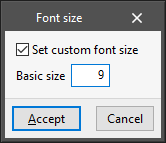
Font size
Used to set the font size on the screen to adjust its readability. The program must be restarted for the changes to take effect.
- Set custom font size (optional)
- Basic size
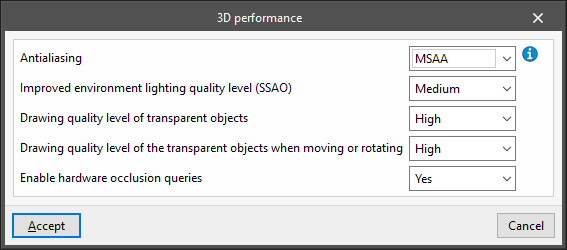
- Antialiasing
Antialiasing, also known as edge smoothing, is a process that improves the appearance of an image by reducing the level of pixelation at the edges of geometric primitives. Depending on the technique used, the hardware available on the PC and the configuration of the video card driver, the graphics performance may be affected. The available configuration options are:- No
No edge smoothing technique is applied. The graphics speed is as fast as possible. The edges of the geometric primitives in the image are clearly pixelated when they are not aligned with the horizontal and vertical directions of the screen. - FXAA
This is a software technique that can be applied with any video card. The image quality is good and the impact on graphics speed is minimal. This is the recommended setting for work areas. - MSAA
This technique can only be applied with video cards that support it. The image quality is good, and the edge definition of geometric primitives is excellent at 4 samples and above. However, depending on the PC hardware, the graphics speed may be affected. This is the recommended value for display areas. - FX+MSAA
Combines the two previous techniques and produces an image of excellent quality.
- No
- Improved environment lighting quality level (SSAO)
- Low / Medium / High / Maximum
- Drawing quality level of transparent objects
- Low / High
- Drawing quality level of the transparent objects when moving or rotating
- Low / High
- Enable hardware occlusion queries
- Yes / No
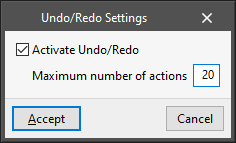
Undo/Redo
This activates and configures the actions related to the "Undo" and "Redo" options, available at the top left of the program's interface.
- Activate Undo/Redo (optional)
- Maximum number of actions
Options in the "Help" menu
The "Help" menu option is located in the upper right-hand corner of the interface.

Program documentation
Provides access to explanatory text on the documentation of the programs and their location, both within its interface and through external resources.
Program License Contract
Allows users to consult the license contract for the programs. This document is displayed and must be accepted when the program is installed.
Responsability Clause
Allows users to check the responsability clause. This document is displayed and must be accepted when the program is installed.
About
Checks the information about the program, including the version and, in the case of programs that include paid modules, the number of the license being used and the permissions it contains. By clicking on "License" it is also possible to read licenses on the network, as well as to use, release or manage the electronic licence.
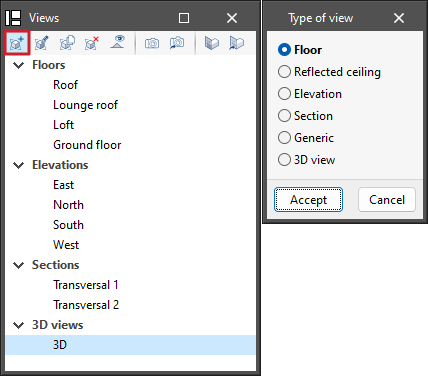
Managing views
Programs with the "Views" section can create different views to make navigation and the architectural modelling process easier. The following types can be created: plan, reflected ceiling, elevation, section, generic and 3D view.
The following options are also available in the top toolbar:
- Create: creates a new 2D or 3D view of the model.
- Edit: modifies the properties of the current view.
- Duplicate: copies the current view.
- Delete: deletes the current view.
- Show references: by selecting this option, references to other views will be displayed in the active view.
- Save the start scene: sets the current position of the view as the start scene.
- Go to start scene: orients the current view to the position of the start scene.
- Define: specifies the working plane associated with the current view. The work plane serves as the basis for the entry of the model components.
- Go to the workplane: orients the current view to the position of the work plane.
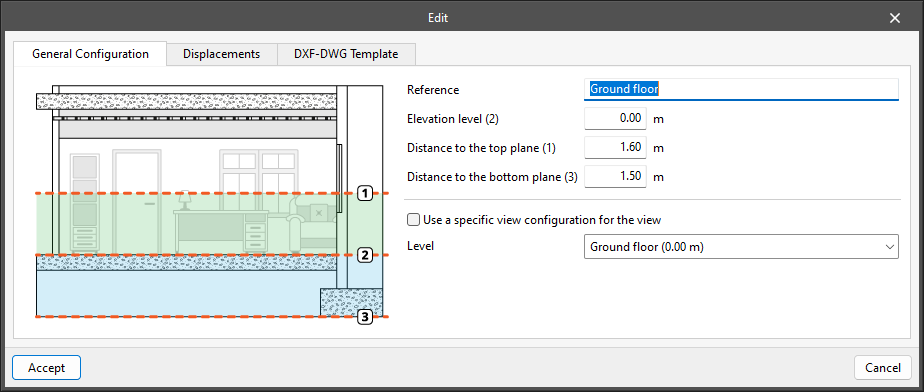
View range
In the "Edit" panel of the view, users can specify the distance to each of the planes from the origin of the view.
All view types, except the 3D view, have an associated region bounded by two planes, which determines the elements to be represented in the view.
In elevation views, section views and generic plans, the rear plane is the plane perpendicular to the direction of view in a positive direction. The front plane is the same but in a negative direction.
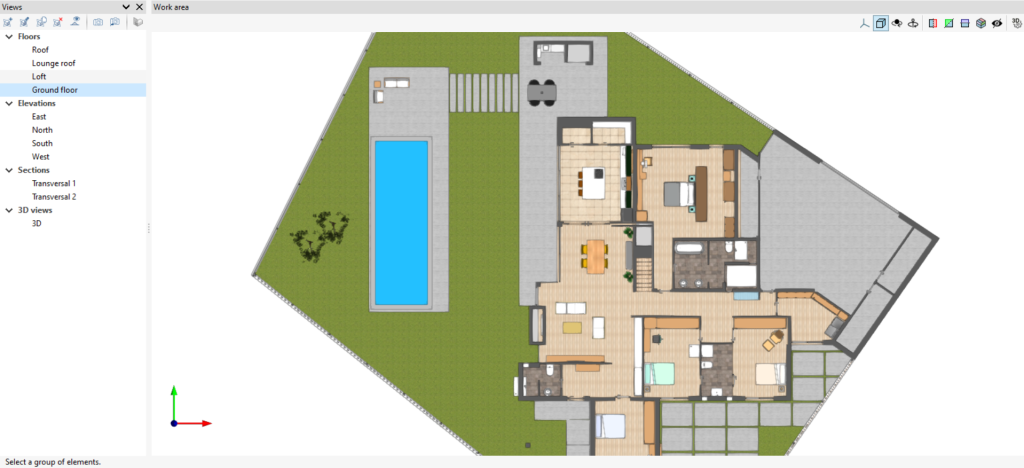
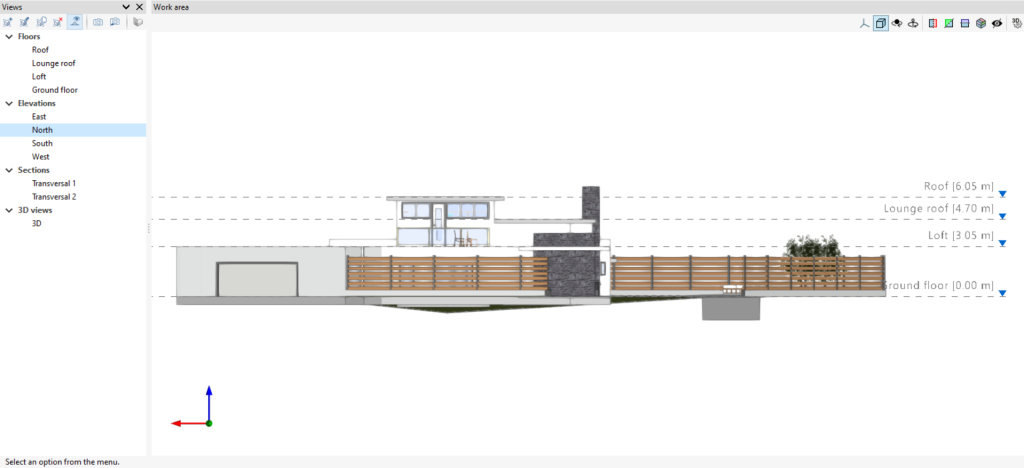
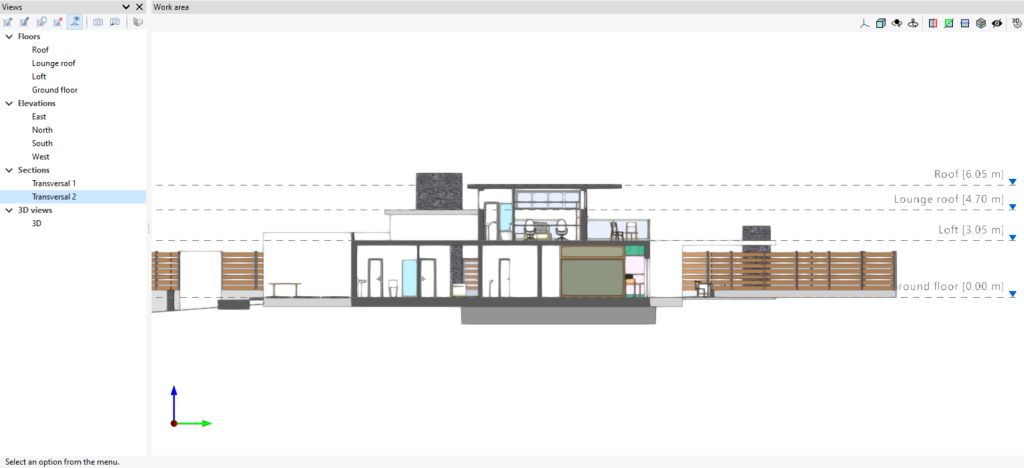

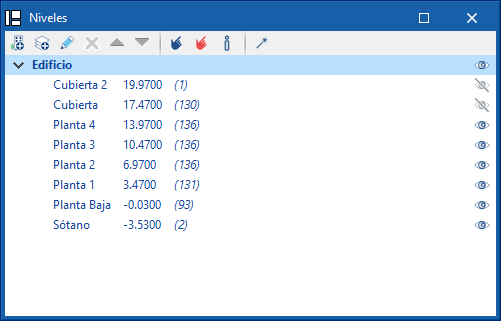
Level management
The "Levels" section makes it easy to associate elements of the model to various views, such as building plans or other reference planes. There is a drop-down list of buildings and levels defined in the model.
The toolbar allows new buildings and levels to be added to the model. Next to each level, the elevation is shown along with the number of associated model components in brackets. It is also possible to activate or deactivate their visibility in the work area.
With the "Assign elements to a level" option, components of the model can be selected from the work area and associated to the level selected in the list. The "Unassign elements to a level" option allows the reverse operation to be carried out.
From the "Information on the level of an element" option, users can inspect an object from the workspace and obtain its current level.
Finally, the "Automatic assignment" option associates the components of the model to the defined levels automatically. To do this, the geometry of the element is analysed and the level immediately below it is searched for.
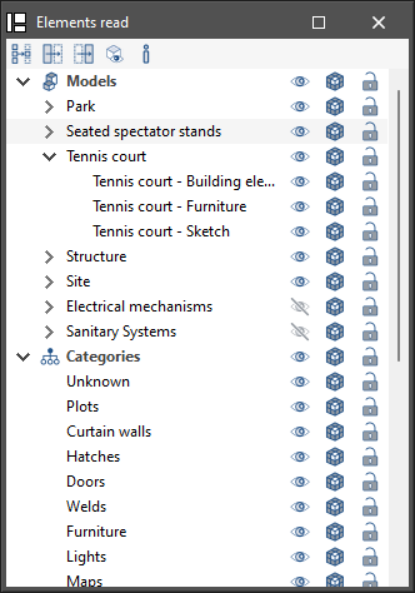
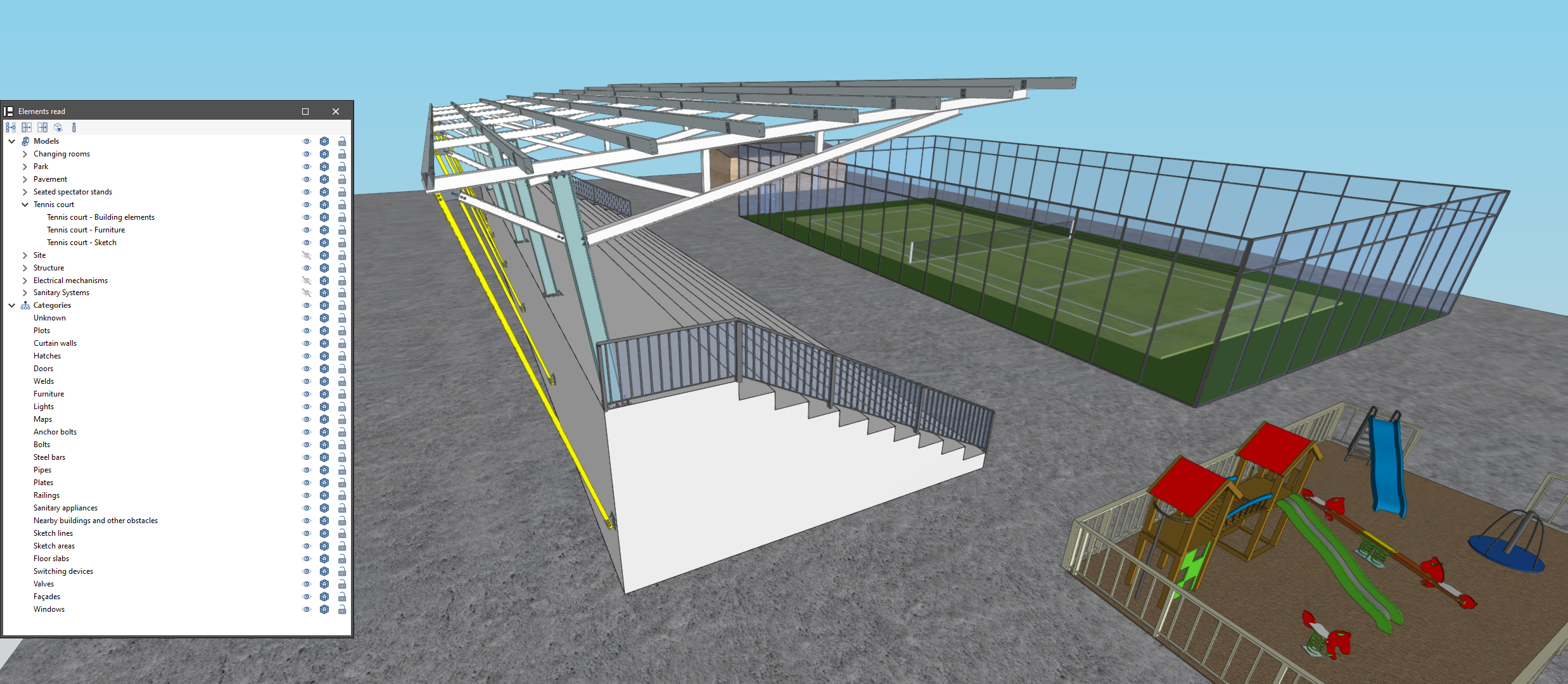
Managing elements read
The management of the elements from the digital model of the building, obtained from the associated BIM project, is carried out from the "Elements read" menu located on the left sidebar of the application.
The elements read are structured in the form of a tree according to two types of classification:
- By "Models": users can inspect each contribution linked to the job and, within this, each associated 3D model.
- By "Categories": allows users to group the "Elements read" into families according to their characteristics.
Three buttons are displayed next to each component of the tree:
- Visible
Enables or disables the visibility of the elements. - Visualisation mode
Allows users to toggle between normal, transparent and wired display modes. - Snap
Allows users to enable or disable object snaps of the elements.
The following actions can be carried out via the toolbar in the top left-hand corner:
- Isolate selection
Allows users to isolate elements of the 3D model. By selecting the elements of the 3D model to be isolated and clicking the right mouse button, the rest of the elements of the model will disappear. - Hide
Allows users to hide the selected elements. By selecting the elements of the 3D model to be hidden and right-clicking on them, they will disappear. - Show all
Shows all hidden elements. - Appearance
Allows users to choose between normal drawing or monochrome drawing. - BIM information
Displays a panel with the attributes associated with the selected component.

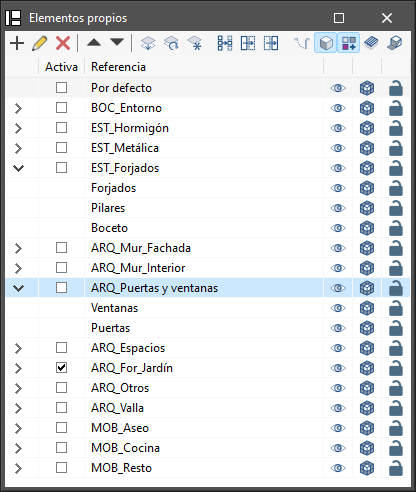
Own element management
In this section, the elements of the job opened by the program the user is working with are organised in layers that can be created, deleted, edited, sorted, shown or hidden according to their preferences. Within each layer, the elements can be displayed in grouped categories, which can be expanded or collapsed by clicking on the arrows on the left.
Depending on the program being used, the following options and controls appear next to each component of the tree:
- Visible
Enables or disables the visibility of the elements. - Visualisation mode
Allows users to choose between normal, transparent and wired display modes. - Snap
Activates or deactivates object snaps of the elements.
In the top toolbar a number of options for managing layers can be found:
- Add
Create a new layer. - Edit
Edits the selected layer reference. - Delete
Deletes the selected layer reference. - Move selected element up/down the list
Moves the selected layer one place up or down in the list. - Assign layer (Ctrl + A)
This makes it easier to change the element from one layer to another. The program allows you to select the layer where the element is to be assigned. - Update layers
Regenerates the display of all layers and makes them visible. - Isolate layer
Isolates the active layer, hiding the other layers available in the project. - Isolate selection (Ctrl + I)
Selects a number of elements to remain visible; those not selected will be hidden. - Hide elements (Ctrl + H)
Controls the visibility of each element. - Show elements (Ctrl + U)
Undoes the "Isolate selection" and "Hide elements" actions mentioned above.
Options for entering elements on the "Workspace"
The option bar for entering elements is located at the top left of the "Work area" window and appears when entering or editing an element in the model. This bar has the following options, which depend on the active view and the element(s) being entered or edited:

- Force elevation (optional)
Defines the position of the new element in the model.- If this option is active:
- If a component of the model is snapped, its position will be projected onto the work plane of the view selected in the drop-down menu, where the new element will be inserted, adjusted with the "Displacement" indicated on the right.
- If no component is snapped, the new element will be inserted at the cursor position and on the working plane of the view selected in the drop-down menu, adjusted with the "Displacement" indicated on the right.
- If this option is left deactivated:
- If a component of the model is snapped, the new element will be inserted at the exact position of that component, even if it is outside the working plane of the selected view.
- If no component is snapped in, the new element will be inserted at the cursor position and on the work plane of the selected view in the "Views" panel.
- If this option is active:
- Select views (drop down)
This drop-down menu is used to select one of the views created in the "Views" panel to support the operation of the "Force elevation" option:- In 2D views such as elevations, sections or plans, the selector is locked to the view selected in the "Views" panel; this means that no other view can be selected.
- In 3D views, any of the views created in the "Views" panel can be selected.
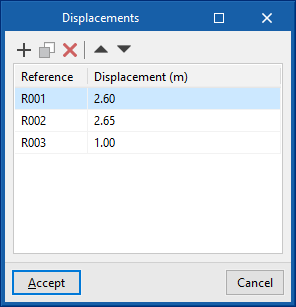
- Displacement (optional)
Used to enter a displacement value, either positive or negative, which will be applied to the position of the working plane of the view selected in the drop-down menu above. The option to the right of this field is used to save and load displacements for the entire job, indicating their reference and value.
- Points
This section is activated when inserting points in the workspace to define the geometry of a new element and has the following options:- Erase the last entered point
- Erase all entered points
Visibility monitoring tools to support the modelling
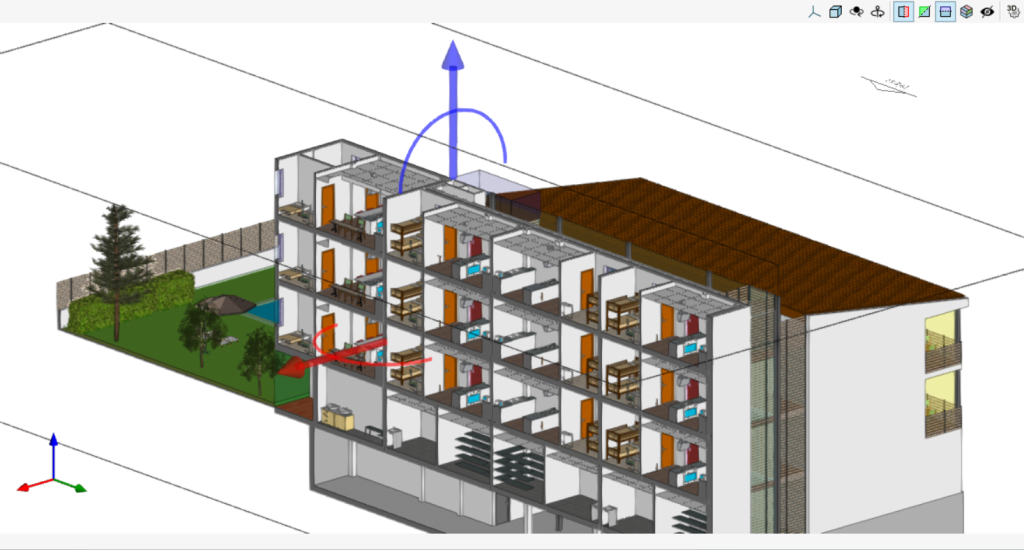
In the top right corner of the 3D viewing area is a toolbar that allows users to control the visibility of the model during the modelling process.
This bar offers various options to make it easier to manage and visualise the project. Some of the options are shown in the following image.
The first section covers the options for controlling the display modes of the model:
- Projection: opens a window that allows users to select predefined projections, such as top view, front view, isometric view, orthogonal view, etc.
- Projection type: modifies the type of projection from axonometric to conic and vice versa.
- Rotation around a point: activates or deactivates the rotation of the scene around a point of an object located under the cursor.
- Rotation around the camera: activates or deactivates the rotation of the scene around the vertical axis of the camera.
The following 5 options allow users to create sections for viewing the BIM model from different perspectives and to create customised views.
- Section perpendicular to the global "X" axis: allows users to define a section of the model perpendicular to the global "X" axis.
- Section perpendicular to the global "Y" axis: allows users to define a section of the model perpendicular to the global "Y" axis.
- Section perpendicular to the global "Z" axis: allows users to define a section of the model perpendicular to the global "Z" axis.
- Clip volume: allows users to define a display volume using 6 cutting planes that is formed from the geometric envelope of the scene content.
- Show/Hide section planes: allows users to manage the visibility of the lines and symbols of the sections created.
Licenses and related modules
CYPE programs are activated via electronic licenses which may contain one or more modules. The list of modules compatible with each program may vary depending on the product purchased and the type of license.
To consult the list of modules compatible with this program, go to "CYPE program modules".
Please note that the list of modules available in the license will depend on the product purchased.