Introduction
IFC Builder is a free CYPE app designed for creating and maintaining IFC models of buildings.
Architectural models generated with IFC Builder can be imported by a wide variety of acoustic and energy simulation apps as well as structural and MEP analysis apps linked to BIMserver.center.
Workflows supported by the program
As IFC Builder is an Open BIM tool that is connected to the BIMserver.center platform, it offers different workflow options.
Data entry
Free modelling / with templates
- Defining the architectural elements of the building by freely entering them into IFC Builder.
- Defining the architectural elements of the building in IFC Builder from DXF-DWG, DWF templates or images (.jpeg, .jpg, .bmp, .wmf).
Automatic entry: importing IFC format models
- Importing the model in IFC format with the geometry of a building. This allows users to generate the floor plan of the building and the geometry of walls and partitions, floor slabs and openings (such as windows and doors).
Data output
- Exporting the building model in IFC format.
- Exporting the information generated with IFC Builder to the BIMserver.center platform. This allows authorised project participants to view and export the building geometry to different programs such as CYPECAD, CYPETHERM EPlus, CYPESOUND, CYPEPLUMBING, CYPELEC Electrical Mechanisms, CYPELEC Distribution, CYPEGAS, CYPEHVAC, CYPEHVAC Radiant Floor, CYPELUX, CYPEFIRE, CYPEFIRE Hydraulic Systems and CYPETEL Wireless, among others.
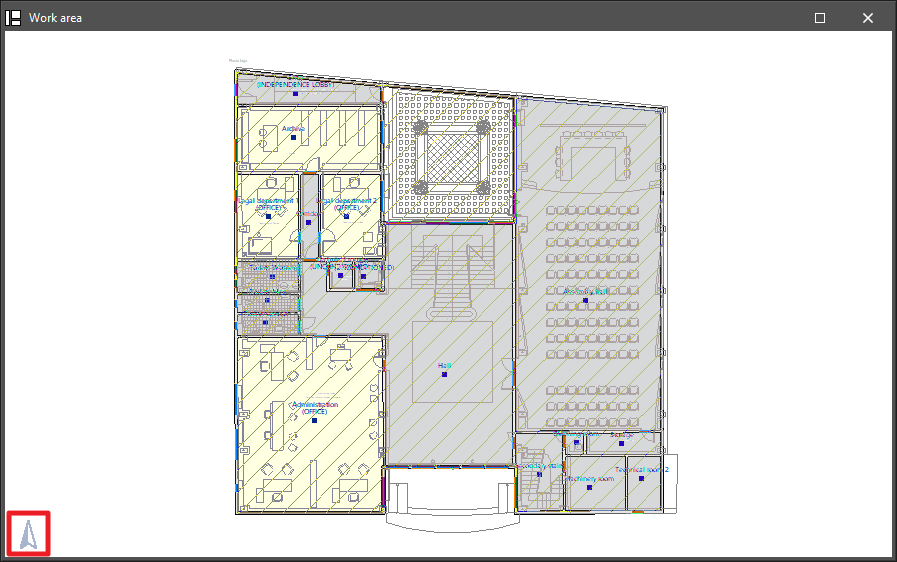
Work environment
The IFC Builder interface features a work environment that makes building modelling quick and easy, with a system of dockable windows that can be customised to adapt the workspace to the project's needs.
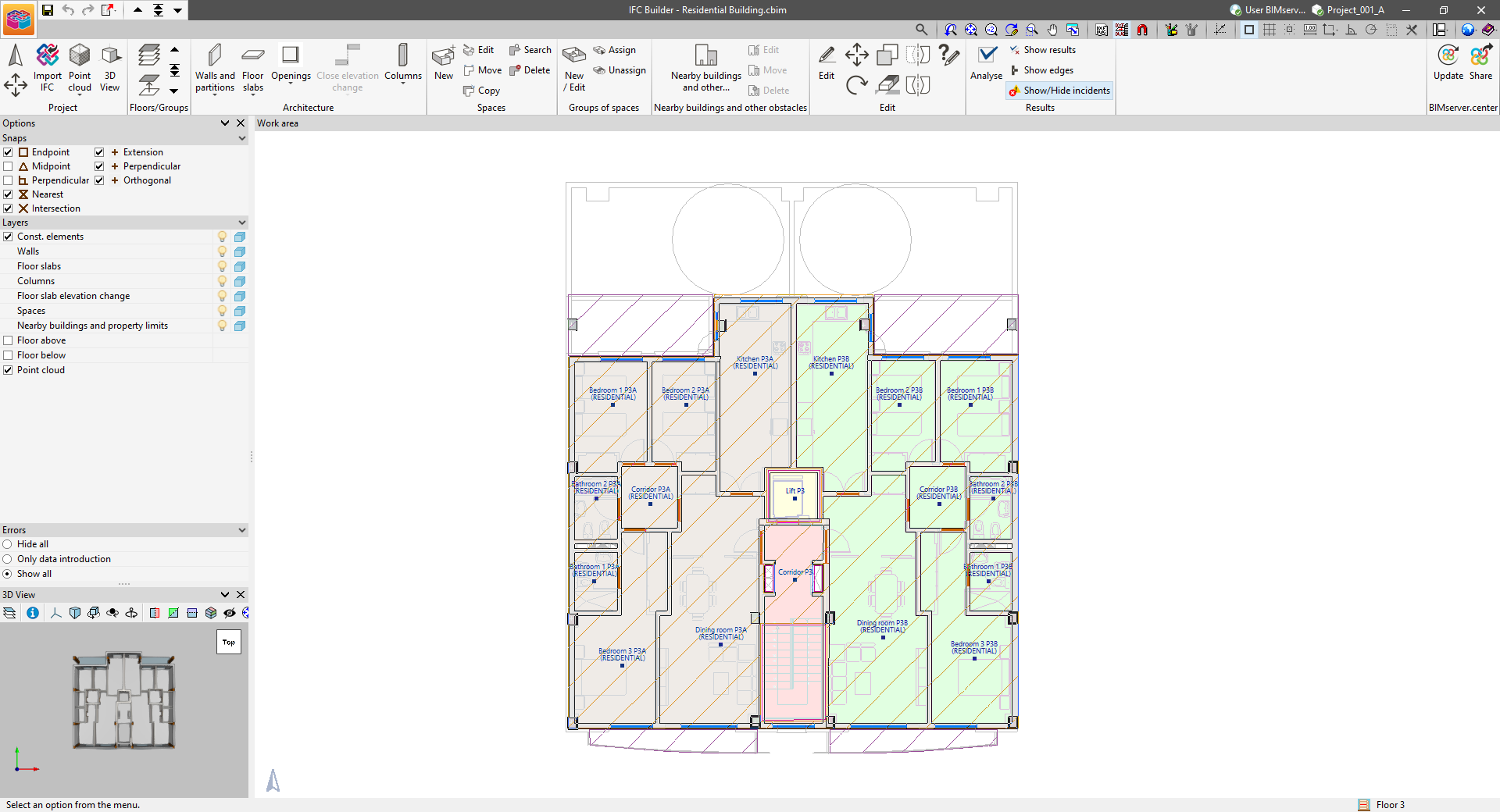
The program interface displays the following:
- A top toolbar, which contains the tools for managing the project characteristics, entering and editing the building's construction elements, entering and grouping the spaces, checking the geometry, and exporting the model to BIMserver.center;
- The modelling area on the right-hand side of the screen, where all elements of the project are entered, edited and displayed floor by floor;
- Several panels on the left-hand side with tools to configure the snaps of the elements in the model, manage the visibility of the layers, hide or show errors and display the 3D view.
Defining the general characteristics of the project
The following options can be found in the "Project" group of the main toolbar:

Orientation
Allows users to enter the orientation of the model by indicating the direction and the north direction. The icon showing the north direction is located in the bottom left corner of the work area. By default, north points to the top of the screen.
Move the building
Moves the entire building as a whole, including all floors, to the specified coordinates.
Import IFC
Launches the "Automatic entry. CAD/BIM model import" assistant. Once completed, it replaces the geometry of the model with the geometry imported from the IFC file.
Importing the model from IFC files
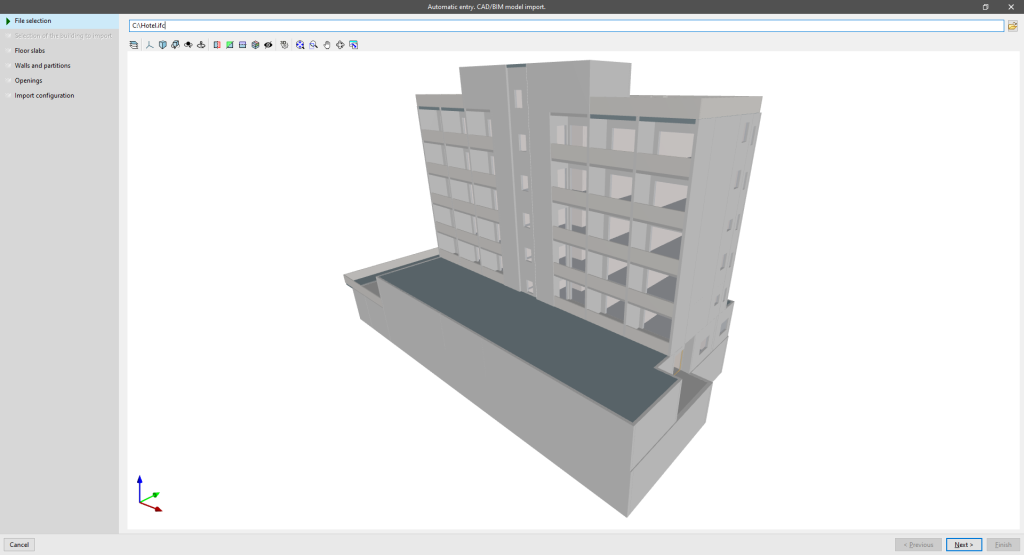
When creating a new job in IFC Builder, or by using the "Import IFC" option in the "Project" group of the main toolbar, users can import a model in IFC format generated by CAD/BIM programs, such as Allplan®, Archicad®, and Revit®. This allows IFC Builder to access data from programs that have BIM (Building Information Modeling) technology and automatically incorporate the building's construction elements.

When using this option, the program launches the “Automatic entry. CAD/BIM model import" assistant, which presents the following data definition sequence:
Selection of the building to import
If the IFC file includes information on several buildings, the program requires users to select the building to be imported.
The IFC class interpreted in this step is the following:
- IfcBuilding
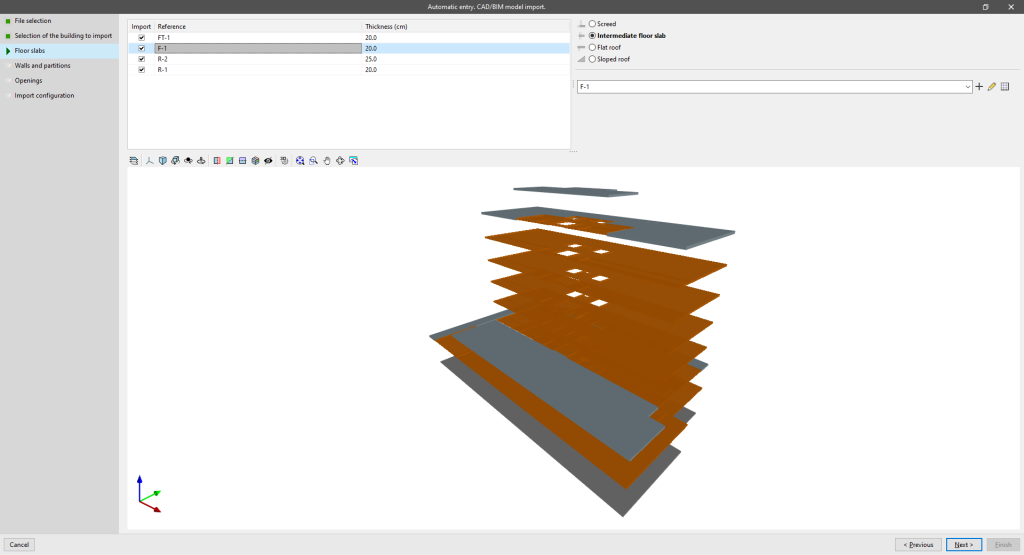
Floor slabs
Allows users to view the reference and thickness of the slabs defined in the IFC file, to select the slabs to be imported, and to create and assign their typologies in IFC Builder.
The IFC class interpreted in this step is the following:
- IfcSlab
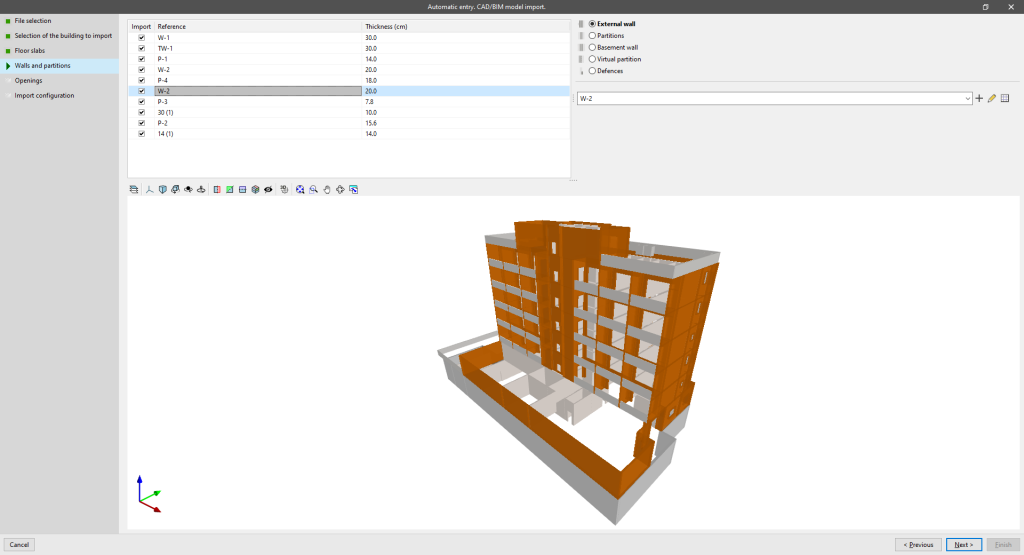
Walls and partitions
Allows users to view the reference and thickness of the walls and partitions defined in the IFC file, to select the walls and partitions to be imported, and to create and assign their typologies in IFC Builder.
The IFC classes interpreted in this step are the following:
- IfcWall
- IfcWallStandardCase
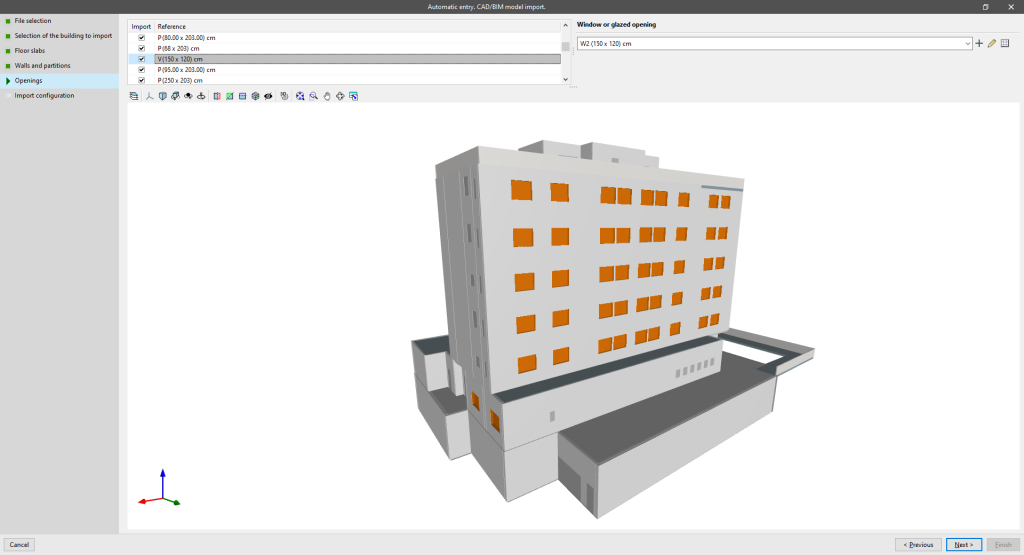
Openings
Allows users to view the reference of the openings defined in the IFC file, to select the openings to be imported, and to create and assign their typologies in IFC Builder.
The IFC classes interpreted in this step are the following:
- IfcDoor
- IfcWindow
- IfcOpeningElement
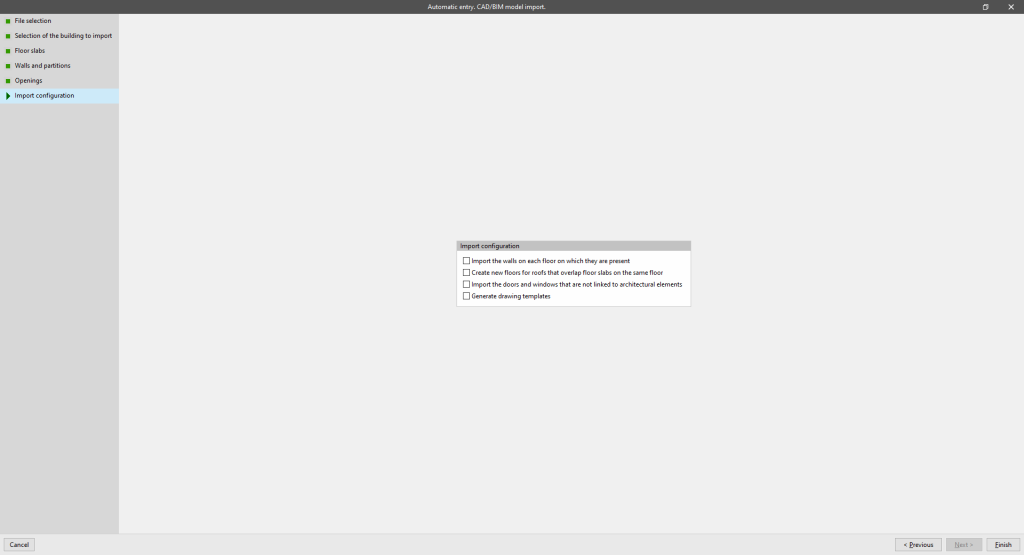
Import configuration
Allows users to activate the following import configuration options:
- Import the walls on each floor on which they are present (optional)
- Create new floors for roofs that overlap floor slabs on the same floor (optional)
- Import the doors and windows that are not linked to architectural elements (optional)
- Generate drawing templates (optional)
The reading of IFC files and the import of their data through this assistant is unidirectional, and an update of the data cannot be performed if the information in the IFC file changes. However, in this case, a new IFC import could be carried out.
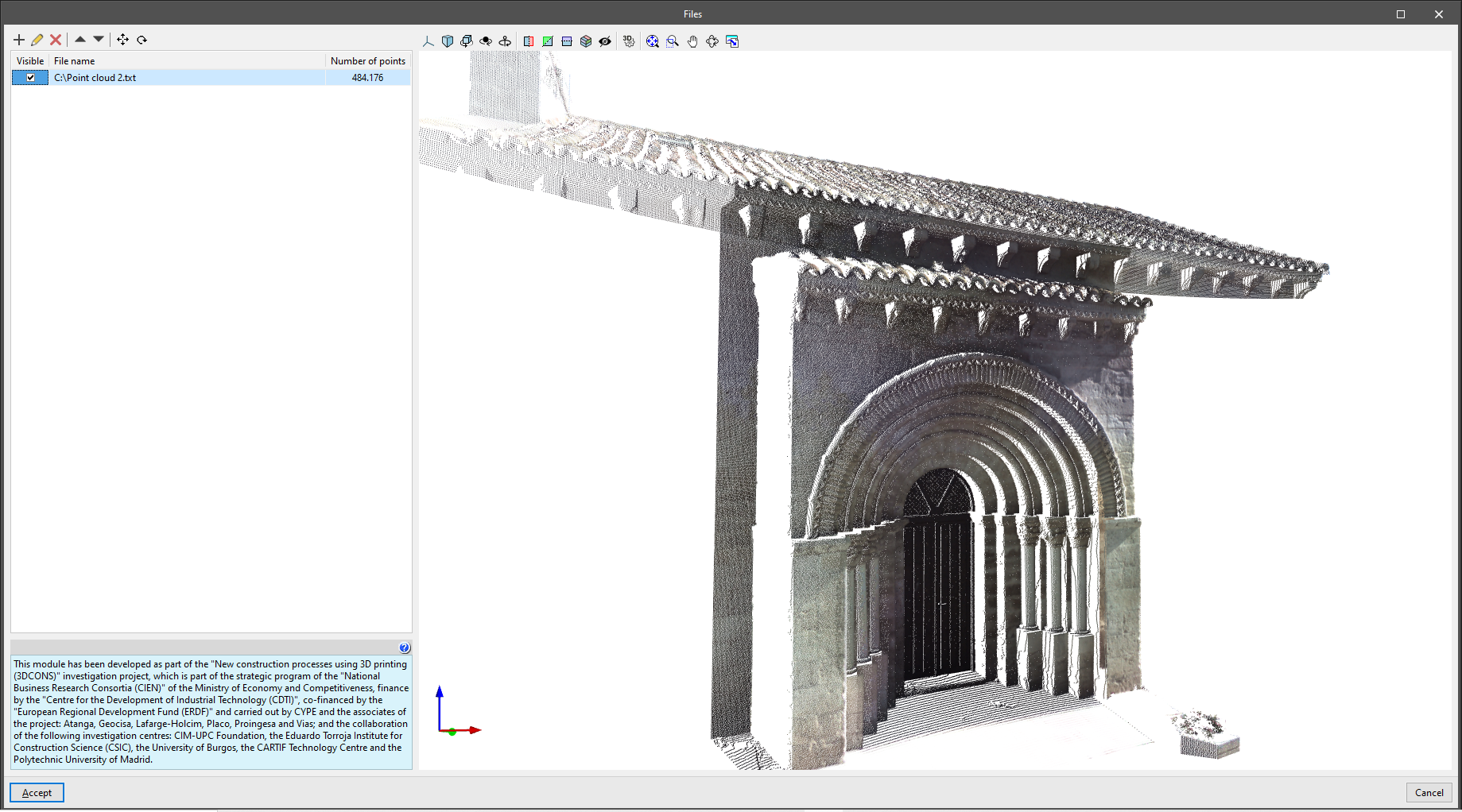
Reading point clouds
IFC Builder can read a representation both in 3D and on plan from point cloud files (*.pts; *.ptx; *.txt; *.xyz), which can be used as a support to model reality quickly and accurately from a BIM environment.
A point cloud is the result of one or more 3D laser scans consisting of a set of vertices in a three-dimensional coordinate system, usually defined by "x", "y" and "z" coordinates, and sometimes incorporating additional data such as colour using RGB values.

The "Point cloud" menu in the main toolbar of the program's general interface contains the following options:
- Files
- Visibility
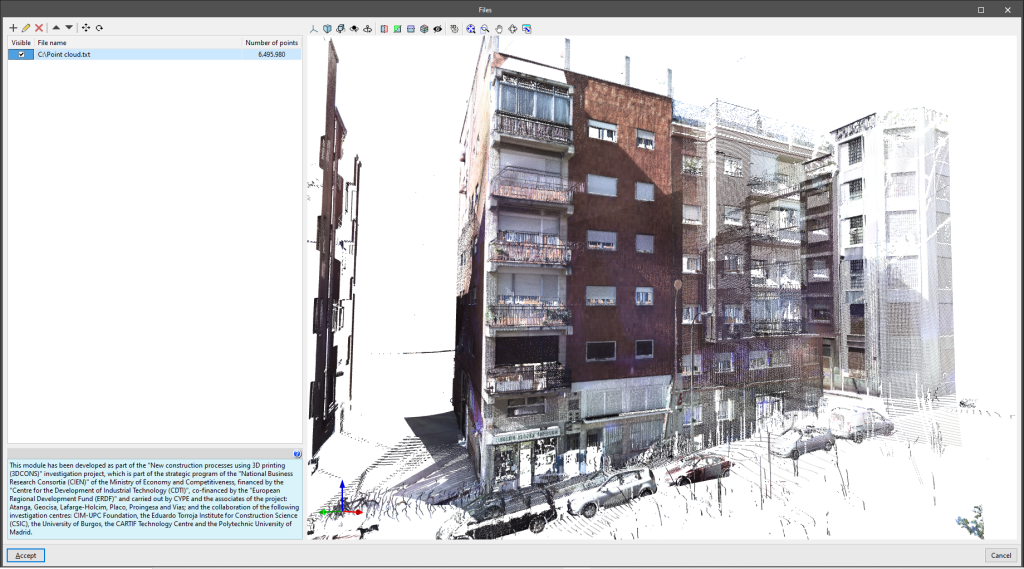
Files
Allows users to select PTS, PTX, TXT or XYZ point cloud files at their location on disk and load them into the program, defining the following information:
- File name
- Show in monochrome (optional)
The loaded point cloud files are displayed in a table with the following parameters:
- Visible
- File name
- Number of points
As added tools, the point cloud can be moved and rotated.
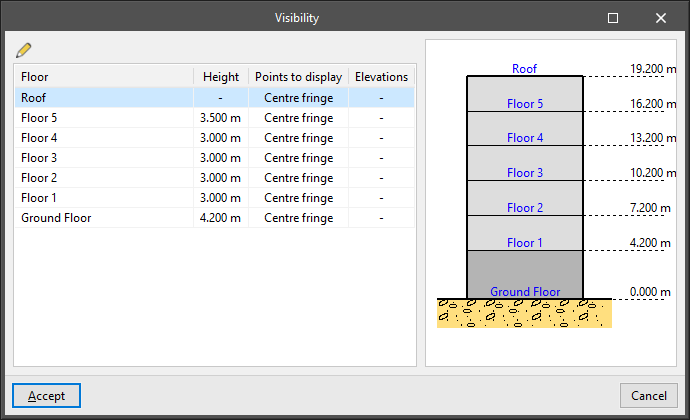
Visibility
Manages the visibility of the points in the point cloud files on the different floors of the building. The following information is shown in the table:
- Floor
- Height
- Points to display (All points / Centre fringe / Height range)
- Elevations (only for "Height range")
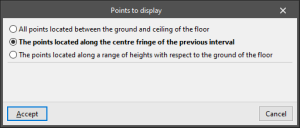
If each floor is edited, the "Points to display" are selected. These points can be:
- All points located between the ground and ceiling of the floor
- The points located along the centre fringe of the previous interval
- The points located along a range of heights with respect to the ground of the floor
- Initial height
- Final height
In this way, the visible points of the point cloud can be used as a visual reference when entering the elements of the model floor by floor.
The 3DCONS project aims to bring 3D printing technologies to the construction industry, both in the field of new construction and in the renovation and restoration of cultural heritage, using point cloud technologies for the reading of existing buildings.
Defining floors and groups
The following options can be found in the "Floors/Groups" group in the main toolbar:

Floors/Groups
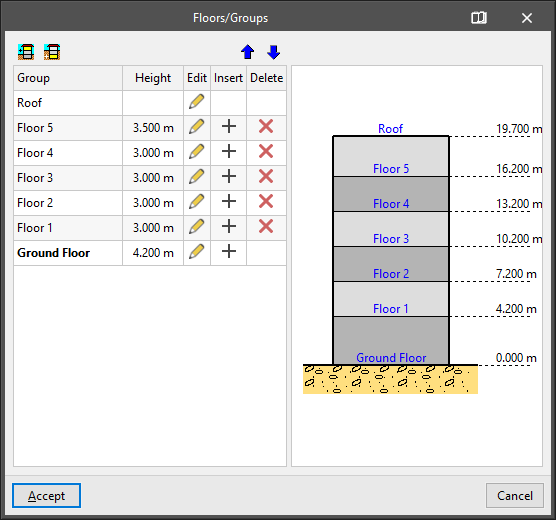
Allows users to define the floors and groups of the building.
A table with the following information appears on the left side of the "Floors/Groups" window:
- Group
Reference of each group of floors. - Height
Height of the floors belonging to each group. - Edit
Allows the characteristics of each group of floors to be edited:- Number of floors in the group (except ground floor and roof floor)
- Height of each floor
- Reference for each floor
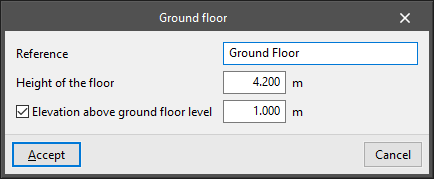
- Elevation above ground floor level (ground floor only)
This option allows users to specify an elevation above the ground level with respect to the base plane of the ground. This allows a semi-buried basement to be defined.
- Insert
Allows a group of floors above or below ground level to be inserted in the position immediately above. - Delete
Deletes the group of floors.
By default, the program always presents a ground floor and a roof floor.
The following tools can be found at the top:
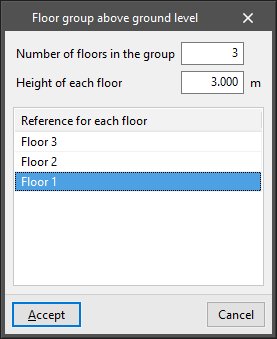
- Floor group above ground level / Floor group below ground level
Allows a floor group to be entered above or below ground level by specifying the following parameters:- Number of floors in the group
It can be a group of one floor or a group of several floors greater than 1 if users want to define a set of several floors that are exactly the same. - Height of each floor
Corresponding to the distance between the top face of the floor slab entered on each floor and the top face of the floor slab on the floor above it. - Reference for each floor
- Number of floors in the group
- Move the building up a floor / Move the building down a floor
These options allow the building to be raised or lowered one storey by changing the position of the base plane of the ground.
On the right-hand side, there is a schematic display of the floors of the building, the ground plan and the reference and height of each floor relating to it.
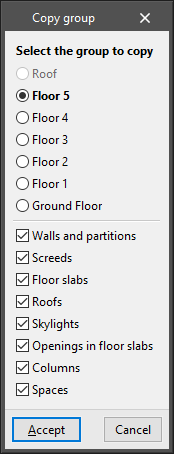
Copy to another group
Allows the elements of another floor group to be copied over the current group, i.e. the one the user is currently in. If data already exists in the group to be copied, this data will be lost.
This option is very useful when the elements of one group are almost the same or very similar to those of another group. Once the copy has been made, the appropriate modifications can be made.
The option opens the "Copy group" window, in which the following aspects are configured:
- Select the group to copy
- Activate or deactivate the types of elements to be copied:
- Walls and partitions
- Screeds
- Floor slabs
- Roofs
- Skylights
- Openings in floor slabs
- Columns
- Spaces
Up a group/Change group/Down a group

These tools allow users to modify the group of floors visible in the working area.
The options "Up a group" and "Down a group" allow users to display the group of floors immediately above or below the one visible on the screen, while from "Change group" they can directly select the group of floors they want to display.
The floor group reference visible on the screen is displayed in the lower right corner of the program's general interface.
Entering architectural elements
The following options can be found in the "Architecture" group in the main toolbar:

With these options, the building elements and structural elements of the building can be entered, depending on what is required for the subsequent analyses.
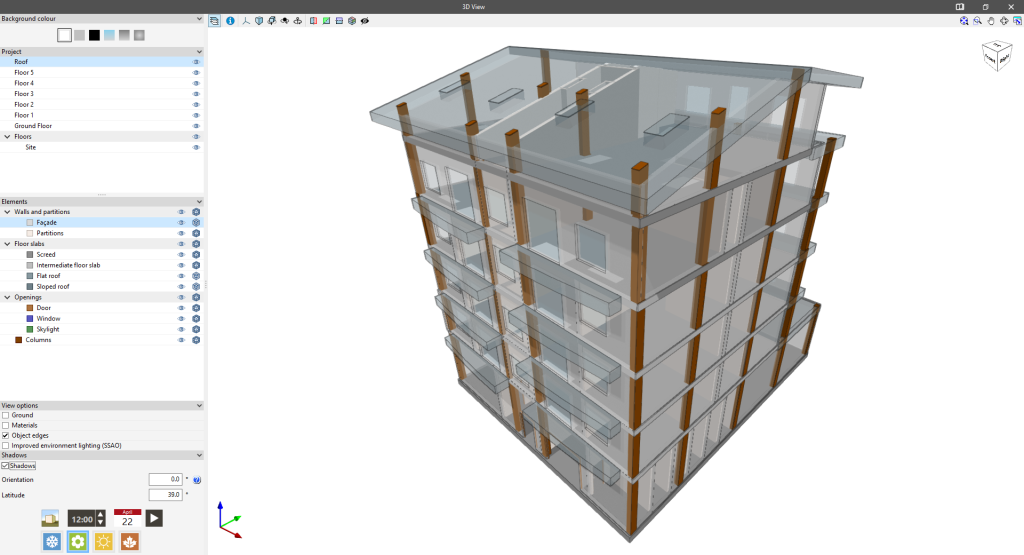
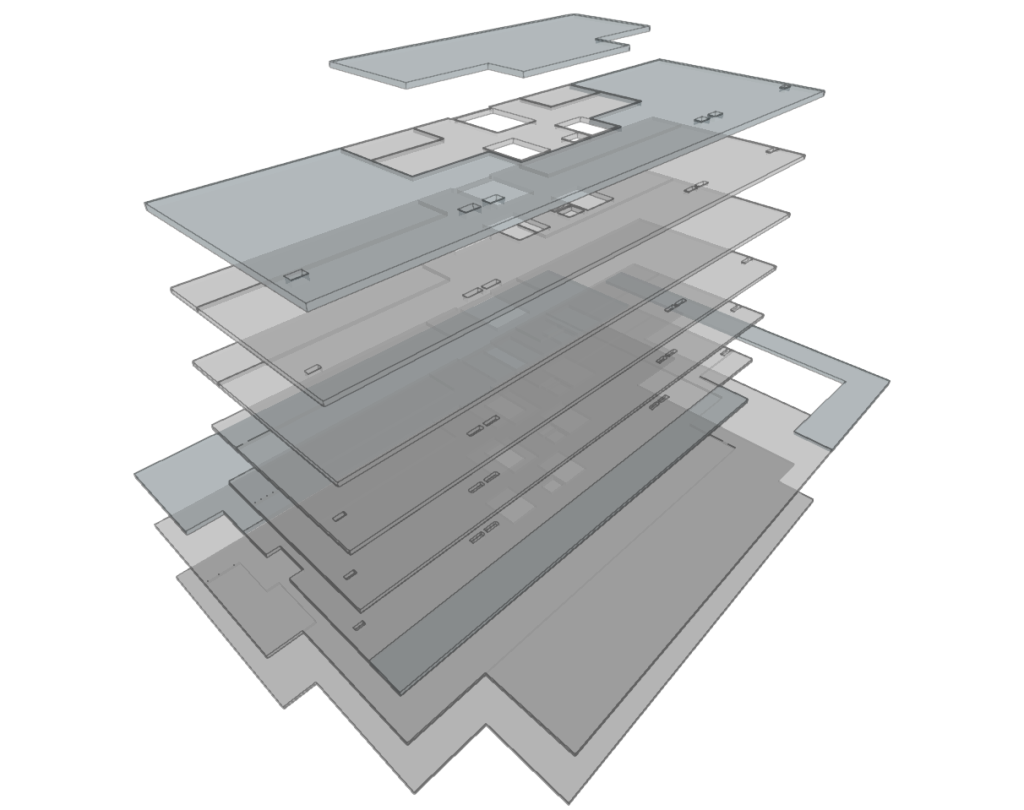
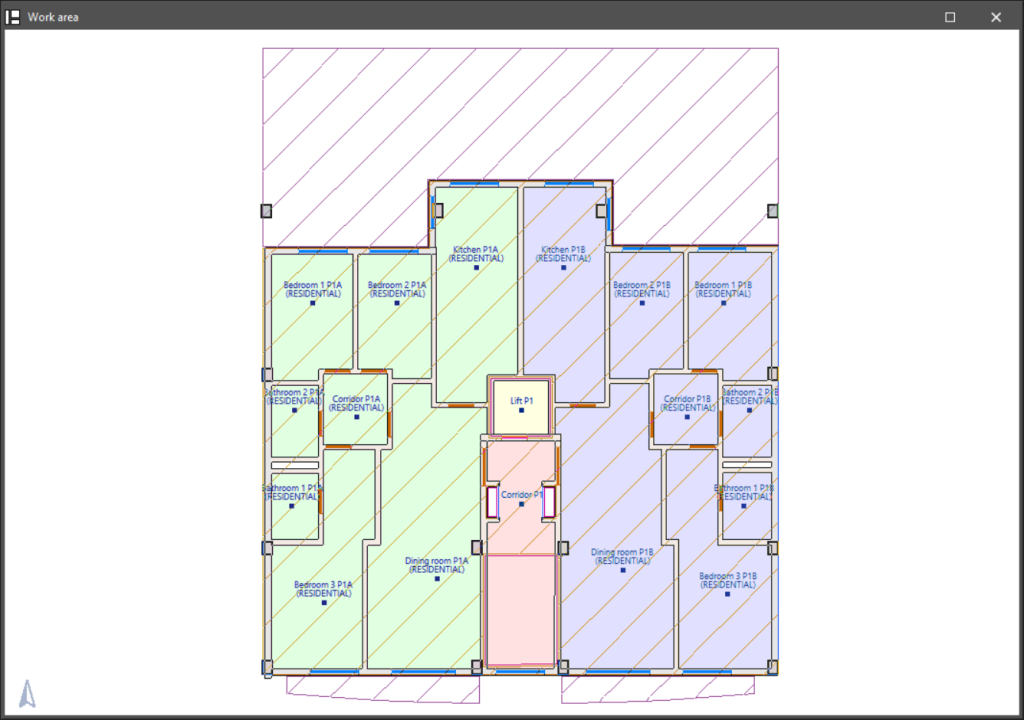
Modelling is carried out floor by floor in a 2D workspace, using 3D elements. The 3D view of the building can be displayed at any time, allowing the modelling process to be controlled.
Building modelling in IFC Builder can be done from scratch, with or without the help of templates or drawings in DXF, DWG, JPEG or BMP format. The use of these templates speeds up manual data entry.
Walls and partitions
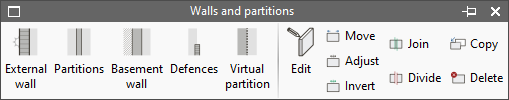
The "Walls and partitions" menu allows users to enter and edit elements of vertical geometry in the model, such as façades, party walls, partition walls, basement walls, defences and virtual partitions.
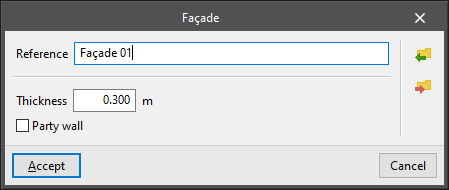
- Façade
Vertical separation element between a building space and the external environment or, if it is a party wall, between a building space and the space belonging to other buildings. The following parameters are defined for each type of façade:- Reference
- Thickness
- Party wall (optional)
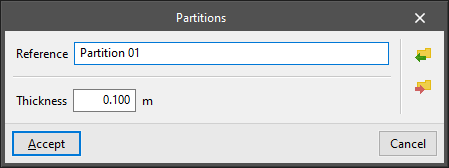
- Partitions
Vertical separation element between two interior spaces of the building. The following parameters are defined for each type of partition:- Reference
- Thickness
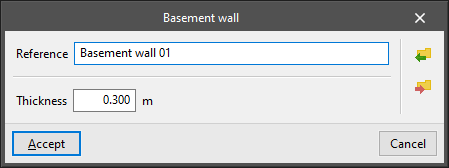
- Basement wall
Vertical separation element between a building space and the ground. The following parameters are defined for each type of basement wall:- Reference
- Thickness
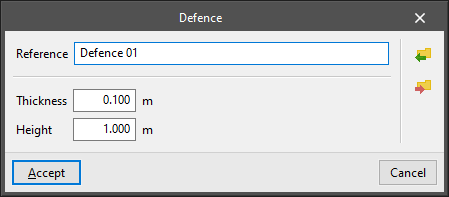
- Defences
This allows users to model railings, balustrades, perimeter parapets and other defences. The following parameters are defined for each type of defence:- Reference
- Thickness
- Height
- Virtual partition
A vertical element with no space delimitation thickness. It can be placed between two rooms in the model that are not separated by a physical barrier in the actual building (e.g. between an open kitchen and the living room).
The tools for editing walls and partitions are as follows:
- Edit
Allows users to edit the wall type to modify its characteristics or change the type assigned to the selected element. - Move
This allows walls and partitions to be repositioned by moving them either parallel to their position or by moving one of their ends. - Adjust
Allows users to adjust the position of the selected wall or partition with respect to the reference line, either by aligning them along one of their faces or along the central axis. - Invert
Reverses the direction in which the partitions are inserted. - Join
Joins two walls. - Divide
Divides a wall in two at a point determined by the user. - Copy
Copies the type from one wall to another. - Delete
Deletes the selected walls and partitions.
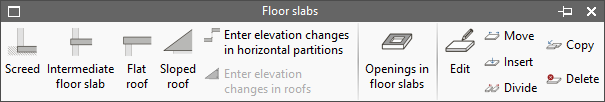
Floor slabs
The "Floor slabs" menu allows users to enter and edit elements of horizontal or inclined geometry in the model, such as screeds, intermediate floor slabs, flat roofs and sloped roofs.
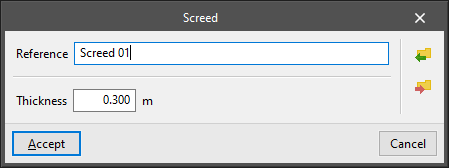
- Screed
Allows users to define screeds and suspended ground floors. The following parameters are defined for each type of slab:- Reference
- Thickness
- Intermediate floor slab
This allows users to enter an internal slab, which separates two rooms of the building, or a floor slab overhang, which separates a room at the top and the external environment at the bottom. The following parameters are defined for each type of intermediate floor slab:- Reference
- Thickness
- Overhang (optional)
- Flat roof
Allows users to enter a flat roof. The following parameters are defined for each type of roof:- Reference
- Thickness
- Sloped roof
Allows you to enter the slope for a sloped roof. The following parameters are defined for each type of roof:- Reference
- Thickness
The program has two options for adjusting the geometry of horizontal floor slabs and sloped roofs:
- Enter elevation changes in horizontal partitions
Allows a positive or negative elevation change to be applied to a floor slab, an intermediate floor slab or a roof with respect to the floor height. This elevation change shifts the floor slab parallel to the ground.
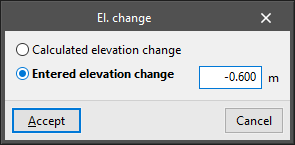
- Enter elevation changes in roofs
Allows a slope to be applied to the points of the polygonal surface that define a roof. This elevation change can be:- Calculated elevation change
The program calculates the elevation change of the point according to the elevation changes entered in the rest of the points of the polygonal surface that defines the roof's perimeter. - Entered elevation change
Users enter the elevation change of the selected point with respect to the height of the floor, either positive or negative.
- Calculated elevation change
From the "Floor slabs" menu, openings can also be entered in floor slabs by drawing their perimeter outline in plan on a previously entered floor slab:
- Openings in floor slabs
The tools for editing floor slabs are as follows:
- Edit
Allows users to edit the type of floor slab to modify its characteristics or change the type assigned to the selected element. - Move
Allows users to modify the shape of a slab by changing the position of the vertices or sides of the polygonal line that defines its perimeter. - Insert
Allows users to insert an additional point on the polygonal line that defines the perimeter of the slab. - Divide
Allows users to split a floor slab in two by drawing a polygonal line between two points on its perimeter. - Copy
Copies the type from one floor slab to another. - Delete
Removes the selected floor slabs.
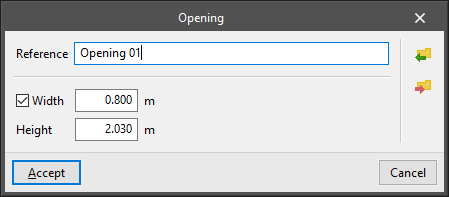
Openings
The "Openings" menu allows users to enter and edit openings such as doors, windows, openings and skylights in the model. It requires the prior entry of the wall or floor slab where the opening will be made.
The types of openings available are as follows:
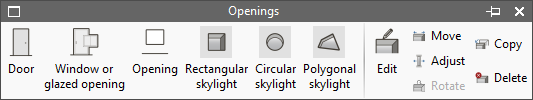
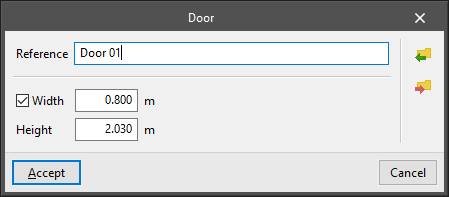
- Door
Enters a door in a wall or partition. The following parameters are defined for each door type:- Reference
- Width (optional)
If the width is deactivated, it will be defined when the door is entered graphically in the floor plan model. - Height
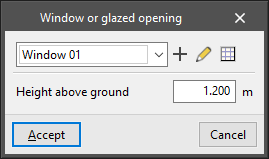
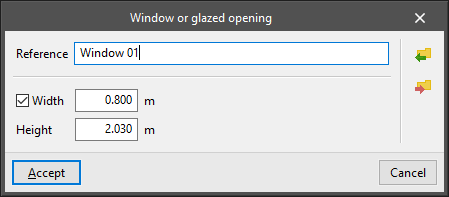
- Window or glazed opening
Enters a glazed opening in a wall or partition. The following parameters are defined:- Type parameters:
- Reference
- Width (optional)
If the width is deactivated, it is defined when the window or glazed opening is entered graphically in the floor plan model. - Height
- Instance parameters:
- Height above ground
- Type parameters:
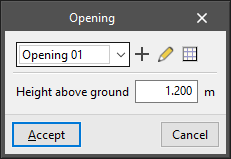
- Opening
Enters an uncovered opening in a wall or partition. The following parameters are defined:- Type parameters:
- Reference
- Width (optional)
If the width is deactivated, it will be defined when the opening is entered graphically in the floor plan model. - Height
- Instance parameters:
- Height above ground
- Type parameters:
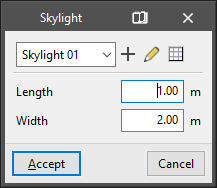
- Rectangular skylight
Allows users to enter a rectangular-shaped skylight in a floor slab. The following parameters are defined:- Type parameters:
- Reference
- Instance parameters:
- Length
- Width
- Type parameters:
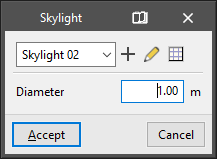
- Circular skylight
Enters a circular-shaped skylight in a floor slab. The following parameters are defined:- Type parameters:
- Reference
- Instance parameters:
- Diameter
- Type parameters:
- Polygonal skylight
Enters a user-defined free-form polygonal skylight in a floor slab. The following parameter is defined for each type of polygonal skylight:- Reference
The tools for editing openings are as follows:
- Edit
Allows users to edit the type of opening to modify its characteristics or change the type assigned to the selected element. - Mover
Shifts an opening that has already been entered:
-For doors and windows or glazed openings, if the width of the opening is fixed, it changes its position to another place in the floor plan, keeping its dimensions constant. If the width is not fixed, it allows users to move one of the ends of the opening along the wall where it is located, increasing or decreasing its size.
-In circular and rectangular skylights, the position of the skylight can be shifted on plan.
-In polygonal skylights, the vertices and sides of the polygon defining the skylight can be moved. - Adjust
Shifts doors and windows to adjust their position to inside beams, outside beams or in the centre of the opening in the wall. - Rotate
Rotates a skylight around an axis perpendicular to the skylight that passes through its geometric centre. - Copy
Copies the type and characteristics from one opening to another. - Delete
Removes the selected openings.
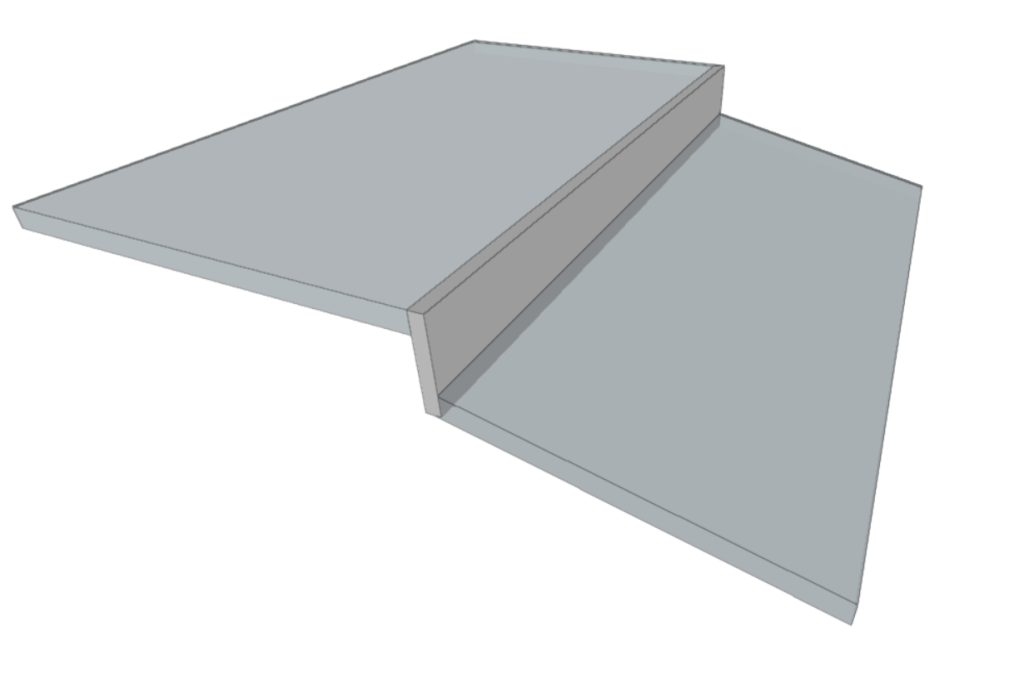
Closing the elevation change
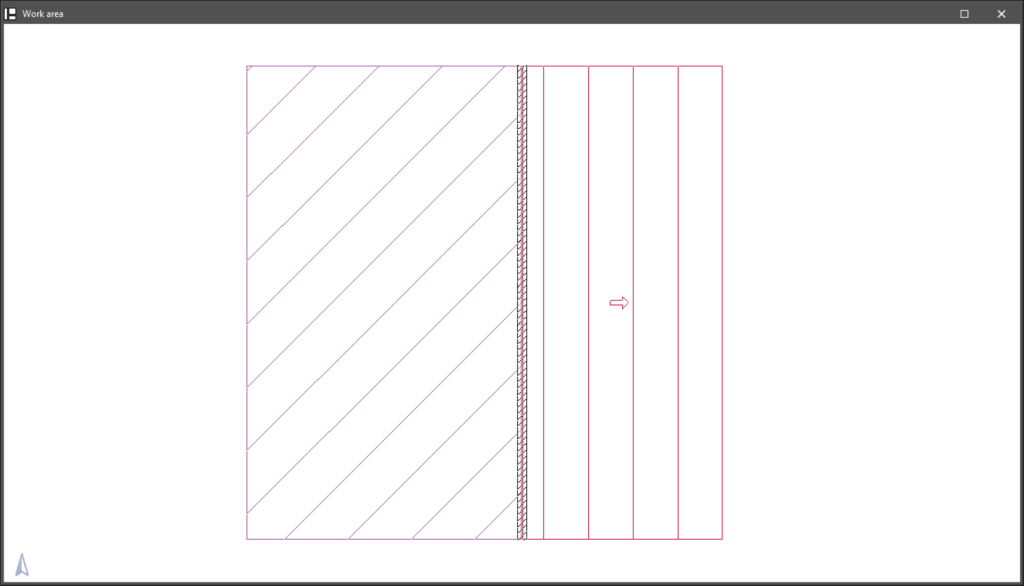
Using this option, a closing can be entered in the slopes previously generated in the border between two floors of the same storey, after using the "Enter elevation changes in horizontal partitions" or "Enter elevation changes in roofs" options.
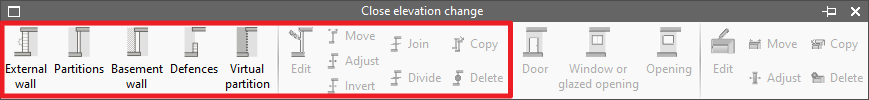
The closing of elevation changes can be categorised as any of the wall and partition types and has the same editing tools:
- External wall
- Partitions
- Basement wall
- Defences
- Virtual partition
- Edit
- Move
- Adjust
- Invert
- Join
- Divide
- Copy
- Delete
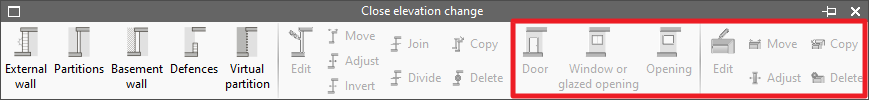
Also, in the menu accessible through this option, openings can be entered in the closings of slopes defined in the model. This menu offers editing tools for these levels:
- Door
- Window or glazed opening
- Opening
- Edit
- Move
- Adjust
- Copy
- Delete
The closings of slopes are represented by a striped pattern on the ground plan.
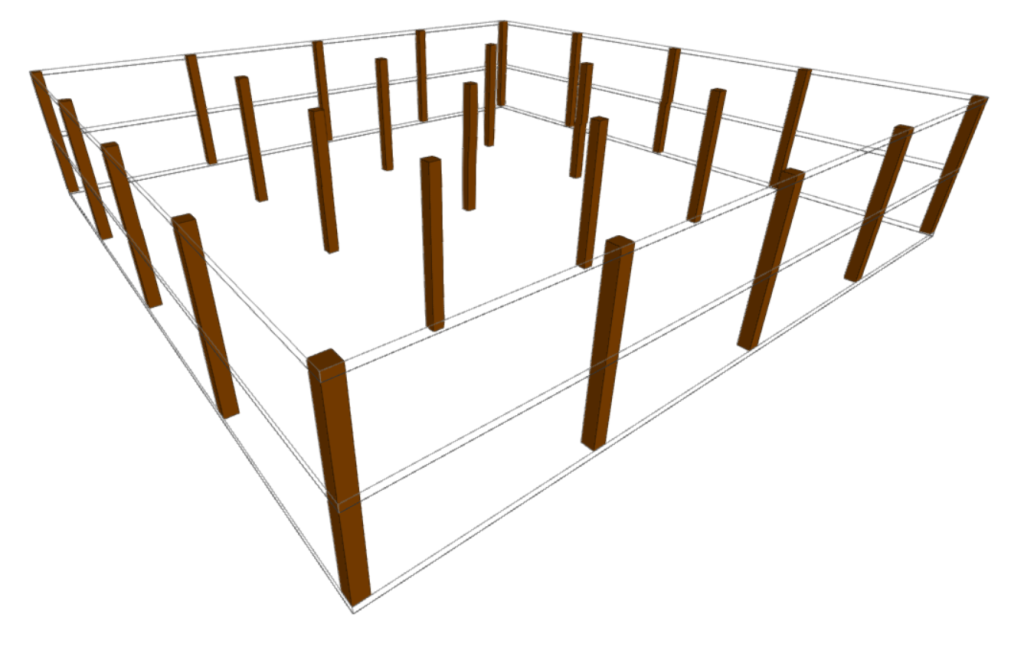
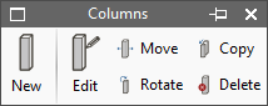
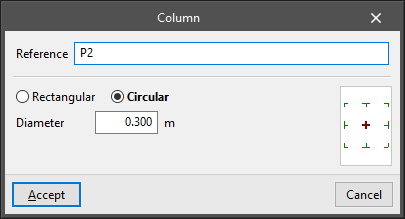
Columns
The "Columns" menu allows users to enter and edit rectangular or circular section columns in the model.
The option available for entering columns is as follows:
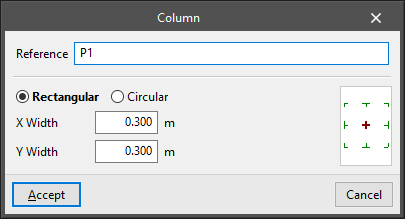
- New
Enters a column after defining the following parameters:- Reference
- Selection of type:
- Rectangular
- X width
- Y width
- Circular
- Diameter
- Rectangular
- Insertion point (centre, faces or corners)
The options available for editing columns are as follows:
- Edit
Allows users to edit the reference, type and characteristics of the selected column. - Move
Moves the selected column. - Rotate
Rotates the selected column on plan. - Copy
Copies the characteristics of one column to another. - Delete
Removes the selected columns.
Entering spaces
The following options are available in the "Spaces" group of the main toolbar:

These options allow the building spaces to be entered and edited after the architectural elements have been defined.
The tool for entering new spaces is as follows:
- New
Allows a new space to be entered into the model. The following parameters must be defined:- Reference
- Exterior (optional)
Indicates that the space entered is an exterior space, such as a balcony or terrace.
The space editing tools are as follows:
- Edit
Edits or consults the type and characteristics that have been associated with the selected space. - Move
Moves the space definition point. - Copy
Copies the characteristics of one space to another. - Search
Searches for a space by entering the text of its reference or part of it. - Delete
Deletes one or more spaces.
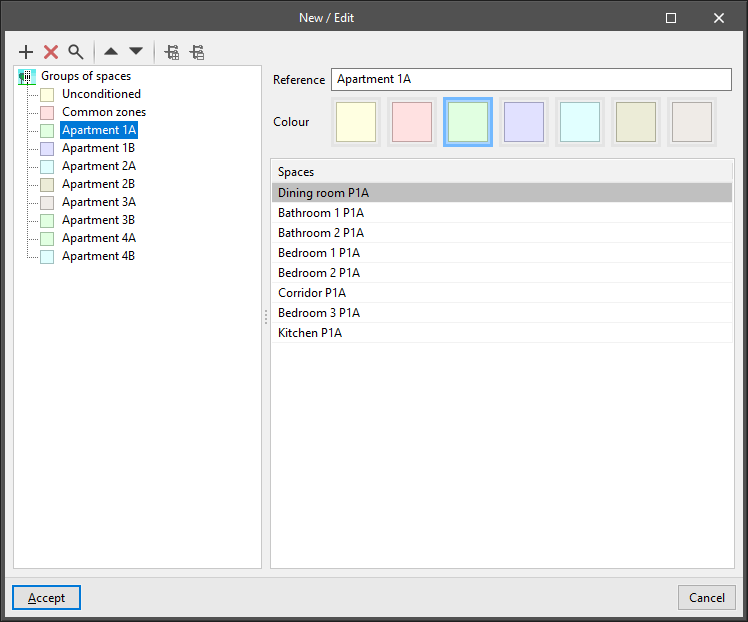
Grouping spaces
The following options are available in the main toolbar in the "Groups of spaces" group:

These tools allow users to group previously entered spaces according to their characteristics to carry out the zoning of the project. This zoning can then be imported into the analysis programs.
The tools for defining groups of spaces are as follows:
- New / Edit
Allows users to access the table of groups of spaces. Several levels of space groups can be created through a group hierarchy system. On the right, the table shows the spaces assigned to each group. Each space group has the following parameters:- Reference
- Colour
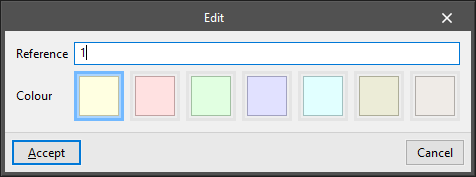
- Assign
Allows users to select a group of spaces and assign it to one or more spaces previously entered in the model.
- Unassign
Allows users to unassign a group of spaces to the selected spaces in the model.
Defining nearby volumes
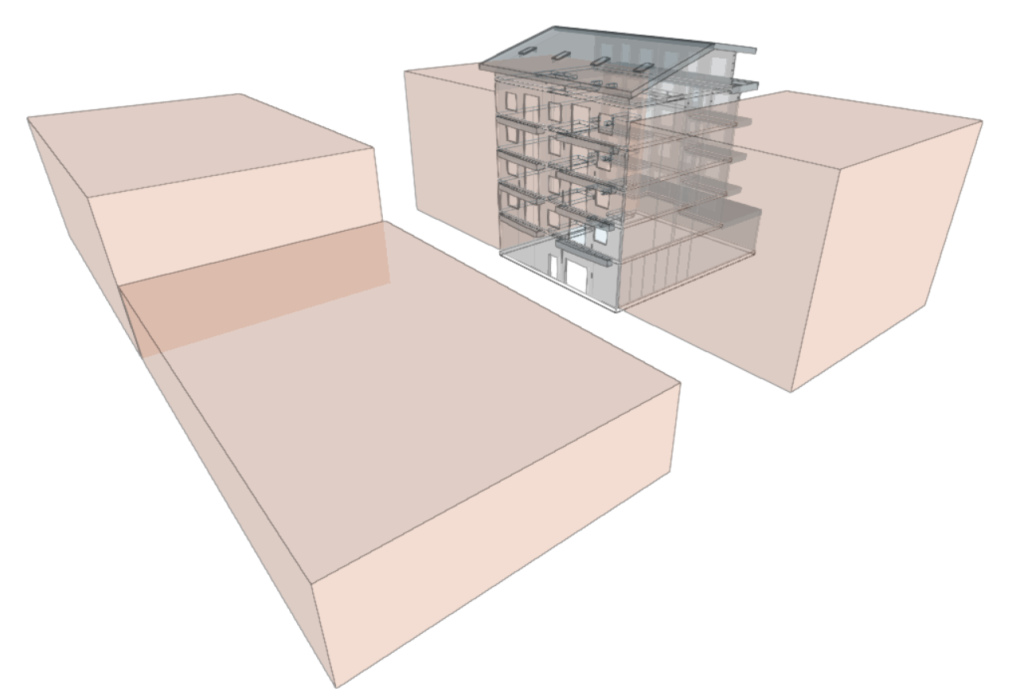
The following options are available in the "Nearby buildings and other obstacles" group of the main toolbar:

These tools allow users to define volumes close to the building, such as other nearby buildings, which can be considered later in the simulations carried out by other programs, especially due to the analysis of shadows cast by them.
The tool for entering nearby volumes is as follows:
- Nearby buildings and other obstacles
Allows users to enter a nearby volume to simulate the existence of a nearby building or other obstacle. The volume outline can be entered on any floor.
This tool requires the definition of the following parameter:- Height
Height of the volume with respect to the ground plane.
- Height
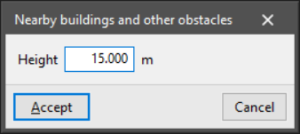
The program will generate a volume by extruding the contour entered on the plan with the defined height and supported on the base plan of the ground.
The tools for editing nearby volumes are as follows:
- Edit
Modifies the height of the selected volume. - Move
Changes the plan layout of a nearby volume by modifying the position of the vertices of its outline. - Delete
Deletes one or more selected volumes.
Editing tools
The following options are available in the "Edit" group of the main toolbar:

The operation of each of these tools is described below.
| Edit | Allows users to select an element of the model and edit its parametric properties. | |
| Move | Allows users to move a group of elements. | |
| Rotate | Allows users to rotate a group of elements. | |
| Copy | Allows users to create a copy of one or more elements. | |
| Delete | Allows users to delete a previously entered element. | |
| Symmetry (move) | Allows users to move a selection of elements with symmetry with respect to a vertical plane defined by two points. | |
| Symmetry (copy) | Allows users to copy a selection of elements with symmetry with respect to a vertical plane defined by two points. | |
| Information | Displays an information box with the data entered. |
Analysis and results of model geometry checking
The following options are available in the "Results" group of the main toolbar:

These tools allow users to check that the defined geometric model contains no modelling errors. We recommend that this check is carried out before exporting the model to other platforms.
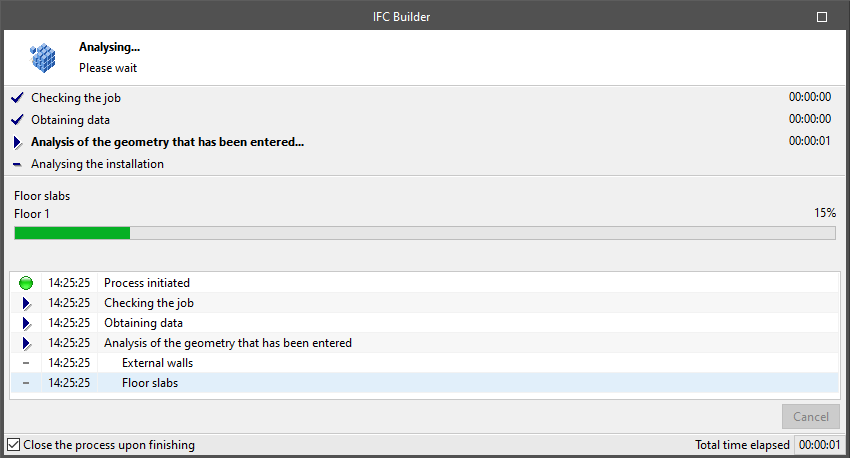
Analyse
Allows users to analyse the geometric checking of the model. The program displays a window showing the progress of the analysis.
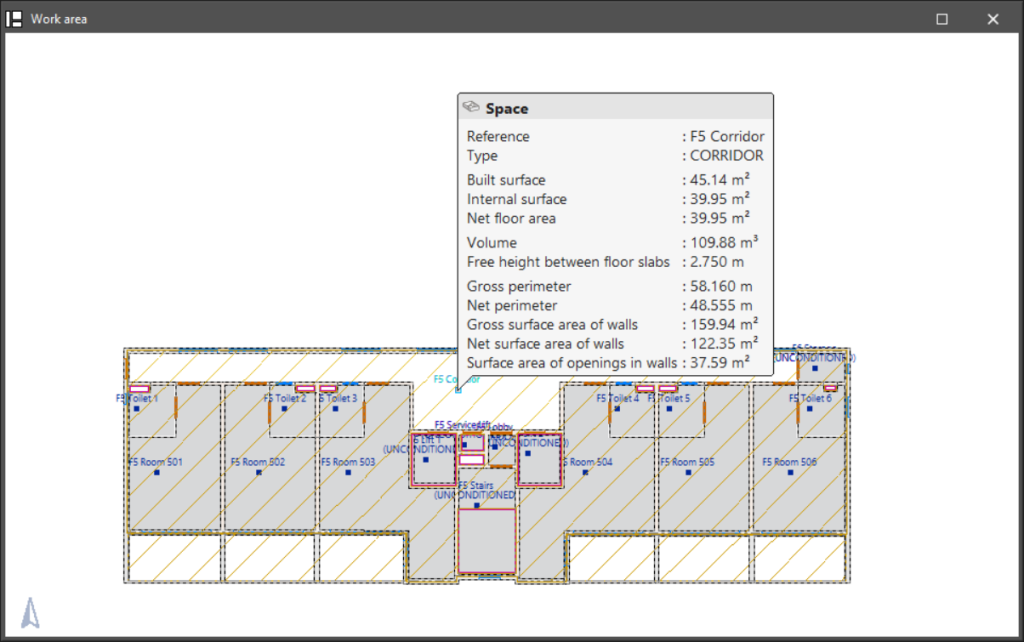
Show results
Displays the results of the last analysis carried out. Hovering the cursor over the spaces in the model displays their geometrical characteristics.
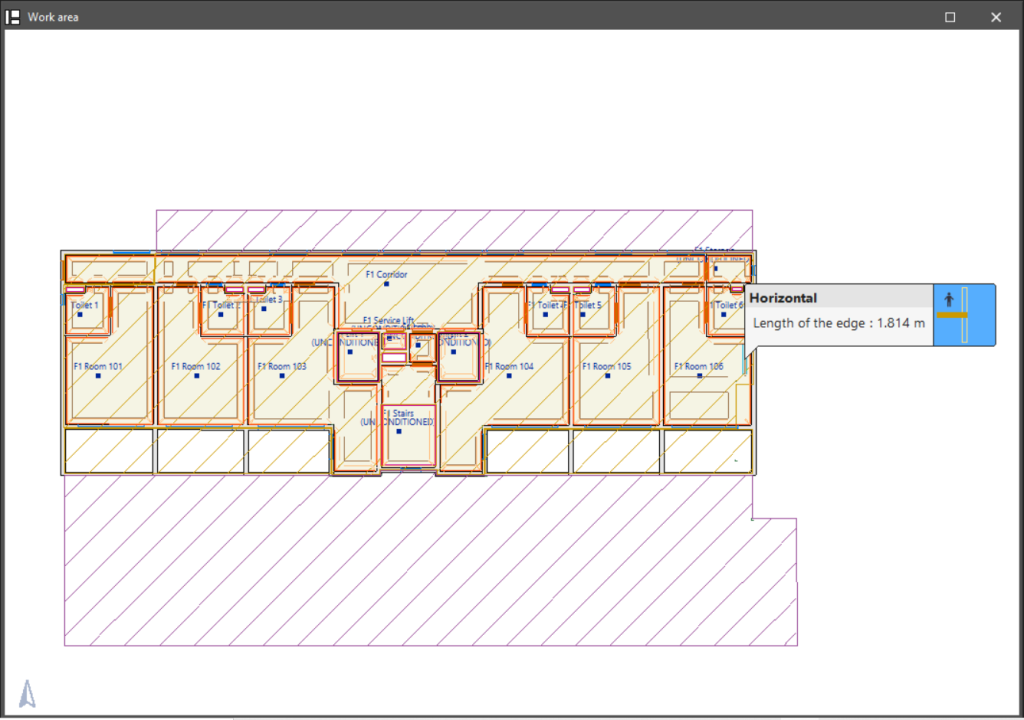
Show edges
Displays the horizontal and vertical edges generated at the intersections between elements. Positioning the cursor over each edge displays its length.
These edges can then be considered by acoustic and energy simulation programs (e.g. thermal bridges).
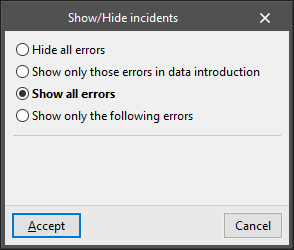
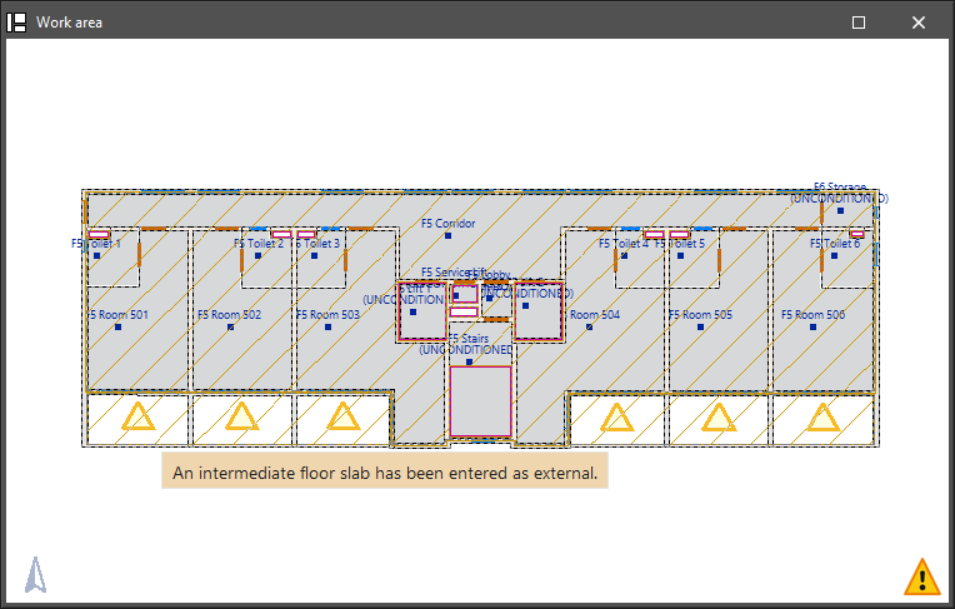
Show/Hide incidents
Highlights elements where an error has occurred using an on-screen warning system. The following options are available:
Hovering the cursor over these elements will display the message describing each error.
Results output
Directly exporting the model in IFC format
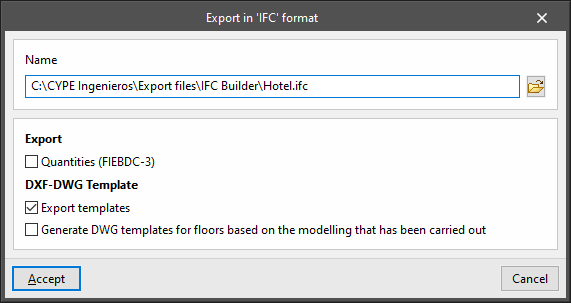
Using the "File" menu, IFC Builder allows users to export the building model directly to an IFC format file that can be saved to disk.
The program allows users to configure the following fields:
- Name
- Export
- Quantities (FIEBDC-3) (optional)
- DXF-DWG Template
- Export templates (optional)
- Generate DWG templates for floors based on the modelling that has been carried out
IFC and GLTF files supported by BIMserver.center
When exporting the project to the BIMserver.center platform, an IFC file and a 3D model in GLTF format are automatically exported for the integration of the building model in the Open BIM project, allowing it to be viewed:
- On the online platform;
- In the BIMserver.center app for iOS and Android;
- In virtual reality and augmented reality;
- In other CYPE programs.
Integration into the BIMserver.center platform
Many of CYPE's programs are connected to the BIMserver.center platform and allow collaborative work to be carried out via the exchange of files in formats based on open standards.
Please note that, to work on BIMserver.center, users can register on the platform free of charge and create a profile.
When accessing a program connected to the platform, the program connects to a project in BIMserver.center. This way, the files of the projects that have been developed collaboratively in BIMserver.center are kept up to date.

Options available in IFC Builder
The "BIMserver.center" group in the main toolbar contains the features needed to use IFC Builder together with other BIMserver.center tools:

The architectural models generated with IFC Builder can then be imported by a wide variety of acoustic and energy simulation and structural and MEP analysis applications linked to BIMserver.center. These apps will interpret the data needed to make the model and the analyses for each speciality, such as the number and height of floors and the geometry of the spaces, walls and partitions, floor slabs, openings or columns, depending on each case.
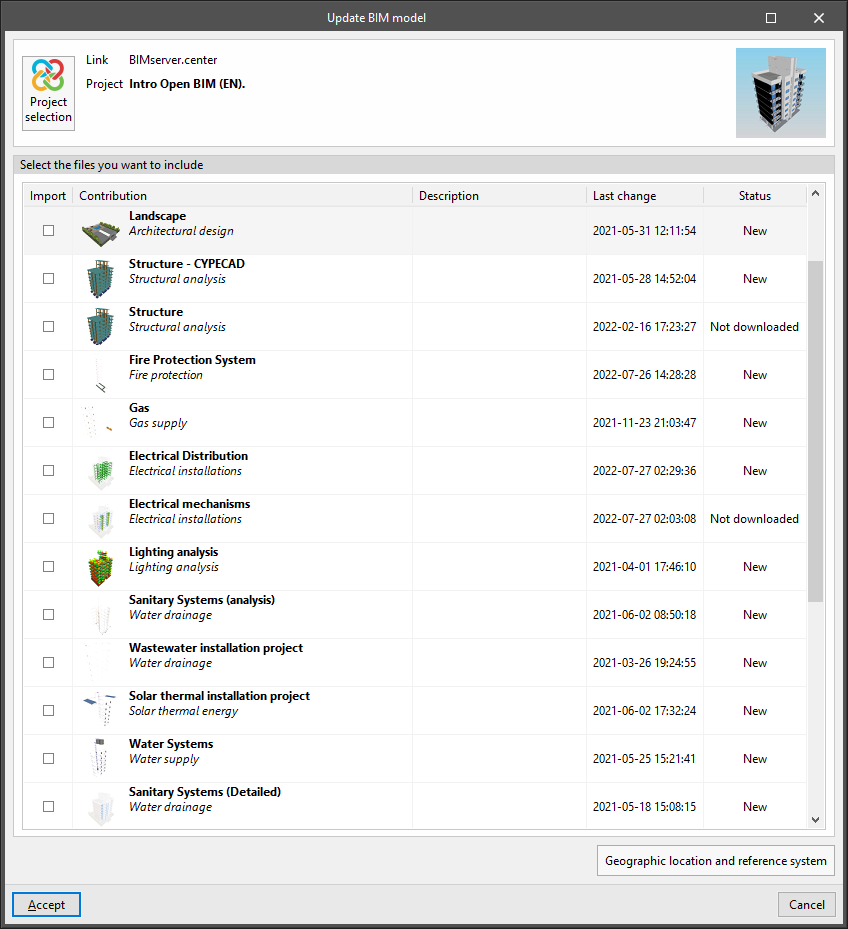
Update
Allows users to update the information contained in the models that were previously imported into the project or to import new models.
Models read from other programs and disciplines can be displayed in the 3D view of IFC Builder.
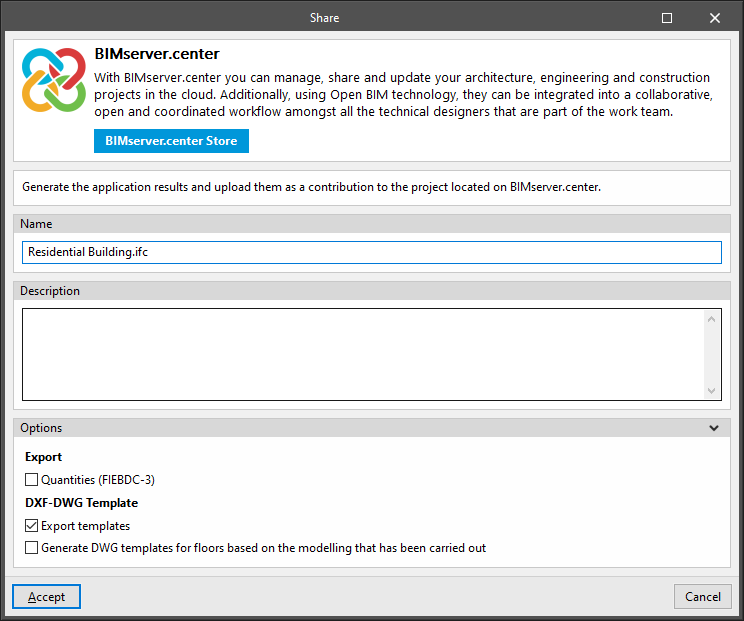
Share
Allows users to export the information of the model developed with IFC Builder to BIMserver.center to share it with other users.
During the export process, users can define information related to the identification of the files to be exported and the types of files that are generated:
- Name
- Description
- Options
- Export
- Quantities (FIEBDC-3) (optional)
- DXF-DWG Template
- Export templates (optional)
- Generate DWG templates for floors based on the modelling that has been carried out (optional)
- Export